Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP55: Prostate Cancer: Localized: Ablative Therapy
MP55-05: 5-year Oncologic Outcomes at a Single-Institution Following Focal Cryotherapy for Prostate Cancer Management
Monday, May 16, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 225
Ashley Monaco*, Glen Head, NY, Jessica Sommer, Garden City, NY, Meredith Akerman, Mineola, NY, Anthony Corcoran, Aaron Katz, Garden City, NY

Ashley Monaco, BS
New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Primary focal cryotherapy (PFC) is a novel therapy for prostate cancer (PCa) and therefore evaluation and prediction of outcomes following PFC are not well established. We aim to identify 5-year oncologic outcomes in patients (pts) who receive PFC and identify potential characteristics that may be associated with treatment failure (TF) and biochemical recurrence (BCR).
Methods: A retrospective review of our IRB approved PCa database was performed. Pts with a five year follow-up post PFC were included. TF was defined as salvage treatment. Biochemical recurrence (BCR) defined by Phoenix criteria (nadir > 2) was also assessed. Univariate analyses compared characteristics in pts with or without TF as well as in pts with or without BCR. Factors associated with TF or BCR, respectively, were included in a multivariable logistic regression model. P<0.05 was significant.
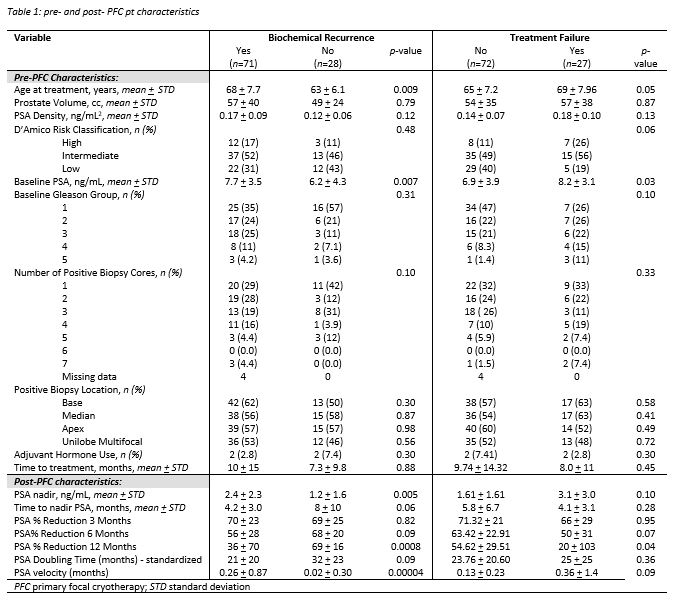
Results: 99 pts met the inclusion criteria from 2010-2017. 71 (72%) had BCR by 5 years however, only 27 (27%) had TF (table 1). While baseline prostate volume, PSA density, D’Amico risk, Gleason group, total number and location of positive cores, time to PFC, or adjuvant hormone use were not associated with TF or BCR, elevated initial PSA was associated with both (each p<0.05). Age was not associated with TF however, pts with BCR were significantly older (p < 0.05). Post PFC, BCR was associated with elevated PSA nadir (p < 0.005), PSA velocity (p < 0.0001), and decreased 12 month PSA % reduction (p < 0.001), which was also significantly associated with TF (p < 0.05), but not at 3 or 6 months. PSA velocity and PSA nadir were not associated with TF. Both time to PSA nadir and PSA doubling time were not associated with TF and BCR. In the final multivariable model, baseline PSA (OR=1.26; 95% CI: 1.07-1.49, p<0.006) and 12 month PSA % reduction (OR: 0.94; 95% CI: 0.90-0.98; p<0.006) were the only significant predictors for BCR. There were no significant predictors of TF.
Conclusions: Though baseline PSA and post PFC 12 month PSA % reduction were significant predictors of BCR, neither pre nor post-treatment pt characteristics were found to predict TF over 5 years. While incidence of BCR post PFC was relatively high, few pts experienced TF. This study suggests markers besides those associated with PSA may be better suited to evaluate and predict PFC outcomes.
Source of Funding: Department of Urology, NYU Langone Hospital – Long Island
Methods: A retrospective review of our IRB approved PCa database was performed. Pts with a five year follow-up post PFC were included. TF was defined as salvage treatment. Biochemical recurrence (BCR) defined by Phoenix criteria (nadir > 2) was also assessed. Univariate analyses compared characteristics in pts with or without TF as well as in pts with or without BCR. Factors associated with TF or BCR, respectively, were included in a multivariable logistic regression model. P<0.05 was significant.
Results: 99 pts met the inclusion criteria from 2010-2017. 71 (72%) had BCR by 5 years however, only 27 (27%) had TF (table 1). While baseline prostate volume, PSA density, D’Amico risk, Gleason group, total number and location of positive cores, time to PFC, or adjuvant hormone use were not associated with TF or BCR, elevated initial PSA was associated with both (each p<0.05). Age was not associated with TF however, pts with BCR were significantly older (p < 0.05). Post PFC, BCR was associated with elevated PSA nadir (p < 0.005), PSA velocity (p < 0.0001), and decreased 12 month PSA % reduction (p < 0.001), which was also significantly associated with TF (p < 0.05), but not at 3 or 6 months. PSA velocity and PSA nadir were not associated with TF. Both time to PSA nadir and PSA doubling time were not associated with TF and BCR. In the final multivariable model, baseline PSA (OR=1.26; 95% CI: 1.07-1.49, p<0.006) and 12 month PSA % reduction (OR: 0.94; 95% CI: 0.90-0.98; p<0.006) were the only significant predictors for BCR. There were no significant predictors of TF.
Conclusions: Though baseline PSA and post PFC 12 month PSA % reduction were significant predictors of BCR, neither pre nor post-treatment pt characteristics were found to predict TF over 5 years. While incidence of BCR post PFC was relatively high, few pts experienced TF. This study suggests markers besides those associated with PSA may be better suited to evaluate and predict PFC outcomes.
Source of Funding: Department of Urology, NYU Langone Hospital – Long Island

.jpg)
.jpg)