Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP57: Prostate Cancer: Localized: Surgical Therapy IV
MP57-18: Rate of bladder neck contracture after open and minimally invasive radical prostatectomy over 18 years at the Veterans Health Administration
Monday, May 16, 2022
10:30 AM – 11:45 AM
Location: Room 225
Mitch Hayes*, Michael Conlin, Portland, OR, Helen Hougen, Portland, FL, Ryan Kopp, Portland, OR

Mitchell T. Hayes, MD
Oregon Health and Science University
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: The rate of vesicourethral anastomotic stricture (VUAS) rate is higher amongst patients who undergo open radical prostatectomy (RP) compared to robotic RP at high-volume academic centers. We sought to compare the VUAS rate between minimally invasive (MIS) and open RP cohorts amongst United States veterans.
Methods: We queried the Veterans Affairs (VA) Corporate Data Warehouse for patients who underwent retropubic RP between 2003 and 2021 by CPT code (55840, 55845, 55866) were included. Patients who did not have a biopsy at the VA. Possible selected covariates were age, preoperative prostate specific antigen (PSA), agent orange exposure, body mass index (BMI), selected comorbidities based on ICD codes, and MIS surgery defined by the CPT code 55866. The primary outcome was undergoing a transurethral incision of a postoperative bladder neck contracture (TUIBNC) within 2 years of surgery by CPT code (52640). The secondary outcome was undergoing any incontinence procedure within 2 years of RP by male sling and artificial urinary sphincter CPT codes. Multivariate logistic regression was performed on the primary and secondary outcome. Stepwise selection was used for model building and restricted cubic spline terms were used for continuous variables. All statistics were performed in R, version 4.0.5.
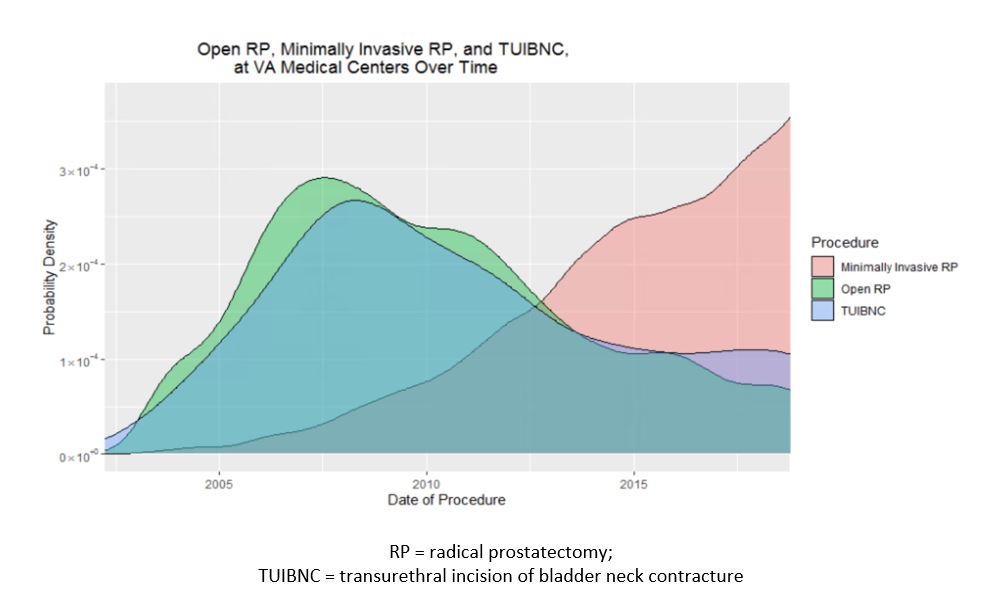
Results: 32,776 patients were included in the analysis. Median patient age was 62 years old and median PSA was 6.04. 57.8% underwent open RP, and 42.3% underwent MIS RP. Overall TUIBNC and incontinence procedure cases within 2 years of surgery were 292 (0.9%) and 725 (2.2%), respectively. Median time to TUIBNC was 8.0 months. On multivariate analysis, after adjusting for age, PSA, and a history of congestive heart failure (CHF), the risk of TUIBNC remained higher with open surgery (OR 7.1, CI 4.7-11.4 p < 0.001). Figure 1 shows the rate of MIS RP, open RP, and TUIBNC over time. On multivariate analysis, after adjusting for age, BMI, a history of myocardial infarction, CHF, and diabetes, incontinence surgery within 2 years of surgery was higher after open RP (OR 1.29, CI 1.08-1.53, p 0.004).
Conclusions: Compared to MIS RP, open RP was associated with a 7-fold increase in rate of VUAS and a 1.3-fold increase in the rate of incontinence requiring a procedure within 2 years of surgery at the VA.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: We queried the Veterans Affairs (VA) Corporate Data Warehouse for patients who underwent retropubic RP between 2003 and 2021 by CPT code (55840, 55845, 55866) were included. Patients who did not have a biopsy at the VA. Possible selected covariates were age, preoperative prostate specific antigen (PSA), agent orange exposure, body mass index (BMI), selected comorbidities based on ICD codes, and MIS surgery defined by the CPT code 55866. The primary outcome was undergoing a transurethral incision of a postoperative bladder neck contracture (TUIBNC) within 2 years of surgery by CPT code (52640). The secondary outcome was undergoing any incontinence procedure within 2 years of RP by male sling and artificial urinary sphincter CPT codes. Multivariate logistic regression was performed on the primary and secondary outcome. Stepwise selection was used for model building and restricted cubic spline terms were used for continuous variables. All statistics were performed in R, version 4.0.5.
Results: 32,776 patients were included in the analysis. Median patient age was 62 years old and median PSA was 6.04. 57.8% underwent open RP, and 42.3% underwent MIS RP. Overall TUIBNC and incontinence procedure cases within 2 years of surgery were 292 (0.9%) and 725 (2.2%), respectively. Median time to TUIBNC was 8.0 months. On multivariate analysis, after adjusting for age, PSA, and a history of congestive heart failure (CHF), the risk of TUIBNC remained higher with open surgery (OR 7.1, CI 4.7-11.4 p < 0.001). Figure 1 shows the rate of MIS RP, open RP, and TUIBNC over time. On multivariate analysis, after adjusting for age, BMI, a history of myocardial infarction, CHF, and diabetes, incontinence surgery within 2 years of surgery was higher after open RP (OR 1.29, CI 1.08-1.53, p 0.004).
Conclusions: Compared to MIS RP, open RP was associated with a 7-fold increase in rate of VUAS and a 1.3-fold increase in the rate of incontinence requiring a procedure within 2 years of surgery at the VA.
Source of Funding: None

.jpg)
.jpg)