Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP40: Bladder Cancer: Upper Tract Transitional Cell Carcinoma I
MP40-09: The Systemic Immune–inflammation Index (SII) as predictor factor of survival in patients undergoing radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma.
Sunday, May 15, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 225
Skander Zouari*, Saadi Ahmed, Setti Boubaker Nouha, Bilel Saidani, Marouene Chakroun, Khadija Medddeb, Mouna Ayadi, Meriem Ksontini, Ahlem Blel, Hamza Boussaffa, Abderrazek Bouzouita, Amine Derouiche, Riadh Ben Slama, Ksontini Feriel, Amel Mezlini, Soumaya Rammeh, Haroun Ayed, Mohamed Chebil, Tunis, Tunisia

Skander Zouari, MD
Charles Nicolle Hospital
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: The systemic immune–infammation index (SII) is an immunological and inflammatory index obtained from the pre-operative leukocyte formulas and based on the count of lymphocytes, neutrophils and platelets. The aim of this study is to assess the prognostic value of SII in patients undergoing radical nephroureterectomy (RNU) for upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC).
Methods: Between 1989 and December 2020, 193 patients underwent RNU for UTUC. Metastatic patients at first presentation, patients with lack of follow up or with missing data were excluded. Calculation of SII is based on the formula: number of neutrophils*platelets/lymphocytes. Patients were stratified into two groups defined on the basis of an SII threshold value obtained from the ROC curve plotting by the XLSTAT software. Correlation of SII to clinical parameters of prognostic interest was made by the student test, the Khi2 test and the Mann Whitney test. The survival curves were obtained using the Kaplan-Meier method (IBM®SPSS®23.0).
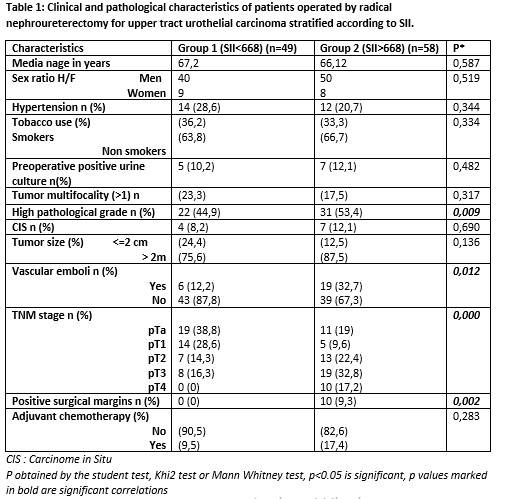
Results: A total of 107 patients were included. Mean age was 66.6 years. Cut-off value for SII in our population was 668. Forty-nine patients were in Group 1 (SII <668) while 58 patients were in Group 2 (SII>668). Main clinical and pathology features are summarized in Table I. SII> 668 was correlated with high histological grade (p=0.009), presence of vascular emboli (p=0.012), advanced TNM stage (p=0.000) and positive surgical margins (p=0.002). Average follow-up was 25.67 months. SII>675 was associated with overall survival (p=0.006) (Figure 1), metastasis (p=0.047) and locoregional recurrence (p=0.034), but not with local recurrence (p=0.082) or intravesical recurrence (p=0.829).
Conclusions: High preoperative SII is significantly associated with higher histological grade, advanced tumor stage and worse survival outcomes in patients operated by RNU for UTUC. It could be a potentially useful pre-operative prognostic tool to identify patients with aggressive tumors and guide decision making strategy.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: Between 1989 and December 2020, 193 patients underwent RNU for UTUC. Metastatic patients at first presentation, patients with lack of follow up or with missing data were excluded. Calculation of SII is based on the formula: number of neutrophils*platelets/lymphocytes. Patients were stratified into two groups defined on the basis of an SII threshold value obtained from the ROC curve plotting by the XLSTAT software. Correlation of SII to clinical parameters of prognostic interest was made by the student test, the Khi2 test and the Mann Whitney test. The survival curves were obtained using the Kaplan-Meier method (IBM®SPSS®23.0).
Results: A total of 107 patients were included. Mean age was 66.6 years. Cut-off value for SII in our population was 668. Forty-nine patients were in Group 1 (SII <668) while 58 patients were in Group 2 (SII>668). Main clinical and pathology features are summarized in Table I. SII> 668 was correlated with high histological grade (p=0.009), presence of vascular emboli (p=0.012), advanced TNM stage (p=0.000) and positive surgical margins (p=0.002). Average follow-up was 25.67 months. SII>675 was associated with overall survival (p=0.006) (Figure 1), metastasis (p=0.047) and locoregional recurrence (p=0.034), but not with local recurrence (p=0.082) or intravesical recurrence (p=0.829).
Conclusions: High preoperative SII is significantly associated with higher histological grade, advanced tumor stage and worse survival outcomes in patients operated by RNU for UTUC. It could be a potentially useful pre-operative prognostic tool to identify patients with aggressive tumors and guide decision making strategy.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)