Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP56: Bladder Cancer: Invasive V
MP56-11: The Association Between Early Post-Radical Cystectomy Acute Kidney Injury And Perioperative Outcome In Enhanced Recovery Era
Monday, May 16, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:45 AM
Location: Room 228
Sina Sobhani*, Hamed Ahmadi, Wenhao Yu, Alireza Ghoreifi, Giovanni Cacciamani, Gus Miranda, Jie Cai, Sumeet Bhanvadia, Anne Schuckman, Monish Aron, Inderbir Gill, Siamak Daneshmand, Mihir Desai, Hooman Djaladat, Los Angeles, CA

Sina Sobhani, BS
Keck Medicine of USC
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: Acute kidney injury (AKI), commonly occurs following radical cystectomy (RC) during index hospitalization, could be associated with increased perioperative morbidity and lengthy hospital stay. Herein, we assess the incidence and predictors of early postoperative AKI (EP-AKI) in RC patients.
Methods: All patients with bladder cancer who underwent intent-to-cure RC with enhanced recovery protocol at our center between 2012-2020 were enrolled in this study. EP-AKI was defined per AKIN criteria: increase in creatinine (Cr) or decrease in GFR > 50% (stage 1), > 100% (stage 2), or >150% (stage 3) compared to preoperative baseline within 72 hours, post-operatively. The association between EP-AKI and demographics, clinicopathologic features and perioperative data/outcome including operative time (OT), blood loss and transfusion, preoperative GFR, length of hospital stay (LOS), 30- and 90-day complication and readmission rate were examined. Predictors of EP-AKI were determined using multivariable analysis (MVA).
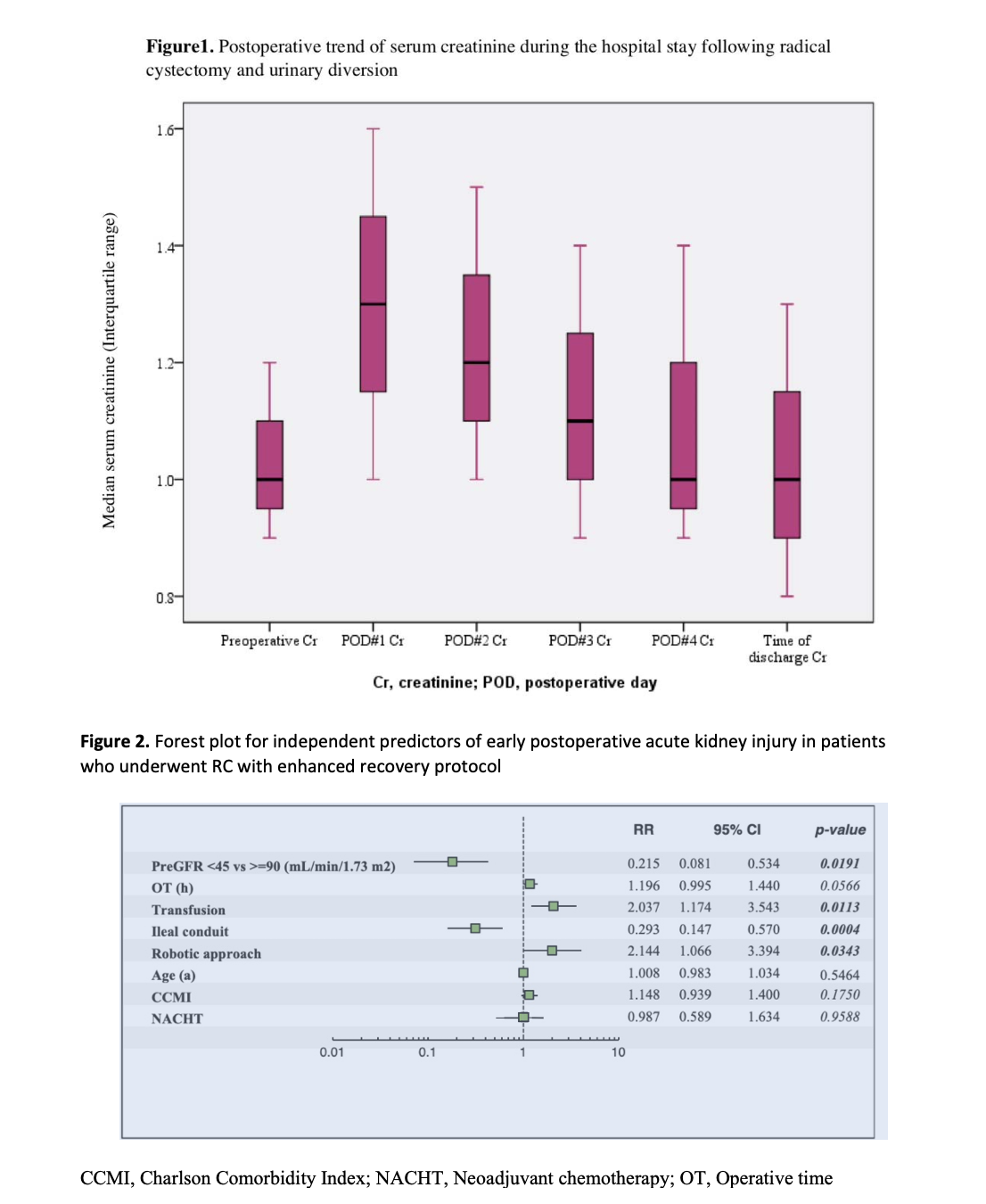
Results: Out of 716 patients who underwent RC with enhanced recovery protocol, 435 met eligibility, of whom 112 (26%) experienced EP-AKI during index hospitalization [90 (21%) stage 1, 17 (4%) stage 2, and 5 (1%) stage 3]. Postoperative trend of serum Cr during hospital stay is shown in Figure 1. Patients with EP-AKI had significantly lower median Pre-Cr (0.9 vs. 1.0; p=0.0004), longer median OT (6.8 vs. 6.0 hours; p<0.0001), and longer mean LOS (6.3 vs. 5.6; p=0.018). Rate of EP-AKI was higher in patients with continent diversion compared to ileal conduits (31% vs. 18%; p=0.001). On MVA, preoperative GFR, transfusion, minimally invasive approach, and continent urinary diversion were independently associated with EP-AKI (Figure 2). EP-AKI was also associated with higher 30- (18% vs. 7%; p=0.0002), and 90-day complication rate (29% vs. 17%; P=0.014). The readmission rate was not significantly different among patients with and without AKI.
Conclusions: A quarter of radical cystectomy patients experience acute kidney injury during index hospitalization that is also associated with lengthier hospital stay and higher perioperative complications. Perioperative transfusion, continent diversion and minimally invasive approach are independently associated with EP-AKI.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: All patients with bladder cancer who underwent intent-to-cure RC with enhanced recovery protocol at our center between 2012-2020 were enrolled in this study. EP-AKI was defined per AKIN criteria: increase in creatinine (Cr) or decrease in GFR > 50% (stage 1), > 100% (stage 2), or >150% (stage 3) compared to preoperative baseline within 72 hours, post-operatively. The association between EP-AKI and demographics, clinicopathologic features and perioperative data/outcome including operative time (OT), blood loss and transfusion, preoperative GFR, length of hospital stay (LOS), 30- and 90-day complication and readmission rate were examined. Predictors of EP-AKI were determined using multivariable analysis (MVA).
Results: Out of 716 patients who underwent RC with enhanced recovery protocol, 435 met eligibility, of whom 112 (26%) experienced EP-AKI during index hospitalization [90 (21%) stage 1, 17 (4%) stage 2, and 5 (1%) stage 3]. Postoperative trend of serum Cr during hospital stay is shown in Figure 1. Patients with EP-AKI had significantly lower median Pre-Cr (0.9 vs. 1.0; p=0.0004), longer median OT (6.8 vs. 6.0 hours; p<0.0001), and longer mean LOS (6.3 vs. 5.6; p=0.018). Rate of EP-AKI was higher in patients with continent diversion compared to ileal conduits (31% vs. 18%; p=0.001). On MVA, preoperative GFR, transfusion, minimally invasive approach, and continent urinary diversion were independently associated with EP-AKI (Figure 2). EP-AKI was also associated with higher 30- (18% vs. 7%; p=0.0002), and 90-day complication rate (29% vs. 17%; P=0.014). The readmission rate was not significantly different among patients with and without AKI.
Conclusions: A quarter of radical cystectomy patients experience acute kidney injury during index hospitalization that is also associated with lengthier hospital stay and higher perioperative complications. Perioperative transfusion, continent diversion and minimally invasive approach are independently associated with EP-AKI.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)