Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP40: Bladder Cancer: Upper Tract Transitional Cell Carcinoma I
MP40-17: LncRNA SNHG16 mediate cisplatin and gemcitabine resistance in upper tract urothelial carcinoma cells by sponging of miR-31-5p
Sunday, May 15, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 225
Wei-Chi Hsu*, Wei-Ming Li, A-Mei Huang, Lin-Li Chang, Hui-Hui Lin, Wen-Jeng Wu, Ching-Chia Li, Hung-Lung Ke *, Kaohsiung City, Taiwan
WeiChi Hsu, PhD
postdoctoral research fellow
Kaohsiung Medical University
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Chemotherapy is suggested perioperatively for advanced upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) to improve recurrence-free and cancer-specific survivals. The standard regimens of chemotherapy are gemcitabine (GEM) and cisplatin (CDDP). After repeated chemotherapy, 30% of the patients will develop drug resistance and the disease will progress. Therefore, it is very important to clarify the mechanism of chemotherapy resistance and overcome it. This study aimed to investigate whether miR-31-5p can enhance the chemosensitivity of CDDP and GEM and the molecular mechanisms.
Methods: In this study, we established BFTC909 derived CDDP-resistant (BFTC909-CR) and GEM-resistant cells (BFTC909-GR). MiR-31-5p expression was analyzed by real-time qPCR in UTUC cell lines. The effects of miR-31-5p combined with CDDP or GEM on the chemosensitivity of cells were analyzed by WST-1. Western blot was applied to detect anti-apoptotic and multidrug resistant protein expression. Silencing of lncRNA was to evaluate CDDP and GEM response by cytotoxicity assay and miR-31-5p levels by real-time PCR.
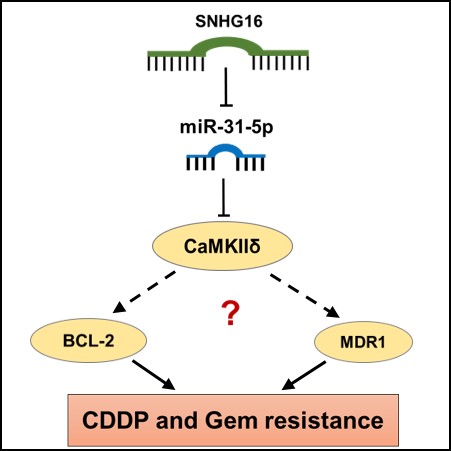
Results: We found that the levels of miR-31-5p were lower in UTUC cell lines than immortalized normal urothelium cells. MiR-31-5p may direct targeted to 3'-UTR of CAMK2D mRNA. The combination of miR-31-5p with CDDP or GEM significantly down-regulated the expression of Bcl-2, Calcium2+/Calmodulin Dependent Protein Kinase II Delta (CaMKIId) and MDR1 as compared with drug treatment alone. Bcl-2, CaMKIId and MDR1 had higher expression in CDDP and GEM resistant cells than parental cells. In addition, we found that lncRNA SNHG16 may direct target to miR-31-5p. SNHG16 knockdown induced miR-31-5p levels in BFTC909 cells and indicated that SNHG16 may negatively regulate the expression of miR-31-5p. Importantly, SNHG16 silencing increased CDDP sensitivity in BFTC909 cells.
Conclusions: Taken together, our study indicated that SNHG16 and miR-31-5p might modulate CDDP or Gem-resistance through regulating CaMKIId, Bcl-2 and MDR1 in UTUC cells.
Source of Funding: This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 109-2314-B-037 -105 -MY3).
Methods: In this study, we established BFTC909 derived CDDP-resistant (BFTC909-CR) and GEM-resistant cells (BFTC909-GR). MiR-31-5p expression was analyzed by real-time qPCR in UTUC cell lines. The effects of miR-31-5p combined with CDDP or GEM on the chemosensitivity of cells were analyzed by WST-1. Western blot was applied to detect anti-apoptotic and multidrug resistant protein expression. Silencing of lncRNA was to evaluate CDDP and GEM response by cytotoxicity assay and miR-31-5p levels by real-time PCR.
Results: We found that the levels of miR-31-5p were lower in UTUC cell lines than immortalized normal urothelium cells. MiR-31-5p may direct targeted to 3'-UTR of CAMK2D mRNA. The combination of miR-31-5p with CDDP or GEM significantly down-regulated the expression of Bcl-2, Calcium2+/Calmodulin Dependent Protein Kinase II Delta (CaMKIId) and MDR1 as compared with drug treatment alone. Bcl-2, CaMKIId and MDR1 had higher expression in CDDP and GEM resistant cells than parental cells. In addition, we found that lncRNA SNHG16 may direct target to miR-31-5p. SNHG16 knockdown induced miR-31-5p levels in BFTC909 cells and indicated that SNHG16 may negatively regulate the expression of miR-31-5p. Importantly, SNHG16 silencing increased CDDP sensitivity in BFTC909 cells.
Conclusions: Taken together, our study indicated that SNHG16 and miR-31-5p might modulate CDDP or Gem-resistance through regulating CaMKIId, Bcl-2 and MDR1 in UTUC cells.
Source of Funding: This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 109-2314-B-037 -105 -MY3).


.jpg)
.jpg)