Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP58: Prostate Cancer: Detection & Screening VII
MP58-06: Diagnostic performance of mixed targeted prostate biopsy approaches using micro-Ultrasound and MRI-fusion biopsies
Monday, May 16, 2022
1:00 PM – 2:15 PM
Location: Room 228
Davide Maffei*, Cesare Saitta, Pier Paolo Avolio, Marco Paciotti, Vittorio Fasulo, Nicola Frego, Pietro Diana, Pieve Emanuele, Italy, Lazzeri Massimo, Rodolfo Hurle, Alberto Rosario Saita, Rozzano, Italy, Giorgio Ferruccio Guazzoni, Pieve Emanuele, Italy, Paolo Casale, Rozzano, Italy, Nicolò Maria Buffi, Giovanni Lughezzani, Pieve Emanuele, Italy

Davide Maffei, MD
Humanitas University
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: MR imaging(MRI) has gained a central role in prostate cancer (PCa) diagnosis. High-resolution micro-ultrasound (mUS) is a new imaging modality enabling real-time targeted prostate biopsies. We compared the diagnostic performance of MRI and mUS for the detection of clinically significant PCa (GS=7; csPCa)
Methods: We prospectively enrolled 685 patients with clinical suspicion of PCa and available MRI. The PRI-MUS protocol was used to identify target lesions on mUS. All subjects received mUS and MRI targeted biopsy as well as systematic biopsies. The csPCa detection rate was assessed and stratified according to the bioptic strategy
Results: Mean age was 65.2 (SD7.8)yr, median PSA was 7.1(IQR 5.0-9.7)ng/mL and median prostate volume was 50 (IQR 35-70)mL. Overall, 41.6% patients were in the repeat biopsy setting. Suspicious lesions were identified by mUS and MRI in 535(78.1%) and 627 (91.5%) patients, respectively. PCa and csPCa were diagnosed in 52.5% and 37.0% of patients.
CsPCa detection rates increased from 27.8% to 38.1% and 67.7% in patients with PRI-MUS 3, 4 and 5 lesions, respectively (p < 0.01). Similarly, csPCa detection rates increased from 18.2% to 39.7% and 65.1% in patients with PI-RADS 3, 4 and 5 lesions, respectively (p < 0.01). MUS-targeted cores were positive for csPCa in 183/258 (70.9%) patients, while combination of mUS-targeted and systematic biopsies detected 246 (95.3%) csPCa. MRI-targeted cores were positive for csPCa in 198 (76.7%) patients, while combination with randomized biopsies detected 250 (96.9%) csPCa. Only 12 csPCa were diagnosed by MRI-targeted cores alone, while 8 csPCa patients were detected uniquely on mUS-targeted cores.
MUS imaging provided high sensitivity with 90.7% csPCa patients (234/258) having at least one PRI-MUS score =3 lesion. NPV was 84.0% (126/150 patients without target lesions classified benign or GS6). PPV and specificity were 43.7% and 29.5% respectively. MRI sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV were 96.9%, 29.5%, 43.7% and 84.0%.
Conclusions: MUS is a promising imaging modality for targeted prostate biopsies, enabling high sensitivity to detect PCa. This work suggests that mUS and MRI both represent essential targeting modalities for csPCa diagnosis, which can similarly maximize the diagnostic performance of prostate biopsies.
Source of Funding: None
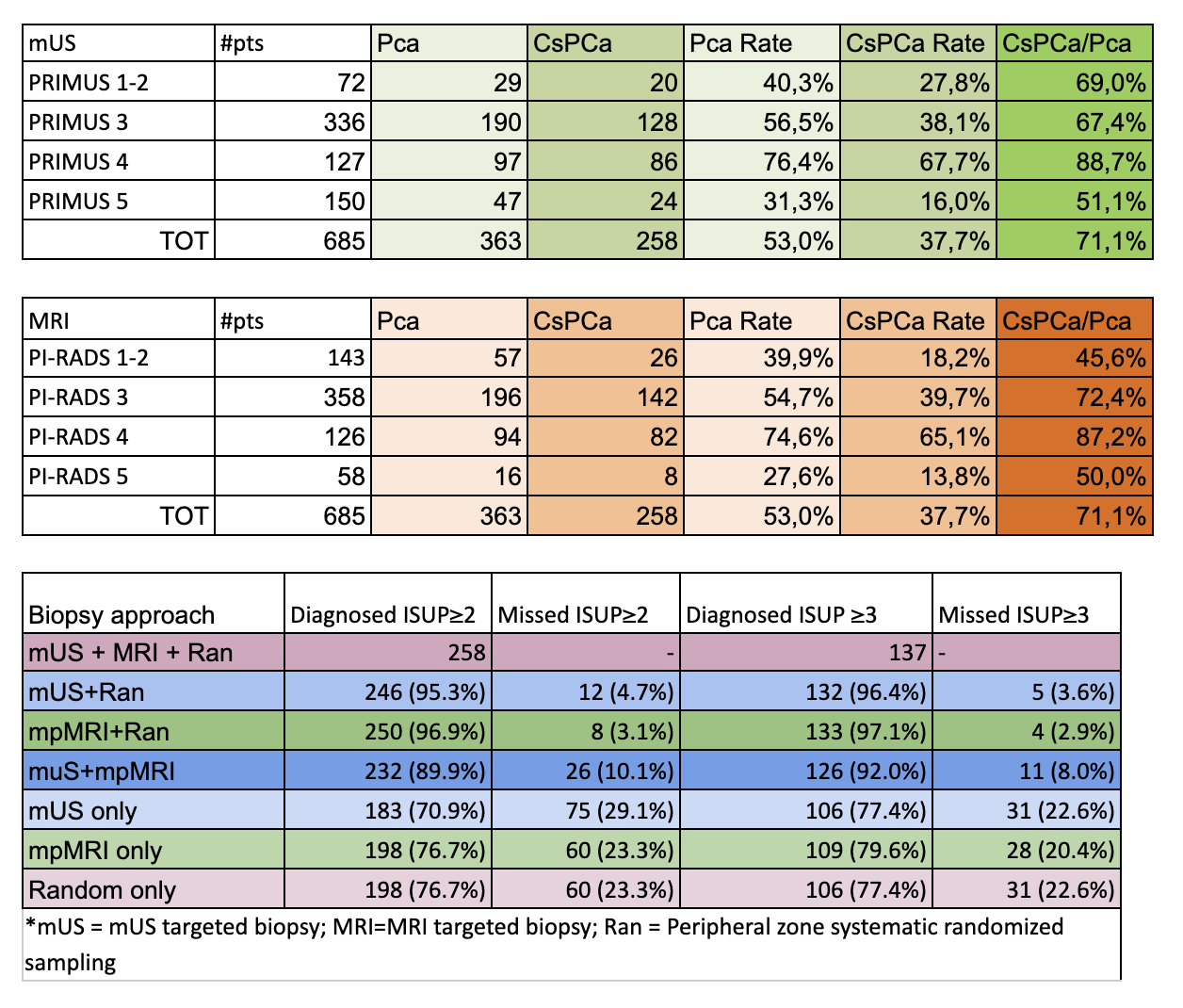
Methods: We prospectively enrolled 685 patients with clinical suspicion of PCa and available MRI. The PRI-MUS protocol was used to identify target lesions on mUS. All subjects received mUS and MRI targeted biopsy as well as systematic biopsies. The csPCa detection rate was assessed and stratified according to the bioptic strategy
Results: Mean age was 65.2 (SD7.8)yr, median PSA was 7.1(IQR 5.0-9.7)ng/mL and median prostate volume was 50 (IQR 35-70)mL. Overall, 41.6% patients were in the repeat biopsy setting. Suspicious lesions were identified by mUS and MRI in 535(78.1%) and 627 (91.5%) patients, respectively. PCa and csPCa were diagnosed in 52.5% and 37.0% of patients.
CsPCa detection rates increased from 27.8% to 38.1% and 67.7% in patients with PRI-MUS 3, 4 and 5 lesions, respectively (p < 0.01). Similarly, csPCa detection rates increased from 18.2% to 39.7% and 65.1% in patients with PI-RADS 3, 4 and 5 lesions, respectively (p < 0.01). MUS-targeted cores were positive for csPCa in 183/258 (70.9%) patients, while combination of mUS-targeted and systematic biopsies detected 246 (95.3%) csPCa. MRI-targeted cores were positive for csPCa in 198 (76.7%) patients, while combination with randomized biopsies detected 250 (96.9%) csPCa. Only 12 csPCa were diagnosed by MRI-targeted cores alone, while 8 csPCa patients were detected uniquely on mUS-targeted cores.
MUS imaging provided high sensitivity with 90.7% csPCa patients (234/258) having at least one PRI-MUS score =3 lesion. NPV was 84.0% (126/150 patients without target lesions classified benign or GS6). PPV and specificity were 43.7% and 29.5% respectively. MRI sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV were 96.9%, 29.5%, 43.7% and 84.0%.
Conclusions: MUS is a promising imaging modality for targeted prostate biopsies, enabling high sensitivity to detect PCa. This work suggests that mUS and MRI both represent essential targeting modalities for csPCa diagnosis, which can similarly maximize the diagnostic performance of prostate biopsies.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)