Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD03: Prostate Cancer: Epidemiology & Natural History I
PD03-03: Association between 5&[alpha]-reductase Inhibitor and Incidence, Tumor Grading and Survival of Prostate Cancer
Friday, May 13, 2022
7:20 AM – 7:30 AM
Location: Room 245
Peng-Yen Wu*, Li-Weng Chang, Sheng-Chun Hung, Jian-Ri Li, Kun-Yuan Chiu, Kevin Lu, Shian-Shiang Wang, Chuan-Shu Chen, Chen-Kuang Yang, Cheng-Che Chen, Shu-Chi Wang, Chia-Yen Lin, Chen-Li Cheng, Taichung, Taiwan
- PW
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: The purpose of the study was to investigate the association between 5a-reductase inhibitor (5ARI) and incidence, tumor grading and survival of prostate cancer.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the data of patients who were diagnosed with benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH). The data was compared between the patients who have ever received 5ARI and those who haven’t.
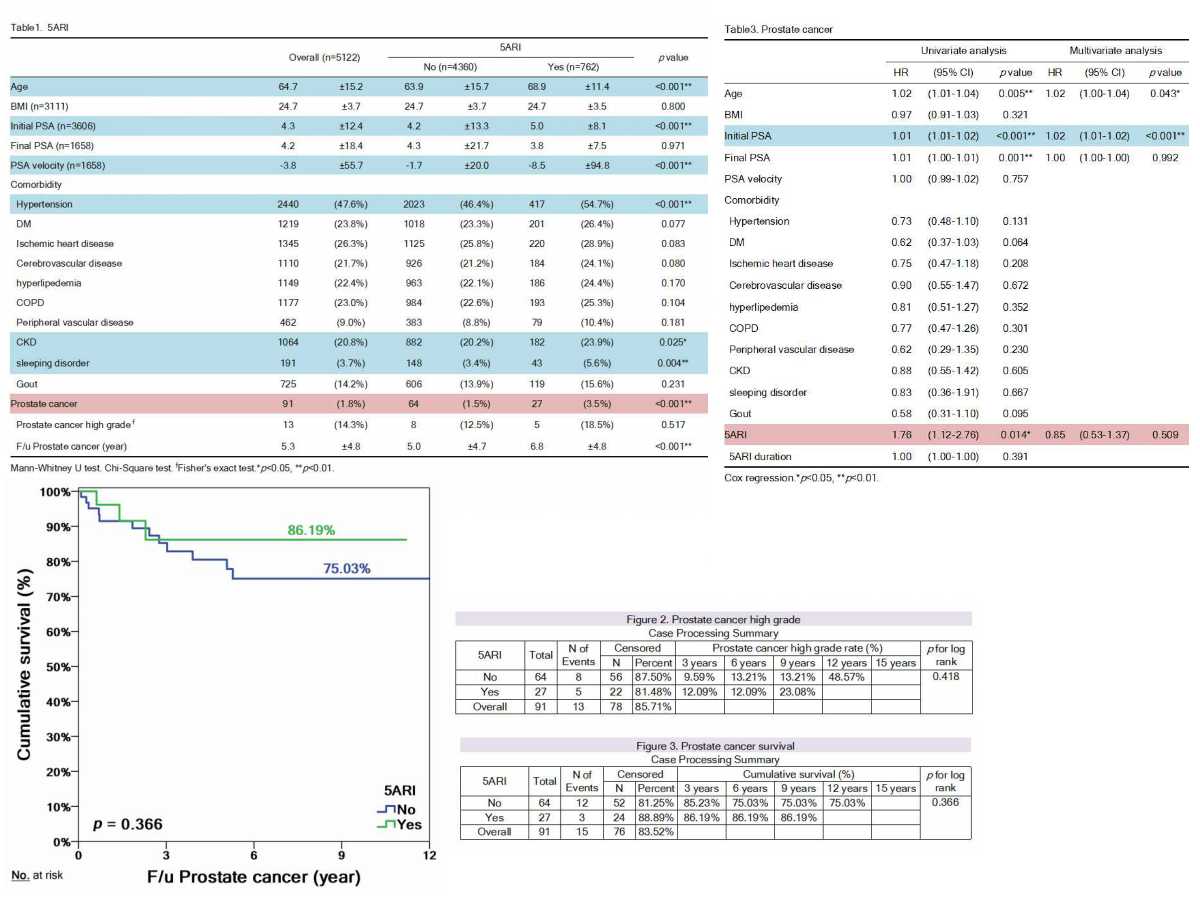
Results: From 2007 to 2012, 5122 patients with BPH diagnosed at Taichung Veterans General Hospital were enrolled in this study. The data was followed until 2020. 762 patients received 5ARI and 4360 didn’t. Comparing the patient characteristics between 5ARI and non-5ARI groups, the patients of 5ARI group were older, had higher initial PSA, and higher prevalence of hypertension, chronic kidney disease and sleeping disorder. The incidence of prostate cancer was found to be significantly higher in the 5ARI group (3.5% vs. 1.5%, p<0.001). In a multivariate model, the initial PSA was an independent risk factor in development of prostate cancer (HR = 1.02, 95% CI (1.01 - 1.02)). On the contrary, the impact of 5ARI on development of prostate cancer was found to be non-significant (HR = 0.85, 95% CI (0.53 - 1.37), p=0.509) after multivariate analysis. The subgroup analysis within the patients with newly diagnosed prostate cancer was performed, comparing the patients with high-grade and low-grade prostate cancer. The patients with high-grade prostate cancer had higher initial PSA. The use of 5ARI was found to be not associated with of high-grade prostate cancer, while the incidence of high-grade prostate cancer between 5ARI group and non-5ARI group showed no significant difference (p=0.418). The overall survival of the patients with prostate cancer showed no difference between 5ARI and non-5ARI groups (86.19% vs. 75.03%, p=0.366).
Conclusions: Our data demonstrated a higher incidence of prostate cancer among the patients who ever received treatment with 5ARI, and this may attribute to the higher age or higher initial PSA. After analysis with multivariate model, the use of 5ARI showed no impact on development of prostate cancer. The incidence of high-grade prostate cancer and overall survival showed no difference between 5ARI and non-5ARI groups.
Source of Funding: nil
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the data of patients who were diagnosed with benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH). The data was compared between the patients who have ever received 5ARI and those who haven’t.
Results: From 2007 to 2012, 5122 patients with BPH diagnosed at Taichung Veterans General Hospital were enrolled in this study. The data was followed until 2020. 762 patients received 5ARI and 4360 didn’t. Comparing the patient characteristics between 5ARI and non-5ARI groups, the patients of 5ARI group were older, had higher initial PSA, and higher prevalence of hypertension, chronic kidney disease and sleeping disorder. The incidence of prostate cancer was found to be significantly higher in the 5ARI group (3.5% vs. 1.5%, p<0.001). In a multivariate model, the initial PSA was an independent risk factor in development of prostate cancer (HR = 1.02, 95% CI (1.01 - 1.02)). On the contrary, the impact of 5ARI on development of prostate cancer was found to be non-significant (HR = 0.85, 95% CI (0.53 - 1.37), p=0.509) after multivariate analysis. The subgroup analysis within the patients with newly diagnosed prostate cancer was performed, comparing the patients with high-grade and low-grade prostate cancer. The patients with high-grade prostate cancer had higher initial PSA. The use of 5ARI was found to be not associated with of high-grade prostate cancer, while the incidence of high-grade prostate cancer between 5ARI group and non-5ARI group showed no significant difference (p=0.418). The overall survival of the patients with prostate cancer showed no difference between 5ARI and non-5ARI groups (86.19% vs. 75.03%, p=0.366).
Conclusions: Our data demonstrated a higher incidence of prostate cancer among the patients who ever received treatment with 5ARI, and this may attribute to the higher age or higher initial PSA. After analysis with multivariate model, the use of 5ARI showed no impact on development of prostate cancer. The incidence of high-grade prostate cancer and overall survival showed no difference between 5ARI and non-5ARI groups.
Source of Funding: nil


.jpg)
.jpg)