Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP56: Bladder Cancer: Invasive V
MP56-07: Predictors of response following neoadjuvant cisplatin based chemotherapy for muscle invasive urothelial bladder cancer using molecular profile
Monday, May 16, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:45 AM
Location: Room 228
Ahmed Elkarta*, Ahmed Elhefnawy, Hassan Abol-Enein, Ahmed Shokeir, Mansoura, Egypt

Ahmed Elsherbiny Elkarta, MD, MBBS
Urology and Nephrology center, Mansoura University, Egypt
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Despite Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) before radical cystectomy (RC) improves 5-year survival by 5-10% many patients who receive NAC didn’t get survival benefit and bear the burden of side effects only. Literature has an increasing evidence of the potential role of DNA damage repair (DDR) genes & molecular markers to predict NAC response, however, Currently still no clinically applied reliable predictors for NAC response, as results were cuffed by small number of patients ,retrospective nature & heterogeneity of NAC regimen received. We studied molecular predictors in a prospective study with unified NAC regimen.
Methods: Between December 2019 and August 2021, tumor biopsies were obtained from patients with urothelial MIBC (T2-4a N0 M0) who were fit for RC and eligible for cisplatinum based NAC. Patients received Gemcitabine & Cisplatinum for at least 3 cycles. m-RNA expression levels of DDR (BRACA1, ERCC1) & CTR gene in resected tissue were measured. The response to chemotherapy was assessed following NAC by MRI & pathologically. Patients with stage = pT1 were considered responders. Bivarite and multivariate analysis were used to define predictors for NAC response before RC. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to delineate cutoff value copes with the best sensitivity and specificity for significant continuous data.
Results: 95 patients were included in the study with mean age (SD) 63.04 (6.98) years and the majority were males (91.6%). 36 patients (37.9%) showed complete pathological response to NAC. Bivariate analysis showed that higher mRNA expression level of CTR, lower radiological stage preoperatively and lower mRNA gene expression levels of BRACA1 and ERCC1 were associated with good response to NAC preoperatively.
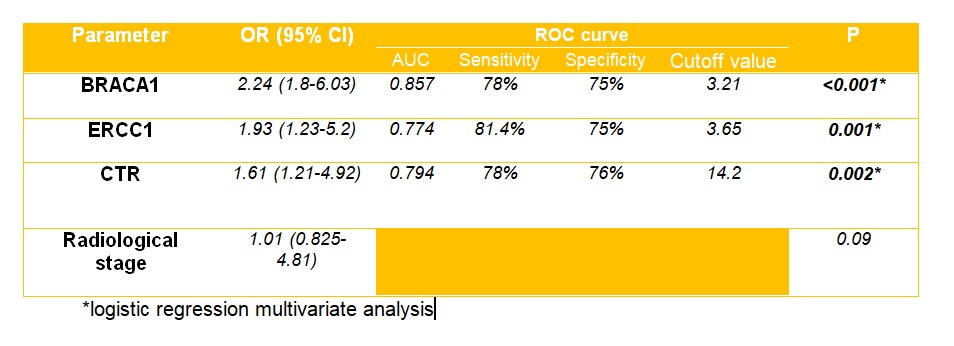
The best cutoff value for mRNA expression of these genes was delineated in table 1. Lower levels of gene expression of BRACA1, ERCC1& higher expression of CTR were the only factors which remained statistically significant in multivariate analysis by logistic regression (table 1)
Conclusions: Molecular profile has a decisive role in identifying patients who will get benefit from preoperative NAC. Lower mRNA expression levels of the genes ERCC1 (=3.65), BRACA1 (=3.21) in addition to higher gene expression of CTR (>14.2) were predictors for good response to cisplatinum based NAC in MIBC.
Source of Funding: No source of funding
Methods: Between December 2019 and August 2021, tumor biopsies were obtained from patients with urothelial MIBC (T2-4a N0 M0) who were fit for RC and eligible for cisplatinum based NAC. Patients received Gemcitabine & Cisplatinum for at least 3 cycles. m-RNA expression levels of DDR (BRACA1, ERCC1) & CTR gene in resected tissue were measured. The response to chemotherapy was assessed following NAC by MRI & pathologically. Patients with stage = pT1 were considered responders. Bivarite and multivariate analysis were used to define predictors for NAC response before RC. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to delineate cutoff value copes with the best sensitivity and specificity for significant continuous data.
Results: 95 patients were included in the study with mean age (SD) 63.04 (6.98) years and the majority were males (91.6%). 36 patients (37.9%) showed complete pathological response to NAC. Bivariate analysis showed that higher mRNA expression level of CTR, lower radiological stage preoperatively and lower mRNA gene expression levels of BRACA1 and ERCC1 were associated with good response to NAC preoperatively.
The best cutoff value for mRNA expression of these genes was delineated in table 1. Lower levels of gene expression of BRACA1, ERCC1& higher expression of CTR were the only factors which remained statistically significant in multivariate analysis by logistic regression (table 1)
Conclusions: Molecular profile has a decisive role in identifying patients who will get benefit from preoperative NAC. Lower mRNA expression levels of the genes ERCC1 (=3.65), BRACA1 (=3.21) in addition to higher gene expression of CTR (>14.2) were predictors for good response to cisplatinum based NAC in MIBC.
Source of Funding: No source of funding


.jpg)
.jpg)