Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP51: Prostate Cancer: Staging
MP51-07: The prognostic value of the number of positive targeted cores in men with positive multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate. Results from a large, multi-institutional series.
Sunday, May 15, 2022
4:30 PM – 5:45 PM
Location: Room 222
Armando Stabile*, Elio Mazzone, Giorgio Gandaglia, Milan, Italy, Guillaume Ploussard, Razvan-George Rahota, Toulouse, France, Massimo Valerio, Lausanne, Switzerland, Riccardo Campi, Andrea Mari, Florence, Italy, Agostino Mattei, Lucerne, Switzerland, Giancarlo Marra, Turin, Italy, Jean Baptiste Beauval, Mathieu Roumiguiè, Toulouse, France, Luca Afferi, Lucerne, Italy, Marco Moschini, Lucerne, Switzerland, Paolo Gontero, Turin, Italy, Roderick van den Bergh, Utrecht, Netherlands, Junlong Zhuang, Hongqian Tuo, Jiangsu, China, People's Republic of, Nicola Fossati, Lugano, Switzerland, Francesco Montorsi, Alberto Briganti, Milan, Italy

Armando Stabile, MD
Vita-Salute San Raffaele University
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: The prognostic value of the number of positive targeted biopsy (TBx) cores in men with a positive multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) of the prostate is still a matter of debate and whether tumor burden within the Index Lesion (IL) should be considered in patient risk assessment is unknown. We aimed at evaluating the impact of the percentage of positive TBx cores (TBx ratio) on the rate of biochemical recurrence (BCR) after radical prostatectomy (RP).
Methods: Overall, 3,072 patients with positive mpMRI (PI-RADS=3) receiving TBx plus systematic prostate biopsy (SBx) at ten tertiary centres between 2014 and 2021 were identified. Patients received a median of 4 TBx cores. The relationship between TBx ratio and the 2-year probability of BCR after RP was evaluated. A multivariable Cox regression analysis (MVA) tested the relationship between TBx ratio and BCR accounting for PSA, ISUP grade at TBx, pT stage, pathologic ISUP, and nodal invasion (LNI). An interaction term was tested between TBx ratio and ISUP at TBx. A non-parametric loess analysis was used to graphically explore the variation of the 2-year BCR probability and TBx ratio according to ISUP score at TBx.
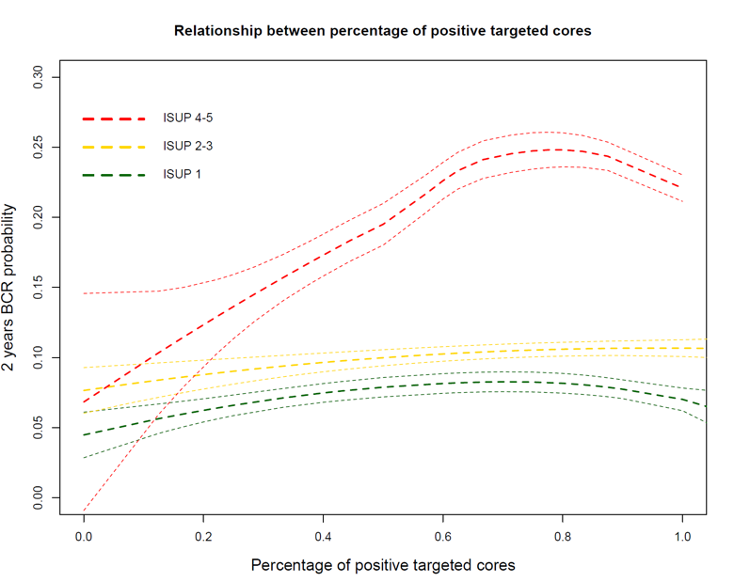
Results: Median age and PSA were 66 years and 7.4 ng/mL, respectively. Overall, 15%, 53% and 32% of patients had PI-RADS 3, 4, and 5. At pathological evaluation, 48%, and 2% of patients had =pT3a disease and LNI. At MVA, TBx ratio (HR: 1.01), PSA (HR: 1.02), pathologic ISUP (HR: 1.45), pT3a (HR: 1.9), T3b (HR: 3.5) and T4 (HR: 10), were predictors of BCR after RP (all p<0.02). The interaction term between TBx ratio and ISUP at TBx was significantly associated with BCR. Figure 1 shows that the 2-year BCR probability increased according to increasing TBx ratio reaching a plateau at roughly 80% of positive TBx cores for patients with ISUP 4-5 at TBx. Conversely, for patients with ISUP 2-3 and ISUP 1, the 2-year BCR probability remained stable regardless of TBx ratio.
Conclusions: Tumor load within the IL was significantly associated with patient outcome only in men with biopsy ISUP grade 4-5. These results should be taken into account during pre-operative treatment planning and overall patient risk assessment.
Source of Funding: None.
Methods: Overall, 3,072 patients with positive mpMRI (PI-RADS=3) receiving TBx plus systematic prostate biopsy (SBx) at ten tertiary centres between 2014 and 2021 were identified. Patients received a median of 4 TBx cores. The relationship between TBx ratio and the 2-year probability of BCR after RP was evaluated. A multivariable Cox regression analysis (MVA) tested the relationship between TBx ratio and BCR accounting for PSA, ISUP grade at TBx, pT stage, pathologic ISUP, and nodal invasion (LNI). An interaction term was tested between TBx ratio and ISUP at TBx. A non-parametric loess analysis was used to graphically explore the variation of the 2-year BCR probability and TBx ratio according to ISUP score at TBx.
Results: Median age and PSA were 66 years and 7.4 ng/mL, respectively. Overall, 15%, 53% and 32% of patients had PI-RADS 3, 4, and 5. At pathological evaluation, 48%, and 2% of patients had =pT3a disease and LNI. At MVA, TBx ratio (HR: 1.01), PSA (HR: 1.02), pathologic ISUP (HR: 1.45), pT3a (HR: 1.9), T3b (HR: 3.5) and T4 (HR: 10), were predictors of BCR after RP (all p<0.02). The interaction term between TBx ratio and ISUP at TBx was significantly associated with BCR. Figure 1 shows that the 2-year BCR probability increased according to increasing TBx ratio reaching a plateau at roughly 80% of positive TBx cores for patients with ISUP 4-5 at TBx. Conversely, for patients with ISUP 2-3 and ISUP 1, the 2-year BCR probability remained stable regardless of TBx ratio.
Conclusions: Tumor load within the IL was significantly associated with patient outcome only in men with biopsy ISUP grade 4-5. These results should be taken into account during pre-operative treatment planning and overall patient risk assessment.
Source of Funding: None.


.jpg)
.jpg)