Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP42: Bladder Cancer: Epidemiology & Evaluation II
MP42-15: Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder with Isolated Lymph Node Metastasis: Natural History and Outcomes Following Surgical Resection
Sunday, May 15, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:45 AM
Location: Room 225
Ernest Morton, Grand Rapids, MI, Sumedh Kaul, Aaron Fleishman, Ruslan Korets, Peter Chang, Andrew Wagner, Boston, MA, Simon Kim, Aurora, CO, Joaquim Bellmunt, Irving Kaplan, Aria Olumi, Boris Gershman*, Boston, MA
- BG
Boris Gershman, MD
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Pathologic lymph node involvement (cN0 pN+) carries a poor prognosis in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder (UCB), and there are limited contemporary data describing the natural history of UCB in such patients following radical cystectomy (RC) with pelvic lymph node dissection (PLND). We therefore utilized a nationwide oncology dataset to examine the natural history and outcomes of cN0 pN+ UCB after RC and PLND.
Methods: We identified patients in the National Cancer Database (NCDB) with cN0 pN+ cM0 UCB from 2006-2015 treated with RC and PLND. The associations of baseline characteristics with all-cause mortality (ACM) were evaluated using Cox regression.
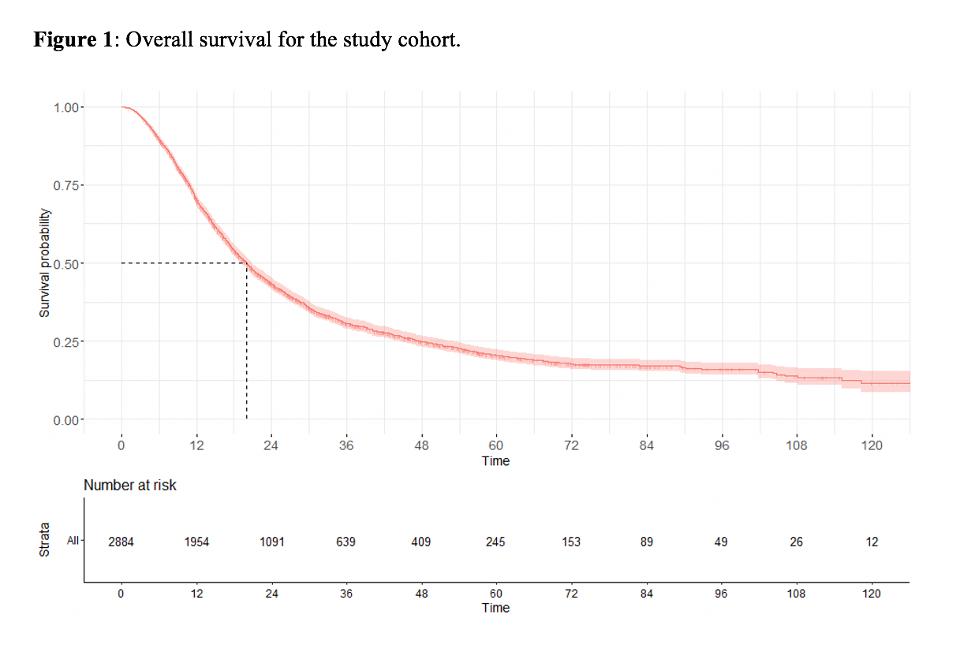
Results: The study cohort consisted of 2,884 patients, including 42% with pN1 and 58% with pN2-3 disease. Of these, 606 (21%) received multiagent neoadjuvant chemotherapy, while 1,172 (41%) received post-operative adjuvant chemotherapy. A median of 15 (IQR 9-23) LNs were removed during PLND. The 5- and 8-year overall survival (OS) for the entire cohort were 20% and 17%, respectively (Fig. 1). Compared to the overall cohort, patients surviving >5 years had lower pN stage (59% vs 42% pN1) and pT stage (41% vs 22% =pT2). On multivariable analysis, higher pT stage (HR 2.84, 95% CI 1.15-5.33 for pT3, HR 3.33, 95% CI 1.76-6.29 for pT4 vs pT0) and pN stage (HR 1.27, 95% CI 1.14-1.42 for pN2-3 vs pN1) were associated with worse ACM, while greater number of LNs removed (HR 0.99, 95% CI 0.98-0.99) and receipt of adjuvant chemotherapy (HR 0.62, 95% CI 0.56-0.69) were associated with improved ACM (Table 1).
Conclusions: While OS for cN0 pN+ M0 UCB is poor, a subset of patients demonstrates durable long-term survival with 5- and 8-year OS of 20% and 17%, respectively. Higher pT and pN stage represent adverse prognostic characteristics, while greater extent of PLND and administration of adjuvant chemotherapy represent potential interventions associated with improved OS.
Source of Funding: None

Methods: We identified patients in the National Cancer Database (NCDB) with cN0 pN+ cM0 UCB from 2006-2015 treated with RC and PLND. The associations of baseline characteristics with all-cause mortality (ACM) were evaluated using Cox regression.
Results: The study cohort consisted of 2,884 patients, including 42% with pN1 and 58% with pN2-3 disease. Of these, 606 (21%) received multiagent neoadjuvant chemotherapy, while 1,172 (41%) received post-operative adjuvant chemotherapy. A median of 15 (IQR 9-23) LNs were removed during PLND. The 5- and 8-year overall survival (OS) for the entire cohort were 20% and 17%, respectively (Fig. 1). Compared to the overall cohort, patients surviving >5 years had lower pN stage (59% vs 42% pN1) and pT stage (41% vs 22% =pT2). On multivariable analysis, higher pT stage (HR 2.84, 95% CI 1.15-5.33 for pT3, HR 3.33, 95% CI 1.76-6.29 for pT4 vs pT0) and pN stage (HR 1.27, 95% CI 1.14-1.42 for pN2-3 vs pN1) were associated with worse ACM, while greater number of LNs removed (HR 0.99, 95% CI 0.98-0.99) and receipt of adjuvant chemotherapy (HR 0.62, 95% CI 0.56-0.69) were associated with improved ACM (Table 1).
Conclusions: While OS for cN0 pN+ M0 UCB is poor, a subset of patients demonstrates durable long-term survival with 5- and 8-year OS of 20% and 17%, respectively. Higher pT and pN stage represent adverse prognostic characteristics, while greater extent of PLND and administration of adjuvant chemotherapy represent potential interventions associated with improved OS.
Source of Funding: None



.jpg)
.jpg)