Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP41: Surgical Technology & Simulation: Training & Skills Assessment
MP41-12: Effectiveness of Virtual Reality simulation of renal puncture for endoscopic-combined intrarenal surgery.
Sunday, May 15, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:45 AM
Location: Room 228
Atsushi Okada*, Kazuya Ohashi, Yusuke Noda, Tomoki Okada, Ryosuke Chaya, Kengo Kawase, Taiki Kato, Kazumi Taguchi, Shuzo Hamamoto, Keiichi Tozawa, Kenjiro Kohri, Takahiro Yasui, Nagoya, Japan

Atsushi Okada, MD,PhD
Associate Professor
Department of Nephro-urology, Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Renal puncture is the most important process for success and the occurrence of perioperative complications in endoscopic combined intrarenal surgery (ECIRS). To determine the ideal renal puncture line based on patient-specific three-dimensional anatomy, we developed a renal puncture simulation using virtual reality (VR) and examined its usefulness.
Methods: The subjects were 143 patients who underwent ECIRS conducted in our facility from January 2016 to August 2020, which were divided into two groups; conventional group (CON; N = 117) and VR simulation group (VR; N = 26). In the VR group, the stereolithography (STL) files based on the preoperative contrast-enhanced CT images of skin, bones, renal parenchyma, arteries, veins, colleting system, stones, and surrounding organs were built using Ziostation, a medical workstation software. These files were integrated in the VR application Holoeyes XR, and doctors were able to determine the ideal renal puncture line for a collecting system floating in the virtual space of Windows Mixed Reality, an immersive 3D goggle. Furthermore, the distance of the puncture point from the ribs and spinal column was measured, and the information was marked on the skin of the actual patient and used for surgery.
Results: In the VR group, 3D anatomy specific to all patients could be observed with immersive VR goggles, and we were able to determine some ideal puncture lines that connect the skin to the renal papilla, which does not damage the bones, surrounding organs (liver, spleen, intestinal tract), arteries and veins. Based on the information, renal puncture was performed smoothly in all cases. Compared with the CON and VR group, the average operation time were 122.7 minutes vs. 115.6 minutes (p = 0.439), endoscopic stone free rates were 77.2% vs. 76.9% (p = 0.976), and CT-based stone free rates were 42.2% vs, 69.2% (p=0.013), respectively.
Conclusions: Renal puncture using VR is an intuitive simulation that may be useful in determining patient-specific renal puncture points that are effective in the complete removal of stones.
Source of Funding: Japane society of endourology
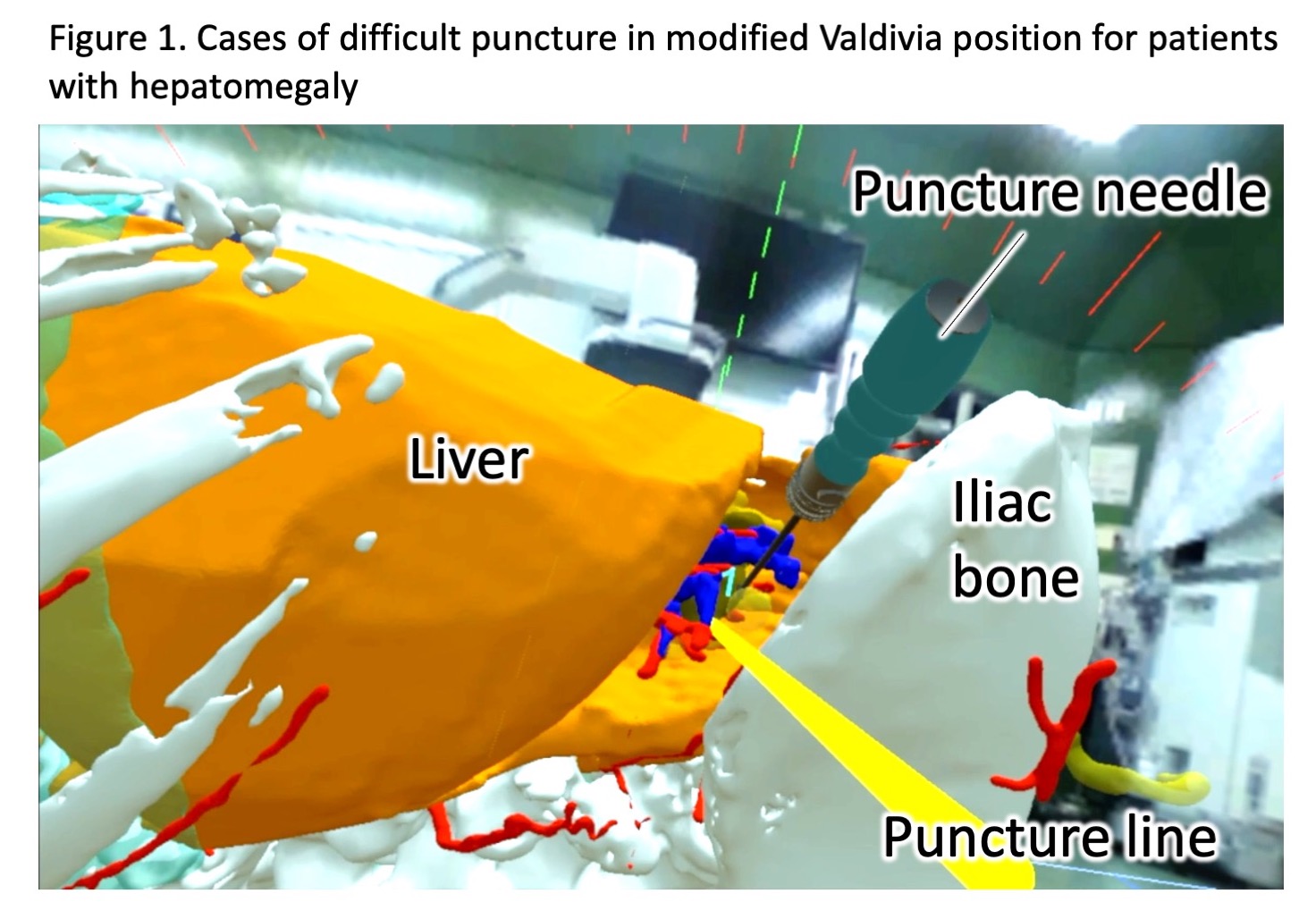
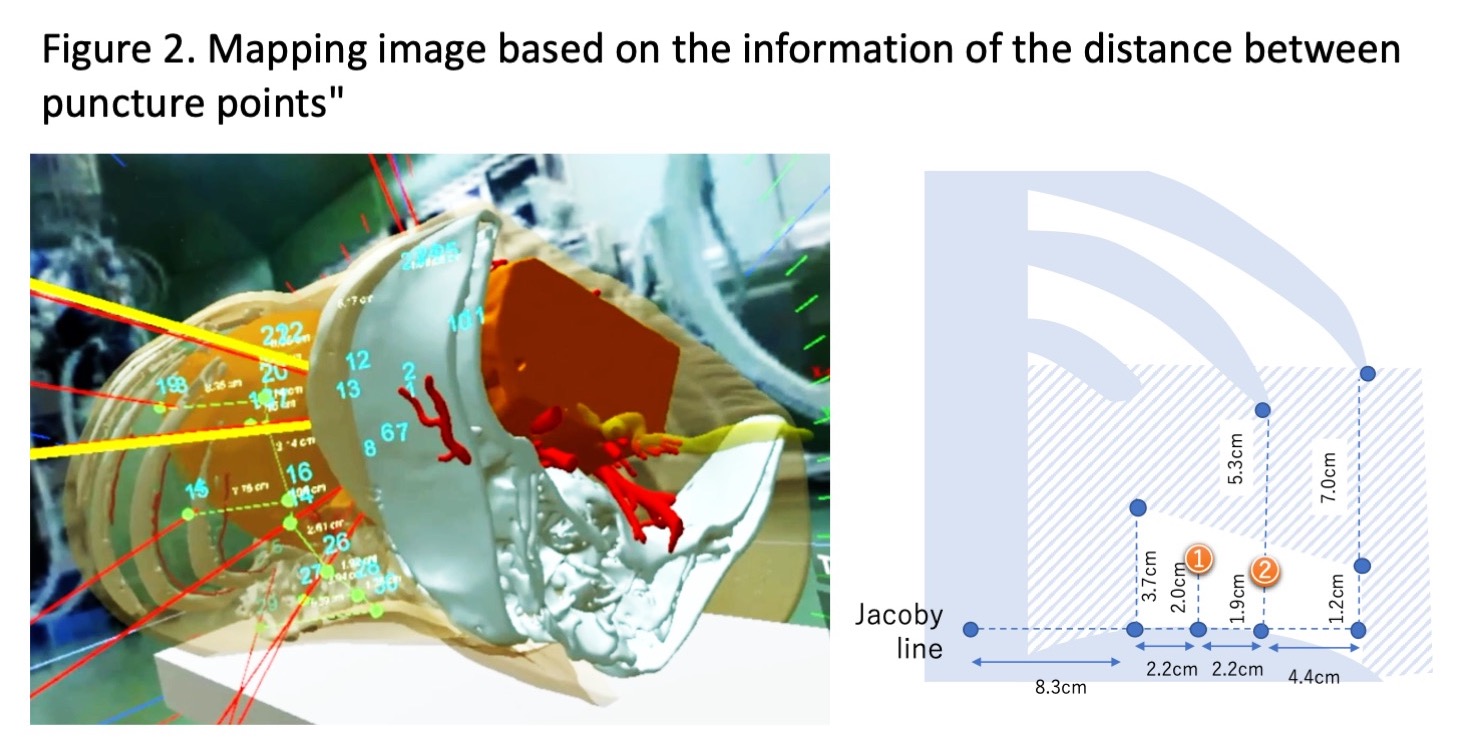
Methods: The subjects were 143 patients who underwent ECIRS conducted in our facility from January 2016 to August 2020, which were divided into two groups; conventional group (CON; N = 117) and VR simulation group (VR; N = 26). In the VR group, the stereolithography (STL) files based on the preoperative contrast-enhanced CT images of skin, bones, renal parenchyma, arteries, veins, colleting system, stones, and surrounding organs were built using Ziostation, a medical workstation software. These files were integrated in the VR application Holoeyes XR, and doctors were able to determine the ideal renal puncture line for a collecting system floating in the virtual space of Windows Mixed Reality, an immersive 3D goggle. Furthermore, the distance of the puncture point from the ribs and spinal column was measured, and the information was marked on the skin of the actual patient and used for surgery.
Results: In the VR group, 3D anatomy specific to all patients could be observed with immersive VR goggles, and we were able to determine some ideal puncture lines that connect the skin to the renal papilla, which does not damage the bones, surrounding organs (liver, spleen, intestinal tract), arteries and veins. Based on the information, renal puncture was performed smoothly in all cases. Compared with the CON and VR group, the average operation time were 122.7 minutes vs. 115.6 minutes (p = 0.439), endoscopic stone free rates were 77.2% vs. 76.9% (p = 0.976), and CT-based stone free rates were 42.2% vs, 69.2% (p=0.013), respectively.
Conclusions: Renal puncture using VR is an intuitive simulation that may be useful in determining patient-specific renal puncture points that are effective in the complete removal of stones.
Source of Funding: Japane society of endourology



.jpg)
.jpg)