Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP24: Kidney Cancer: Localized: Surgical Therapy I
MP24-19: Comparison of One-Year Healthcare Expenditure and Utilizations between Robotic-assisted versus Laparoscopic Surgery among Patients Undergoing Partial and Radical Nephrectomy
Saturday, May 14, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 222
Kennedy Okhawere*, New York, NY, Gediwon Milky, I-Fan Shih, Yanli Li, Sunnyvale, CA, Ketan Badani, New York, NY
- KO
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: There has been widespread adoption of robotic surgery for partial and radical nephrectomy; however, the discordance of the cost of utilization remains an important factor that requires investigation. We sought to compare the cost and healthcare utilization one year after robotic-assisted surgery (RAS) to laparoscopic (LAP) surgery for radical (RN) and partial nephrectomy (PN).
Methods: A retrospective cohort study of patients who underwent RN or PN for kidney cancer was conducted using a US commercial claims database (IBM® MarketScan® Databases) between 2013 and 2018. Outcomes included length of stay and expenditure for index surgery, post-operative 1-year total healthcare expenditure, healthcare utilizations, and total missed days of work due to healthcare utilization. Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) based on baseline patient characteristics was applied to compare RAS versus LAP.
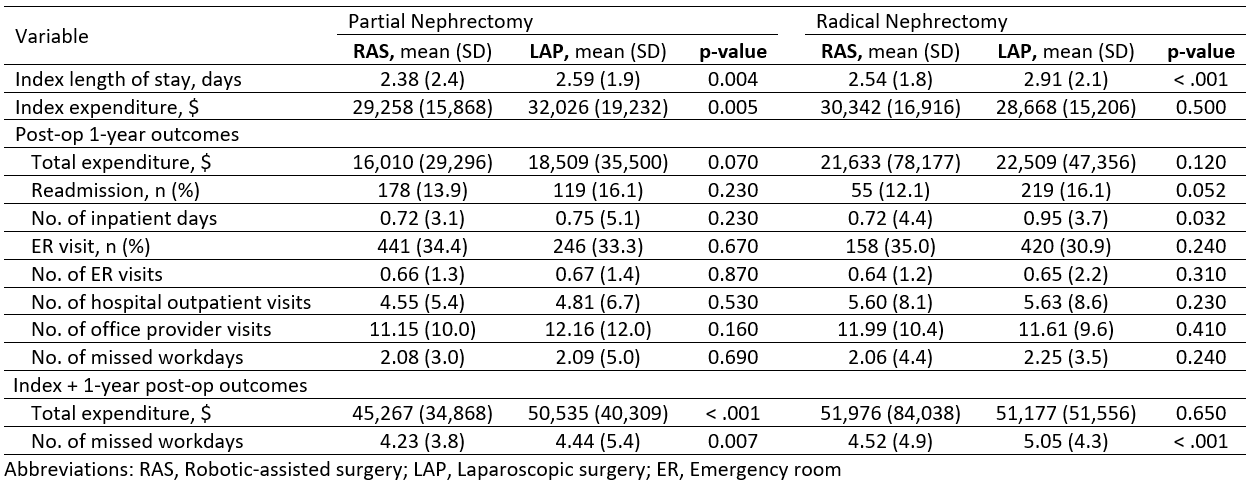
Results: Of 3,824 patients, 2,008 had PN (1,263 RAS vs 745 LAP) and 1,816 had RN (456 RAS vs 1,360 LAP). RAS patients had lower index length of stay than LAP (PN: 2.4 vs 2.6, p = 0.004; and RN: 2.5 vs 2.9, p < 0.001). RAS patients had lower or comparable index expenditure versus LAP (PN: $29,258 vs $32,026, p = 0.005; and RN: $30,342 vs $28,668, p = 0.500). Post-operative 1-year total expenditure was comparable between RAS and LAP (PN: $16,010 vs. $18,509, p = 0.070; and RN: $21,633 vs. $22,509, p = 0.120). RAS patients had lower or comparable post-operative inpatient days than LAP (PN: 0.7 vs 0.9 days, p = 0.032; and RN: 0.7 vs 0.7, p = 0.230). RAS and LAP were comparable in terms of readmission, ER visits, outpatient visits, and post-operative missed workdays.
Conclusions: Our finding suggested that RAS had comparable health care utilization and total one-year post discharge cost to LAP for both partial and radical nephrectomy. Further research is warranted to evaluate the impact of surgical approach on post-operative kidney functions and consequent economic burdens.
Source of Funding: Intuitive Surgical Inc.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study of patients who underwent RN or PN for kidney cancer was conducted using a US commercial claims database (IBM® MarketScan® Databases) between 2013 and 2018. Outcomes included length of stay and expenditure for index surgery, post-operative 1-year total healthcare expenditure, healthcare utilizations, and total missed days of work due to healthcare utilization. Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) based on baseline patient characteristics was applied to compare RAS versus LAP.
Results: Of 3,824 patients, 2,008 had PN (1,263 RAS vs 745 LAP) and 1,816 had RN (456 RAS vs 1,360 LAP). RAS patients had lower index length of stay than LAP (PN: 2.4 vs 2.6, p = 0.004; and RN: 2.5 vs 2.9, p < 0.001). RAS patients had lower or comparable index expenditure versus LAP (PN: $29,258 vs $32,026, p = 0.005; and RN: $30,342 vs $28,668, p = 0.500). Post-operative 1-year total expenditure was comparable between RAS and LAP (PN: $16,010 vs. $18,509, p = 0.070; and RN: $21,633 vs. $22,509, p = 0.120). RAS patients had lower or comparable post-operative inpatient days than LAP (PN: 0.7 vs 0.9 days, p = 0.032; and RN: 0.7 vs 0.7, p = 0.230). RAS and LAP were comparable in terms of readmission, ER visits, outpatient visits, and post-operative missed workdays.
Conclusions: Our finding suggested that RAS had comparable health care utilization and total one-year post discharge cost to LAP for both partial and radical nephrectomy. Further research is warranted to evaluate the impact of surgical approach on post-operative kidney functions and consequent economic burdens.
Source of Funding: Intuitive Surgical Inc.

.jpg)
.jpg)