Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP56: Bladder Cancer: Invasive V
MP56-09: Radiomics-based deep-learning improves CT-staging of lymph node status for bladder cancer patients
Monday, May 16, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:45 AM
Location: Room 228
Eva Gresser, Piotr Woznicki, Katharina Messmer, Wolfgang Kunz, Alexander Buchner, Christian Stief, Jens Ricke, Munich, Germany, Dominik Nörenberg, Mannheim, Germany, Gerald Schulz*, Munich, Germany

Gerald Bastian Schulz, MD,FEBU
Assistant Professor
Department of Urology, Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Munich
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Lymph-node assessment in patients with advanced bladder cancer is decisive for the allocation to optimal treatment algorithms. Although contrast-enhanced CT imaging has been the standard for years, sensitivity and specificity is limited. Here, we investigated the diagnostic efficacy of quantitative radiomics features derived from pre-radical cystectomy CT scans to detect lymph node metastases. Results were compared to the radiologists’ assessment.
Methods: Patients undergoing radical cystectomy because of bladder cancer who had received a preoperative contrast-enhanced CT examination were identified. Primary tumor, as well as iliac, obturator, and perivesical lymph nodes were segmented and each node was visually assessed for the presence of metastasis. The dataset was split into training (250 patients), validation (53 patients), and test (121 patients) cohorts. We compared machine learning models trained on extracted quantitative radiomics features with end-to-end deep learning methods and radiologists to assess the value of radiomics for non-invasive predictions of lymph node status (LN-/LN+).
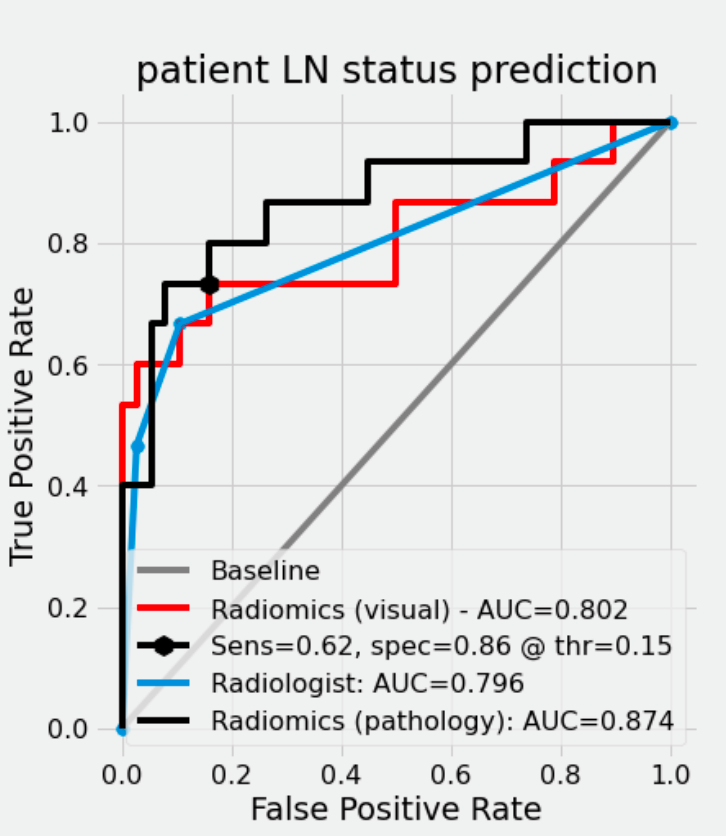
Results: In the pathology report, 101/404 patients had histologically proven lymph node metastases (pN+) and 303/404 were metastasis-free (pN0). The radiomics model trained with histopathology labels achieved an AUC ROC of 0.87 in the test dataset (CI: 0.75-0.99), compared with AUC=0.80 (CI: 0.66-0.94) for radiologists. Radiomics model outperformed the deep learning baseline (AUC=0.70, p<0.05). At the same sensitivity threshold of 0.67, our model had a specificity of 0.95 (CI: 0.87-1.0) compared to 0.89 for the radiologist (CI: 0.78-0.97).
Conclusions: Radiomics-based evaluation of CT-imaging data improves lymph-node staging in bladder cancer patients.
Source of Funding: University Hospital, LMU Munich
Methods: Patients undergoing radical cystectomy because of bladder cancer who had received a preoperative contrast-enhanced CT examination were identified. Primary tumor, as well as iliac, obturator, and perivesical lymph nodes were segmented and each node was visually assessed for the presence of metastasis. The dataset was split into training (250 patients), validation (53 patients), and test (121 patients) cohorts. We compared machine learning models trained on extracted quantitative radiomics features with end-to-end deep learning methods and radiologists to assess the value of radiomics for non-invasive predictions of lymph node status (LN-/LN+).
Results: In the pathology report, 101/404 patients had histologically proven lymph node metastases (pN+) and 303/404 were metastasis-free (pN0). The radiomics model trained with histopathology labels achieved an AUC ROC of 0.87 in the test dataset (CI: 0.75-0.99), compared with AUC=0.80 (CI: 0.66-0.94) for radiologists. Radiomics model outperformed the deep learning baseline (AUC=0.70, p<0.05). At the same sensitivity threshold of 0.67, our model had a specificity of 0.95 (CI: 0.87-1.0) compared to 0.89 for the radiologist (CI: 0.78-0.97).
Conclusions: Radiomics-based evaluation of CT-imaging data improves lymph-node staging in bladder cancer patients.
Source of Funding: University Hospital, LMU Munich


.jpg)
.jpg)