Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP23: Bladder Cancer: Invasive III
MP23-13: Assessment of baseline functional status and recovery following robot-assisted radical cystectomy with intracorporeal urinary diversion
Saturday, May 14, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 225
Rand Wilcox Vanden Berg*, Ashwin Ramaswamy, Bernard Bochner, Alvin Goh, New York, NY
- RW
Rand N. Wilcox Vanden Berg, MD
New York Presbyterian - Weill Cornell Medicine
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Open and robot-assisted radical cystectomies (ORC and RARC, respectively) have been shown to have equivalent oncologic outcomes. RARC is associated with longer operative times, but also with shorter length of stay and decreased operative blood loss. Despite the recent increase in use of intracorporeal urinary diversion (ICUD), few studies to date have analyzed health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and related functional recovery in the perioperative period in patients undergoing RARC with ICUD
Methods: We reviewed patients undergoing RARC with ICUD between 2017 - 2021. Patients were prospectively administered the Short Form Health Survey (SF-12), the Lawton-Brody Instrumental Activities of Daily Living Scale (Lawton-Brody), and the Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living (Katz). SF-12 responses were used to calculate the physical component summary (PCS) and mental component summary (MCS). Demographic characteristics and survey results were compared using the Mann-Whitney and chi-square tests for continuous and categorical variables, respectively. p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
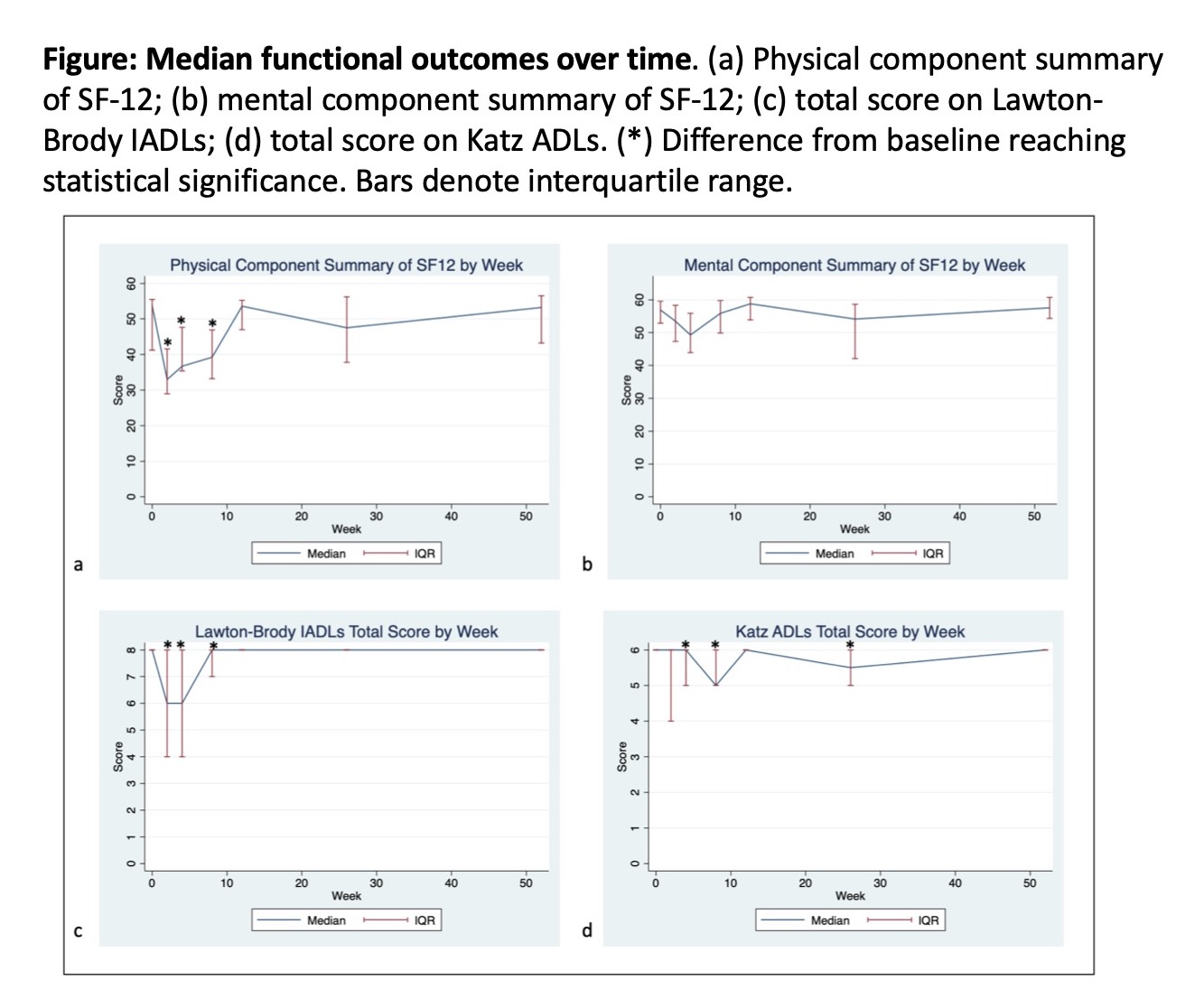
Results: 85 patients met inclusion criteria; 20.0% were female and median age was 69.7 years (IQR 63.4-74.2). Median operative time, blood loss, and length of stay were 424 min (IQR 373-479), 200 mL (IQR 100-300), and 4 days (IQR 4-6), respectively. Functional scores decreased from baseline at 2 weeks post-surgery on the SF-12(PCS) (-20.7, p < 0.01) and Lawton-Brody (-2, p < 0.01) questionnaires, and at 4 weeks on the Katz questionnaire (-0.6, p = 0.05); they all returned to baseline levels by 12 weeks (figure). While not significant, there was an increase over baseline in the SF-12(PCS) at 1 year. Median follow up was 362 days (IQR 96-640).
Conclusions: The post-operative period had a decrease in functional status (ADLs, IADLs) and the physical domain of HRQOL, which recovered in the 3 post-operative months. This pattern and timeframe of functional recovering can help guide future studies of comparative recovery (eg, between RARC and ORC) and inform future trials of the best window of opportunity for interventions into accelerating functional recovery.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: We reviewed patients undergoing RARC with ICUD between 2017 - 2021. Patients were prospectively administered the Short Form Health Survey (SF-12), the Lawton-Brody Instrumental Activities of Daily Living Scale (Lawton-Brody), and the Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living (Katz). SF-12 responses were used to calculate the physical component summary (PCS) and mental component summary (MCS). Demographic characteristics and survey results were compared using the Mann-Whitney and chi-square tests for continuous and categorical variables, respectively. p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: 85 patients met inclusion criteria; 20.0% were female and median age was 69.7 years (IQR 63.4-74.2). Median operative time, blood loss, and length of stay were 424 min (IQR 373-479), 200 mL (IQR 100-300), and 4 days (IQR 4-6), respectively. Functional scores decreased from baseline at 2 weeks post-surgery on the SF-12(PCS) (-20.7, p < 0.01) and Lawton-Brody (-2, p < 0.01) questionnaires, and at 4 weeks on the Katz questionnaire (-0.6, p = 0.05); they all returned to baseline levels by 12 weeks (figure). While not significant, there was an increase over baseline in the SF-12(PCS) at 1 year. Median follow up was 362 days (IQR 96-640).
Conclusions: The post-operative period had a decrease in functional status (ADLs, IADLs) and the physical domain of HRQOL, which recovered in the 3 post-operative months. This pattern and timeframe of functional recovering can help guide future studies of comparative recovery (eg, between RARC and ORC) and inform future trials of the best window of opportunity for interventions into accelerating functional recovery.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)