Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP23: Bladder Cancer: Invasive III
MP23-03: Initial experience using indocyanine green in robotic-assisted ureteroenteric anastomosis
Saturday, May 14, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 225
Monica Peradejordi Font*, Alba Sierra del Rio, Claudia Mercader Barrull, Alberto Tello Delsors, Raul Martos Calvo, Barcelona, Spain, Jaime Durruti, Santiago de Chile, Chile, Joan Sureda Riera, Antoni Vilaseca Cabo, Laura Izquierdo Reyes, Maria Jose Ribal Caparros, Antonio Alcaraz Asensio, Mireia Musquera Felip, Barcelona, Spain
- MP
Monica Roser Peradejordi Font, MD (she/her/hers)
Hospital Clinic de Barcelona
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) with intracorporeal urinary diversion (ICUD) has opened new horizons minimizing surgical aggressivity. Da Vinci surgical system® has an integrated fluorescence capability that uses near-infrared technology that permits to evaluate ureteral vascularity in a real time using indocyanine green (ICG). The objective of this study is to determine the possible benefit of using ICG to assess ureteral vascularity intraoperatively and consequently reduce uretero-ileal benign strictures.
Methods: Between January 2018 and December 2020, 109 RARC with ICUD were performed at our institution. In February 2019 we introduced ICG to assess ureteral vascularity intraoperatively. After discarding patients with cutaneous ureterostomies (8), 101 patients were retrospectively analyzed. Patients and tumor characteristics, surgical and histopathological reports were reviewed. The length of the ureteric segments excised, postoperative outcomes and complications were compared between the two groups.
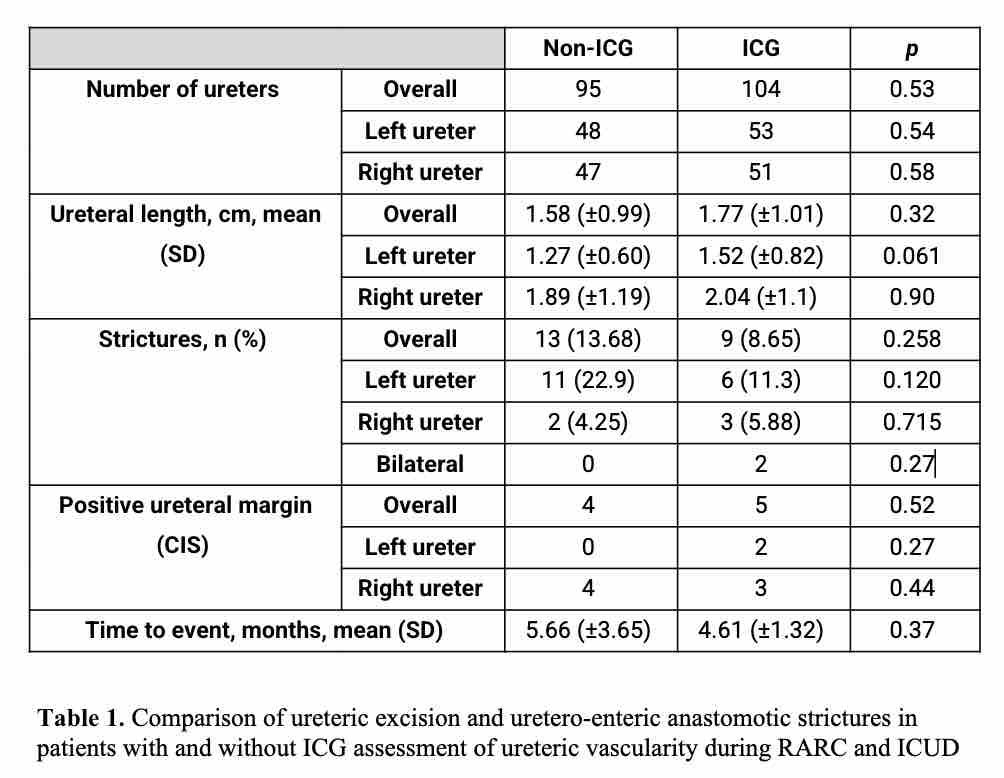
Results: Patients were mostly male (87.13%), with a mean age of 68.5 (±6.5) years. ICG was administrated in 53 patients (52.4%). There were no differences in baseline patients and tumor characteristics between groups. Ureteroenteric anastomosis was mostly in a Bricker fashion. In 6 patients a Wallace anastomosis was performed, none of them received ICG. 3 patients presented a unique renal unit. There were no differences in the mean length of resected ureter between both groups (1.58 ± 0.99 cm in non-ICG group vs 1.77 ± 1.01 cm in ICG group, p: 0.32). Ureteral CIS positive margin was present in 9 ureters (4 in non-ICG and 5 ureters in the ICG group (p: 0.52). After a mean follow-up of 20.67 months (SD 10.34), 22 (11.05%) renal units presented with benign ureteroenteric anastomotic strictures (UES), 9 in ICG and 13 in non-ICG (p: 0.258). We did not find differences in terms of other complications between both groups except for urinary tract infection that was higher in the non-ICG group (p: 0.02).
Conclusions: The use of intravenous indocyanine green with near-infrared fluorescence to assess distal ureteric vascularity during RARC does not reduce the incidence of ureteroenteric stenosis in our series. Larger studies with longer follow-up are needed to confirm our findings.
Source of Funding: There is no source of funding to disclose.
Methods: Between January 2018 and December 2020, 109 RARC with ICUD were performed at our institution. In February 2019 we introduced ICG to assess ureteral vascularity intraoperatively. After discarding patients with cutaneous ureterostomies (8), 101 patients were retrospectively analyzed. Patients and tumor characteristics, surgical and histopathological reports were reviewed. The length of the ureteric segments excised, postoperative outcomes and complications were compared between the two groups.
Results: Patients were mostly male (87.13%), with a mean age of 68.5 (±6.5) years. ICG was administrated in 53 patients (52.4%). There were no differences in baseline patients and tumor characteristics between groups. Ureteroenteric anastomosis was mostly in a Bricker fashion. In 6 patients a Wallace anastomosis was performed, none of them received ICG. 3 patients presented a unique renal unit. There were no differences in the mean length of resected ureter between both groups (1.58 ± 0.99 cm in non-ICG group vs 1.77 ± 1.01 cm in ICG group, p: 0.32). Ureteral CIS positive margin was present in 9 ureters (4 in non-ICG and 5 ureters in the ICG group (p: 0.52). After a mean follow-up of 20.67 months (SD 10.34), 22 (11.05%) renal units presented with benign ureteroenteric anastomotic strictures (UES), 9 in ICG and 13 in non-ICG (p: 0.258). We did not find differences in terms of other complications between both groups except for urinary tract infection that was higher in the non-ICG group (p: 0.02).
Conclusions: The use of intravenous indocyanine green with near-infrared fluorescence to assess distal ureteric vascularity during RARC does not reduce the incidence of ureteroenteric stenosis in our series. Larger studies with longer follow-up are needed to confirm our findings.
Source of Funding: There is no source of funding to disclose.


.jpg)
.jpg)