Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP47: Kidney Cancer: Epidemiology & Evaluation/Staging/Surveillance III
MP47-03: Mayo Clinic Validation of The American Urologic Association Risk Groups for Localized Renal Cancer
Sunday, May 15, 2022
2:45 PM – 4:00 PM
Location: Room 228
Andrew Zganjar*, Abhinav Khanna, Dan Joyce, Paige Nichols, Christine Lohse, John Cheville, Sounak Gupta, Aaron Potretzke, R. Houston Thompson, Bradley Leibovich, Stephen Boorjian, Vidit Sharma, Rochester, MN

Andrew J. Zganjar, MD
Mayo Clinic, Rochester
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: The prognosis of patients treated with surgery for localized renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is associated with multiple factors, which has led to the development of prognostic models to predict progression-free survival (PFS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS). The AUA guidelines recently introduced a new risk group stratification system based on tumor stage and grade to guide surveillance after surgery. We sought to evaluate the new AUA risk groups using PFS and CSS at the suggested follow-up intervals and then compare its performance to that of our published institutional risk models.
Methods: We queried our Nephrectomy Registry to identify adults treated with radical or partial nephrectomy for unilateral, M0, clear cell RCC or papillary RCC from 1980–2012. Chromophobe RCC was excluded because the AUA risk groups rely on tumor grade but the WHO/ISUP does not endorse grading this subtype. PFS and CSS were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. Predictive abilities were evaluated using c-indexes from Cox proportional hazards regression models.
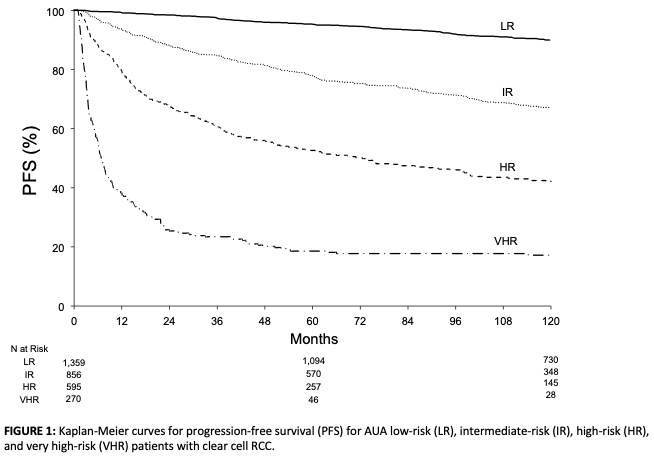
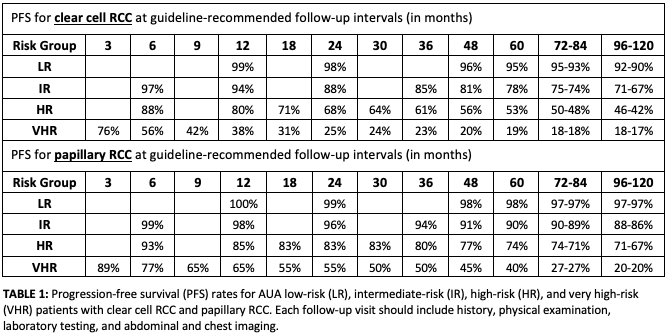
Results: 3,191 patients with clear cell RCC and 633 patients with papillary RCC were included with a median follow-up of 144 and 118 months, respectively. PFS rates by AUA risk group for patients with clear cell RCC and papillary RCC are summarized in Table 1 and (for clear cell RCC) Figure 1. For patients with clear cell RCC, c-indexes for the AUA risk groups and our model were 0.780 and 0.815, respectively (p < 0.001) for PFS, and 0.811 and 0.857, respectively (p < 0.001), for CSS. For patients with papillary RCC, c-indexes for the AUA risk groups and our model were 0.775 and 0.751, respectively (p=0.002) for PFS, and 0.830 and 0.803, respectively (p=0.2) for CSS.
Conclusions: The new AUA risk stratification system has robust c-indexes for PFS and CSS in patients with clear cell RCC and papillary RCC after surgery for localized RCC. A limitation of the AUA risk stratification system is that it does not apply to chromophobe RCC as it relies on tumor grade, yet the WHO/ISUP does not currently endorse grading chromophobe RCC.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: We queried our Nephrectomy Registry to identify adults treated with radical or partial nephrectomy for unilateral, M0, clear cell RCC or papillary RCC from 1980–2012. Chromophobe RCC was excluded because the AUA risk groups rely on tumor grade but the WHO/ISUP does not endorse grading this subtype. PFS and CSS were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. Predictive abilities were evaluated using c-indexes from Cox proportional hazards regression models.
Results: 3,191 patients with clear cell RCC and 633 patients with papillary RCC were included with a median follow-up of 144 and 118 months, respectively. PFS rates by AUA risk group for patients with clear cell RCC and papillary RCC are summarized in Table 1 and (for clear cell RCC) Figure 1. For patients with clear cell RCC, c-indexes for the AUA risk groups and our model were 0.780 and 0.815, respectively (p < 0.001) for PFS, and 0.811 and 0.857, respectively (p < 0.001), for CSS. For patients with papillary RCC, c-indexes for the AUA risk groups and our model were 0.775 and 0.751, respectively (p=0.002) for PFS, and 0.830 and 0.803, respectively (p=0.2) for CSS.
Conclusions: The new AUA risk stratification system has robust c-indexes for PFS and CSS in patients with clear cell RCC and papillary RCC after surgery for localized RCC. A limitation of the AUA risk stratification system is that it does not apply to chromophobe RCC as it relies on tumor grade, yet the WHO/ISUP does not currently endorse grading chromophobe RCC.
Source of Funding: None



.jpg)
.jpg)