Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP32: Surgical Technology & Simulation: Instrumentation & Technology I
MP32-18: Device-Related Complications During Renal Cryoablation: Insights from the Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience (MAUDE) Database
Saturday, May 14, 2022
2:45 PM – 4:00 PM
Location: Room 225
Srinath Kotamarti*, Zoe Michael, Durham, NC, David Silver, Ervin Teper, Brooklyn, NY, Alireza Aminsharifi, Hershey, PA, Thomas Polascik, Durham, NC, Ariel Schulman, Brooklyn, NY
- SK
Srinath Kotamarti, MD
Fellow
Duke University Medical Center
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Cryoablation offers a treatment option ideally for renal masses <3 cm in well-selected candidates. However, little is known regarding device-related complications associated with the procedure. We provide an analysis of reports from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience (MAUDE) database.
Methods: Reports on renal cryoablation submitted to the MAUDE database from 2015 to 6/2021 were analyzed. Cases were examined to identify patient morbidity related to a potential device malfunction, as well as manufacturer assessment. Complications were graded based on an established MAUDE complication stratification. Fisher’s Exact test was utilized to analyze for associations between device-related adverse events and severity of post-treatment sequelae.
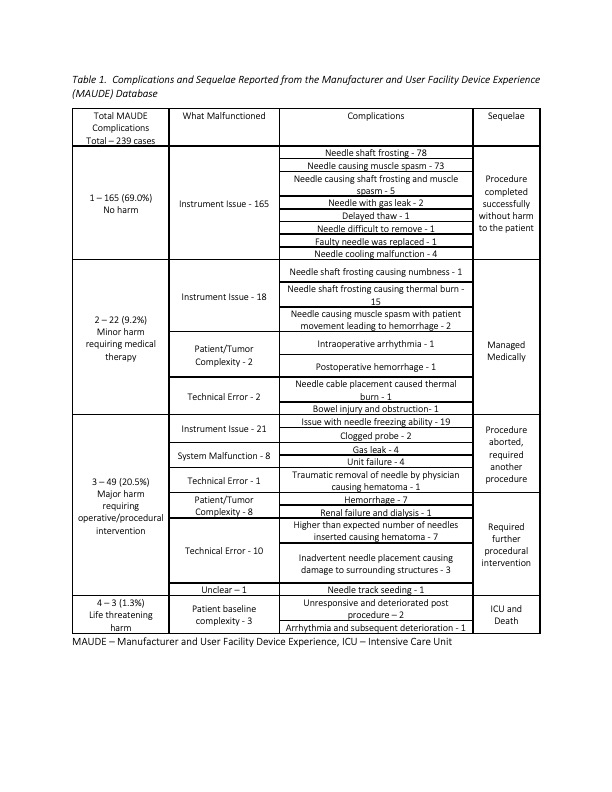
Results: A total of 239 unique cases were identified and tabulated (Table 1). Adverse events were related to issues with the needles/system, technical error, or patient/tumor complexity. There were 187 (78.6%) minor complications (MAUDE 1-2) and 52 (21.4%) major complications (MAUDE 3 to 4). The manufacturer performed formal device review in 164 (68.6%) cases, accepting responsibility in 41. All three reported patient deaths (MAUDE 4) appeared to be a consequence of poor baseline health. Major complications were seen in a higher proportion of non-device-related adverse events (23 of 27 cases, 85.2%) compared to device-related events (29 of 212 cases, 13.7%); these frequencies were significantly different on statistical analysis (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: While renal cryoablation is associated with low overall perioperative morbidity, there was a spectrum of device-related and procedural complications reported in recent years. Device-related adverse events were often associated with minor complications, and major complications were often seen in patients with comorbidities, more complex tumors, and after technical error. These findings highlight the need for standardized reporting of complications and optimized patient selection, particularly in regard to patient comorbidity and tumor characteristics, to ensure the best outcomes.
Source of Funding: N/A
Methods: Reports on renal cryoablation submitted to the MAUDE database from 2015 to 6/2021 were analyzed. Cases were examined to identify patient morbidity related to a potential device malfunction, as well as manufacturer assessment. Complications were graded based on an established MAUDE complication stratification. Fisher’s Exact test was utilized to analyze for associations between device-related adverse events and severity of post-treatment sequelae.
Results: A total of 239 unique cases were identified and tabulated (Table 1). Adverse events were related to issues with the needles/system, technical error, or patient/tumor complexity. There were 187 (78.6%) minor complications (MAUDE 1-2) and 52 (21.4%) major complications (MAUDE 3 to 4). The manufacturer performed formal device review in 164 (68.6%) cases, accepting responsibility in 41. All three reported patient deaths (MAUDE 4) appeared to be a consequence of poor baseline health. Major complications were seen in a higher proportion of non-device-related adverse events (23 of 27 cases, 85.2%) compared to device-related events (29 of 212 cases, 13.7%); these frequencies were significantly different on statistical analysis (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: While renal cryoablation is associated with low overall perioperative morbidity, there was a spectrum of device-related and procedural complications reported in recent years. Device-related adverse events were often associated with minor complications, and major complications were often seen in patients with comorbidities, more complex tumors, and after technical error. These findings highlight the need for standardized reporting of complications and optimized patient selection, particularly in regard to patient comorbidity and tumor characteristics, to ensure the best outcomes.
Source of Funding: N/A


.jpg)
.jpg)