Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP55: Prostate Cancer: Localized: Ablative Therapy
MP55-17: Salvage Local Treatment for recurrent prostate cancer after focal therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Monday, May 16, 2022
8:45 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 225
Oliver Claros*, Sao Paulo, Brazil, Rafael Tourinho, Salvador, Brazil, Saulo Teles, Lucas Takemura, Pedro Costa, Sao Paulo, Brazil, Rafael Sanchez-Salas, Paris, France, Bruno Nahar, Abhishek Bhat, Miami, FL, Ruben Olivares, Santiago, Chile, Gustavo Lemos, Arie Carneiro, Sao Paulo, Brazil
- OC
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Therapeutic strategies for focal therapy (FT) failure include salvage radical prostatectomy (sRP), salvage radiotherapy(sRT), and repeat focal treatment using the same or a different energy source as the one used in the primary setting (sFT). We evaluated the role of local salvage treatment for post-FT recurrent prostate cancer, considering oncological and functional outcomes and complication rates.
Methods: A systematic review of Pubmed/Medline and Cochrane databases was performed according to PRISMA guidelines. Approved by Prospero (CRD42021258369). The modified Delphi tool was used to assess the quality of the studies.
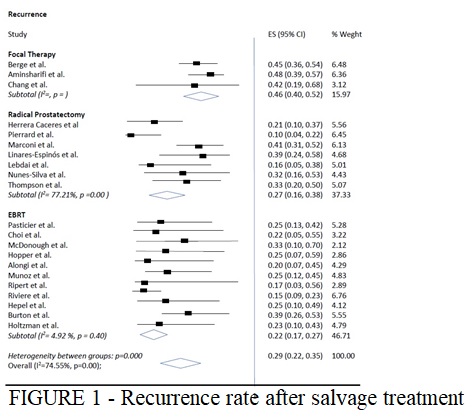
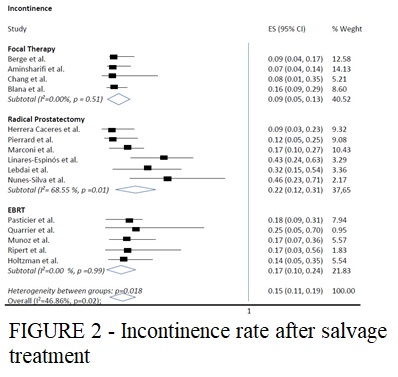
Results: A total of 23 case-series studies comprising 874 patients were included. Overall pooled prevalence of biochemical control was 71% (95% CI 65–78%), with large inter-study heterogeneity (I2=74.55%). Among all salvage modalities, sFT had the worst biochemical control (54%, 95% CI 48– 60%). Patients who underwent sRT had better biochemical control (78%, 95% CI 73–83%), followed by sRP (73%, 95% CI 62–84%). However, sFT had the lowest prevalence of incontinence (9%, 95% CI 5-13%; I2= 0%), followed by sRT (17%, 95% CI 10-24%; I2 = 0%) and sRP (22%, 95% CI 12–31 %; I2 = 68.55%). The overall pooled Clavien Dindo >2 complication rates was 4% (95% CI 2–6%; I2=49.10%) with sRP showing the lowest rates (3% CI 2-7%) and sFT the highest (5% CI 0-10%).
Conclusions: Salvage local treatment post-FT is safe and provides acceptable functional and oncological outcomes. sRT and sRP appear to have better oncological control, while sFT is associated with improved functional outcomes.
Source of Funding: None.
Methods: A systematic review of Pubmed/Medline and Cochrane databases was performed according to PRISMA guidelines. Approved by Prospero (CRD42021258369). The modified Delphi tool was used to assess the quality of the studies.
Results: A total of 23 case-series studies comprising 874 patients were included. Overall pooled prevalence of biochemical control was 71% (95% CI 65–78%), with large inter-study heterogeneity (I2=74.55%). Among all salvage modalities, sFT had the worst biochemical control (54%, 95% CI 48– 60%). Patients who underwent sRT had better biochemical control (78%, 95% CI 73–83%), followed by sRP (73%, 95% CI 62–84%). However, sFT had the lowest prevalence of incontinence (9%, 95% CI 5-13%; I2= 0%), followed by sRT (17%, 95% CI 10-24%; I2 = 0%) and sRP (22%, 95% CI 12–31 %; I2 = 68.55%). The overall pooled Clavien Dindo >2 complication rates was 4% (95% CI 2–6%; I2=49.10%) with sRP showing the lowest rates (3% CI 2-7%) and sFT the highest (5% CI 0-10%).
Conclusions: Salvage local treatment post-FT is safe and provides acceptable functional and oncological outcomes. sRT and sRP appear to have better oncological control, while sFT is associated with improved functional outcomes.
Source of Funding: None.



.jpg)
.jpg)