Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP36: Renal Transplantation & Vascular Surgery
MP36-01: Kidney transplantation with COVID-19 positive donors: A series of 55 cases
Sunday, May 15, 2022
7:00 AM – 8:15 AM
Location: Room 228
Yi-Chia Lin*, Mazhar Kahlil, Mohamed Eltemamy, Hannah Kerr, Venkatech Krishnamurthi, David Goldfarb, Alvin Wee, Cleveland, OH
- YL
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Organs from deceased-donors who tested positive for COVID-19 were thought to be ineligible for transplantation. Despite lack of evidence showing that COVID-19 can be transmitted through urine or blood. We began to transplant kidneys from COVID-positive deceased-donors in February 2021 and this report comprises our early outcomes in this patient cohort.
Methods: From Feb 2021 to Oct 2021, 55 patients underwent kidney transplantation from 34 COVID-19 positive donors. Prior to initiating this clinical practice, formalized selection criteria for organs from COVID-19 positive deceased-donors were adopted by transplant surgeons, transplant nephrologists, and infectious disease physicians. If a deceased-donor suited these pre-determined criteria, individual kidney selection followed our usual programmatic criteria.
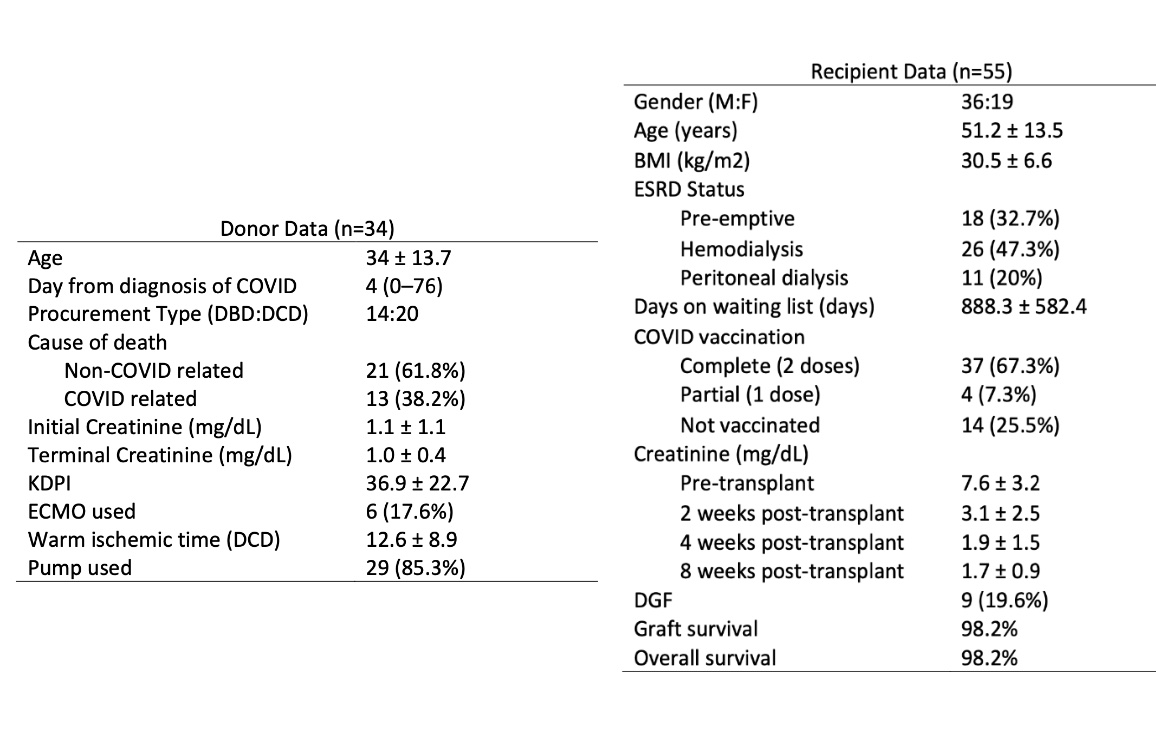
Results: The mean donor age was 34 ± 13.7 years with a mean kidney donor profile index (KDPI) of 36.9 ± 22.7%. All donors had at least 1 positive COVID-19 test from the nasopharyngeal ribonucleic acid swab test within a median of 4 (0-76) days prior to declaration as a deceased-donor. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) was used in 6 donors. The initial and terminal mean creatinine was 1.1 ± 1.1 mg/dl and 1.0 ± 0.4mg/dL. This patient cohort includes 36 male recipients and 19 female recipients. Mean age among all recipients was 51.2 ± 13.5 years. Thirty-seven recipients (66.7%) were dialysis dependent. A similar proportion (67.3%) had received both COVID-19 vaccine doses. Delayed graft function occurred in 19.6% of the recipients. No patient tested positive for COVID-19 after surgery. At a mean follow up duration of 3.5 months, all kidney allografts are functioning, with a mean serum creatinine of 1.6 ± 0.7 mg/dl. One patient underwent allograft nephrectomy at 1.5 months post-transplant due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa vascular infection.
Conclusions: Transplantation of kidneys from COVID-19 positive donors is safe. Outcomes are comparable to kidneys from regular donors.
Source of Funding: none
Methods: From Feb 2021 to Oct 2021, 55 patients underwent kidney transplantation from 34 COVID-19 positive donors. Prior to initiating this clinical practice, formalized selection criteria for organs from COVID-19 positive deceased-donors were adopted by transplant surgeons, transplant nephrologists, and infectious disease physicians. If a deceased-donor suited these pre-determined criteria, individual kidney selection followed our usual programmatic criteria.
Results: The mean donor age was 34 ± 13.7 years with a mean kidney donor profile index (KDPI) of 36.9 ± 22.7%. All donors had at least 1 positive COVID-19 test from the nasopharyngeal ribonucleic acid swab test within a median of 4 (0-76) days prior to declaration as a deceased-donor. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) was used in 6 donors. The initial and terminal mean creatinine was 1.1 ± 1.1 mg/dl and 1.0 ± 0.4mg/dL. This patient cohort includes 36 male recipients and 19 female recipients. Mean age among all recipients was 51.2 ± 13.5 years. Thirty-seven recipients (66.7%) were dialysis dependent. A similar proportion (67.3%) had received both COVID-19 vaccine doses. Delayed graft function occurred in 19.6% of the recipients. No patient tested positive for COVID-19 after surgery. At a mean follow up duration of 3.5 months, all kidney allografts are functioning, with a mean serum creatinine of 1.6 ± 0.7 mg/dl. One patient underwent allograft nephrectomy at 1.5 months post-transplant due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa vascular infection.
Conclusions: Transplantation of kidneys from COVID-19 positive donors is safe. Outcomes are comparable to kidneys from regular donors.
Source of Funding: none


.jpg)
.jpg)