Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP27: Prostate Cancer: Advanced (including Drug Therapy) I
MP27-09: Impact of trough concentrations of abiraterone and D4A on the clinical outcomes of patients with metastatic castration-sensitive and castration-resistant prostate cancer
Saturday, May 14, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:45 AM
Location: Room 222
Yoshiko Takahashi*, Shintaro Narita, Akita, Japan, Masaki Shiota, Fukuoka, Japan, Soki Kashima, Ryohei Yamamoto, Atsushi Koizumi, Kazuyuki Numakura, Mitsuru Saito, Akita, Japan, Masatoshi Eto, Fukuoka, Japan, Masatomo Miura, Tomonori Habuchi, Akita, Japan
- YT
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Previous studies have demonstrated that plasma concentrations of abiraterone acetate (ABI) and its metabolites are associated with the treatment outcomes of patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with ABI. In this study, we assessed the impact of plasma trough concentrations of ABI, D4A, and related polymorphisms on the clinical outcomes of patients with metastatic prostate cancer who received ABI.
Methods: Patients with metastatic prostate cancer treated with ABI between 2016 and 2021 were enrolled. The trough plasma concentrations of ABI and D4A were measured using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC). The impact of HSD3B1 rs1047303 and SRD5A2 rs523349 polymorphisms was also assessed using TaqMan SNP assay.
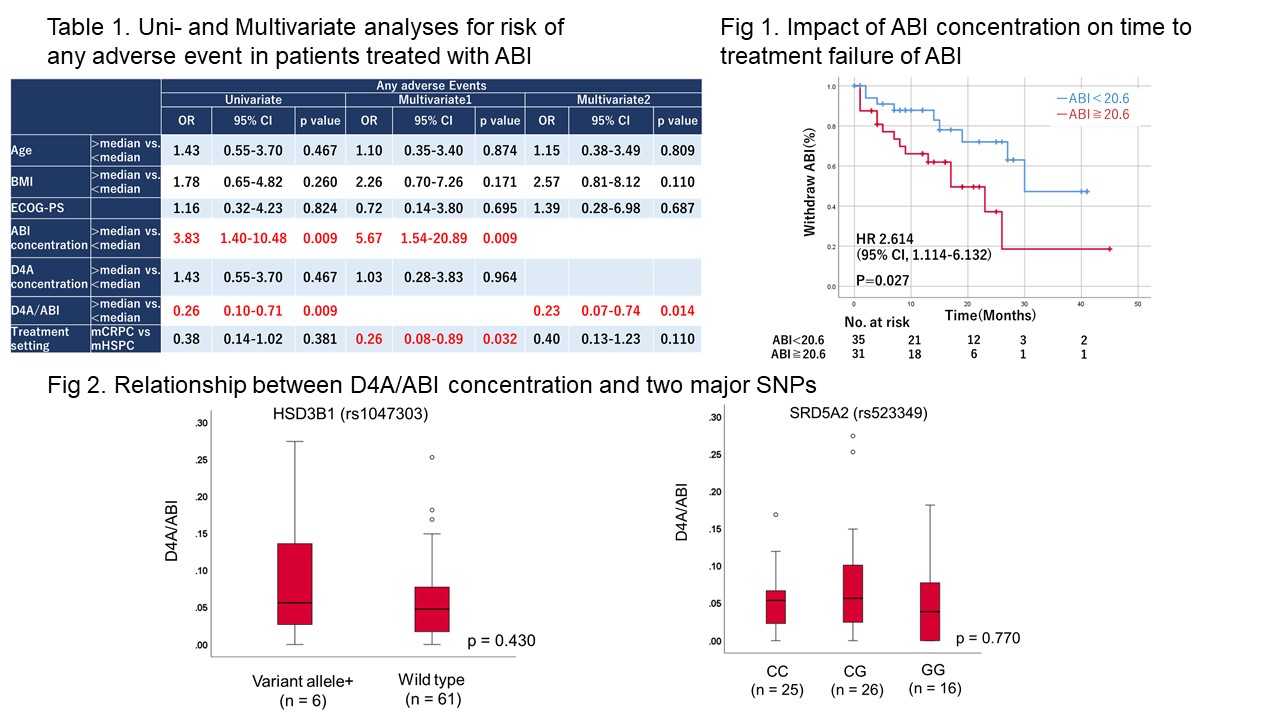
Results: In 68 patients treated with ABI, the median ABI and D4A concentrations were 18.1 and 0.94 ng/mL, respectively. The trough plasma levels of ABI and D4A were not statistically associated with treatment response and overall survival. The high trough level of plasma ABI (= 18.1 ng/mL) was significantly associated with the presence of any adverse events and its independent risk factors based on multivariable analysis (OR, 5.67; 95% CI: 1.54–20.89). Additionally, the time-to-treatment-failure was significantly associated with a higher trough level of ABI (p = 0.027). The risk alleles of two polymorphisms were not statistically associated with the D4A/ABI concentrations.
Conclusions: Trough ABI concentrations might be correlated with the presence of adverse events and treatment failure after ABI administration. ABI concentration monitoring can be a biomarker of the treatment outcomes of patients with prostate cancer.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: Patients with metastatic prostate cancer treated with ABI between 2016 and 2021 were enrolled. The trough plasma concentrations of ABI and D4A were measured using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC). The impact of HSD3B1 rs1047303 and SRD5A2 rs523349 polymorphisms was also assessed using TaqMan SNP assay.
Results: In 68 patients treated with ABI, the median ABI and D4A concentrations were 18.1 and 0.94 ng/mL, respectively. The trough plasma levels of ABI and D4A were not statistically associated with treatment response and overall survival. The high trough level of plasma ABI (= 18.1 ng/mL) was significantly associated with the presence of any adverse events and its independent risk factors based on multivariable analysis (OR, 5.67; 95% CI: 1.54–20.89). Additionally, the time-to-treatment-failure was significantly associated with a higher trough level of ABI (p = 0.027). The risk alleles of two polymorphisms were not statistically associated with the D4A/ABI concentrations.
Conclusions: Trough ABI concentrations might be correlated with the presence of adverse events and treatment failure after ABI administration. ABI concentration monitoring can be a biomarker of the treatment outcomes of patients with prostate cancer.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)