Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP24: Kidney Cancer: Localized: Surgical Therapy I
MP24-15: Positive surgical margins after robot-assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN): does it really matter ? (MARGINS Study – UroCCR 96)
Saturday, May 14, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 222
Arnoult Morrone*, Imad Bentellis, Nice, France, Jean-Christophe Bernhard, Bordeaux, France, Karim Bensalah, Rennes, France, Cécile Champy, Paris, France, Franck Bruyère, Tours, France, Nicolas Doumerc, Toulouse, France, Olivier Jonathan, Lille, France, François Audenet, Bastien Parier, Martin Brenier, Paris, France, Jean-Alexandre Long, Grenoble, France, Thomas Charles, Poitiers, France, Evanguelos Xylinas, Paris, France, Thibaut Waeckel, Caen, France, Florie Gomez, Paris, France, Romain Boissier, Marseille, France, Benjamin Rouget, Libourne, France, Daniel Chevallier, Damien Ambrosetti, Matthieu Durand, Nice, France

Arnoult Morrone, MD
University hospital of Nice
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Oncological impact of positive surgical margins (PSM) after robot-assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN) is still under debate.
We aimed at comparing PSM and Negative Surgical Margins (NSM) in terms of recurrence-free survival (RFS), metastasis-free survival (MFS) and overall survival (OS) after RAPN and to evaluate the risk factors for a PSM to occur.
Methods: We reviewed the charts of 2673 patients in 20 centers who underwent RAPN between April 2010 and February 2021. Two groups were compared: PSM and NSM. Prognostic factors were assessed using, Kaplan-Meyer curves with log-Rank test, cox hazard proportional risk model and logistic regression after univariate comparison.
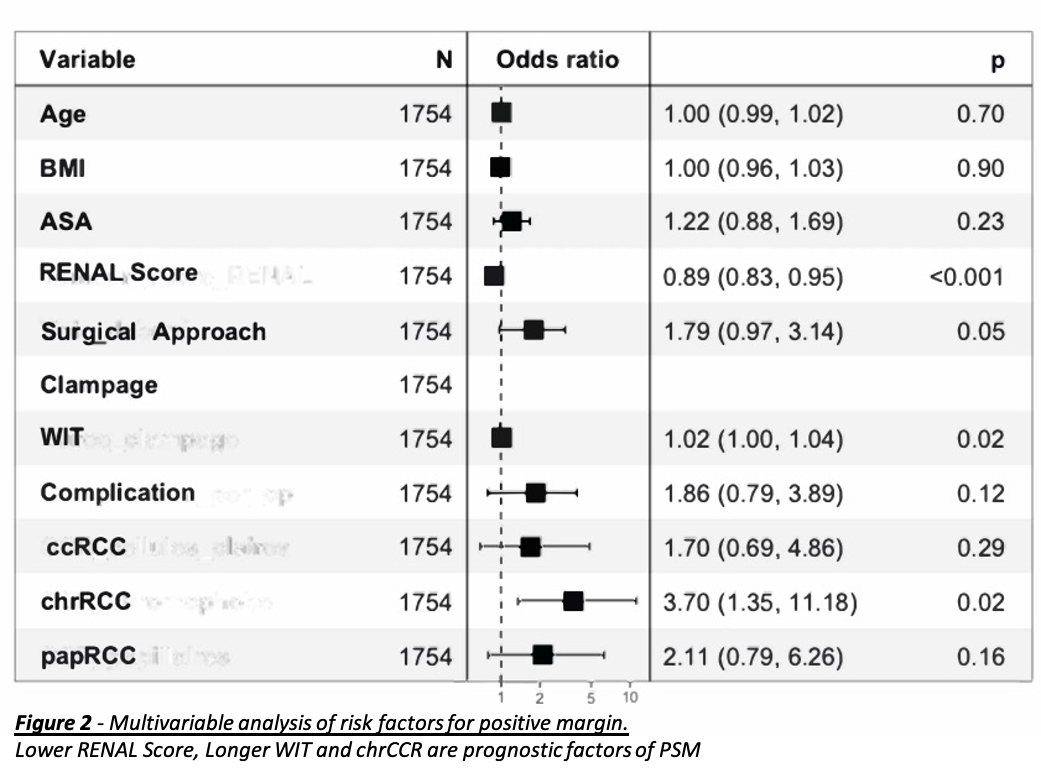
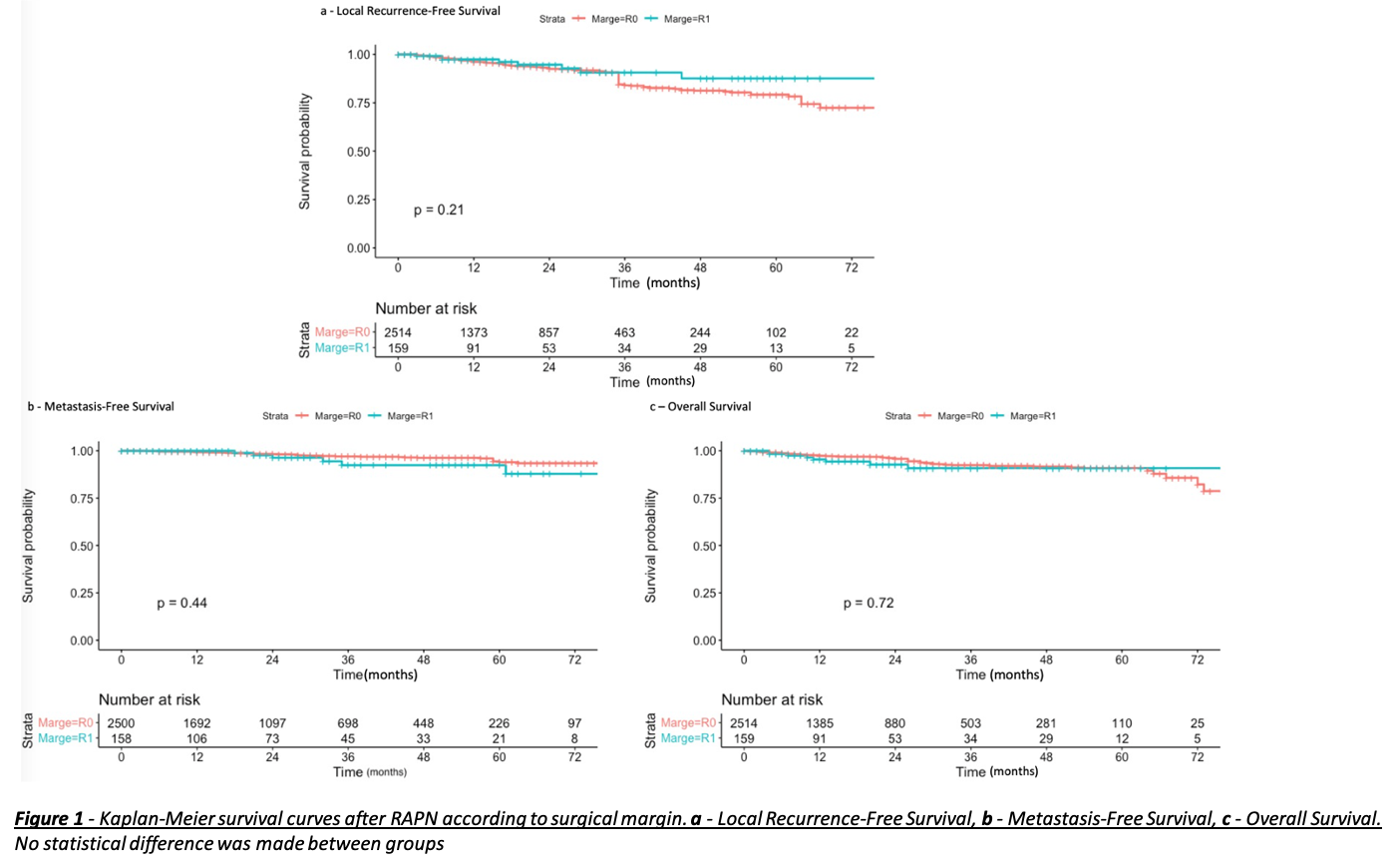
Results: There were 159 patients in the PSM group (5,9%) and 2514 (94,1%) NSM. Median follow-up was 20 (9-38) months after RAPN. Differences were observed for the RENAL score (PSM: 6 vs NSM: 7, p=0,034), the retroperitoneal approach (12.8% vs 6.4% p=0,008), on-clamp procedure (92.4% vs 82.8% p=0,003), warm ischemia time (21.2 vs 18.3, p<0,001) and complications during surgery (7.6% vs 3.8%, p=0,032). Clear-cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC) (59.7% vs 69.1%, p=0,018) and Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma (chrRCC) (18.2% vs 9.0%, p<0,001) also showed an association with PSM. Kaplan-Meier curves and analysis suggest that RFS, MFS and OS are not affected by a PSM (respective p=0,21; 0,72; 0,44) (Figure1). In multivariate analysis predictors of PSM were lower RENAL score (p <0,001), warm ischemia time (WIT) (p=0,02) and chrRCC (p=0,02) (Figure 2).
Conclusions: This large prospective multicentric series reported on no impact of PSM on oncological outcomes for patients including RFS, MFS or OS. Moreover, predictors of PSM are the RENAL score, WIT and chrRCC.
Source of Funding: None.
We aimed at comparing PSM and Negative Surgical Margins (NSM) in terms of recurrence-free survival (RFS), metastasis-free survival (MFS) and overall survival (OS) after RAPN and to evaluate the risk factors for a PSM to occur.
Methods: We reviewed the charts of 2673 patients in 20 centers who underwent RAPN between April 2010 and February 2021. Two groups were compared: PSM and NSM. Prognostic factors were assessed using, Kaplan-Meyer curves with log-Rank test, cox hazard proportional risk model and logistic regression after univariate comparison.
Results: There were 159 patients in the PSM group (5,9%) and 2514 (94,1%) NSM. Median follow-up was 20 (9-38) months after RAPN. Differences were observed for the RENAL score (PSM: 6 vs NSM: 7, p=0,034), the retroperitoneal approach (12.8% vs 6.4% p=0,008), on-clamp procedure (92.4% vs 82.8% p=0,003), warm ischemia time (21.2 vs 18.3, p<0,001) and complications during surgery (7.6% vs 3.8%, p=0,032). Clear-cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC) (59.7% vs 69.1%, p=0,018) and Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma (chrRCC) (18.2% vs 9.0%, p<0,001) also showed an association with PSM. Kaplan-Meier curves and analysis suggest that RFS, MFS and OS are not affected by a PSM (respective p=0,21; 0,72; 0,44) (Figure1). In multivariate analysis predictors of PSM were lower RENAL score (p <0,001), warm ischemia time (WIT) (p=0,02) and chrRCC (p=0,02) (Figure 2).
Conclusions: This large prospective multicentric series reported on no impact of PSM on oncological outcomes for patients including RFS, MFS or OS. Moreover, predictors of PSM are the RENAL score, WIT and chrRCC.
Source of Funding: None.



.jpg)
.jpg)