Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP45: Prostate Cancer: Markers
MP45-09: Discriminative Significance of Prostate Biopsy Decipher Score to Predict Adverse Pathology and Pathological Discordance at Radical Prostatectomy
Sunday, May 15, 2022
1:00 PM – 2:15 PM
Location: Room 225
Ghazal Khajir*, Deepika Kumar, Syed Rahman, Michael Leapman, Angelique Levi, Peter Humphrey, Preston Sprenkle, New Haven, CT
- GK
Ghazal Khajir, MD
Associate research scientist
Department of Urology, Yale school of medicine
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: The predictive value of Decipher test in Grade Group (GG) 3-5, pT3b-T4, or lymph node involvement at radical prostatectomy (RP) is well established. However, little is known about its prognostic significance in other pathological surrogates for metastatic potential, including extraprostatic extension (EPE) and surgical margin, as well as pathologic concordance between biopsy and RP. Therefore, we sought to determine if Decipher score was associated with the presence of those pathological features at RP and biopsy-RP pathological discordance.
Methods: We retrospectively queried an IRB-approved institutional MRI-ultrasound fusion prostate biopsy database of 283 men with Decipher testing on their biopsy tissues. Patients who underwent RP between February 2017 and May 2021 were included in the final analysis. We evaluated associations between clinicopathological variables such as biopsy Decipher score and the presence of positive surgical margin (PSM), EPE, upgrading, and downgrading of biopsy pathology on RP.
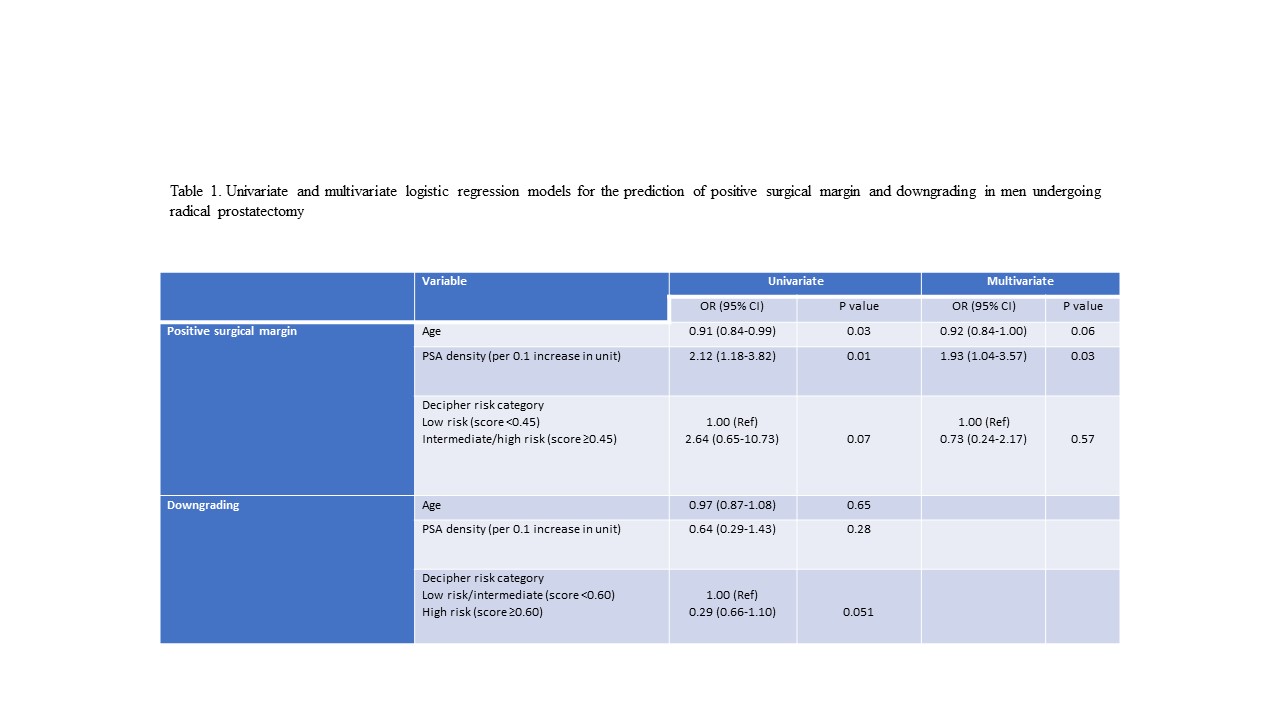
Results: Our cohort included 74 men with biopsy Decipher testing who underwent RP. PSM, EPE, upgrading, and downgrading of biopsy pathology on RP was reported in 35 (47.3%), 30 (40.5%), 7 (9.5%), and 11 (14.9%) men, respectively. Four men (5.4%) had positive lymph nodes on pathology. Among variables entered multivariate analysis (age, PSA density, and Decipher risk category), PSA density remained significantly associated with an increased risk of PSM at RP (OR 1.93, 95%CI 1.04-3.57, p=0.03, Table 1). No studied variables were associated with the presence of EPE or upgrading of biopsy pathology on RP. Moreover, univariable analysis showed that low-intermediate Decipher risk category (score <0.60) was associated with > 3-fold increased odds of downgrading, although this association did not reach conventional levels of statistical significance (OR 3.37, p=0.051, Table 1).
Conclusions: No significant association was found between biopsy Decipher score or risk categories and biopsy-RP pathological discordance or any of the studied pathological features (PSM, EPE). Nevertheless, our study might provide some clues to further investigate the noted lower rate of downgrading in the low-intermediate vs high-risk Decipher risk category.
Source of Funding: N/A
Methods: We retrospectively queried an IRB-approved institutional MRI-ultrasound fusion prostate biopsy database of 283 men with Decipher testing on their biopsy tissues. Patients who underwent RP between February 2017 and May 2021 were included in the final analysis. We evaluated associations between clinicopathological variables such as biopsy Decipher score and the presence of positive surgical margin (PSM), EPE, upgrading, and downgrading of biopsy pathology on RP.
Results: Our cohort included 74 men with biopsy Decipher testing who underwent RP. PSM, EPE, upgrading, and downgrading of biopsy pathology on RP was reported in 35 (47.3%), 30 (40.5%), 7 (9.5%), and 11 (14.9%) men, respectively. Four men (5.4%) had positive lymph nodes on pathology. Among variables entered multivariate analysis (age, PSA density, and Decipher risk category), PSA density remained significantly associated with an increased risk of PSM at RP (OR 1.93, 95%CI 1.04-3.57, p=0.03, Table 1). No studied variables were associated with the presence of EPE or upgrading of biopsy pathology on RP. Moreover, univariable analysis showed that low-intermediate Decipher risk category (score <0.60) was associated with > 3-fold increased odds of downgrading, although this association did not reach conventional levels of statistical significance (OR 3.37, p=0.051, Table 1).
Conclusions: No significant association was found between biopsy Decipher score or risk categories and biopsy-RP pathological discordance or any of the studied pathological features (PSM, EPE). Nevertheless, our study might provide some clues to further investigate the noted lower rate of downgrading in the low-intermediate vs high-risk Decipher risk category.
Source of Funding: N/A


.jpg)
.jpg)