Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD05: Stone Disease: Medical & Dietary Therapy
PD05-08: Pharmacologic Management of Ureteral Stent-Related Symptoms: A Drug-Class and Drug Specific Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
Friday, May 13, 2022
10:40 AM – 10:50 AM
Location: Room 252
David E. Hinojosa-Gonzalez*, Brian H. Eisner, Boston, MA
- DH
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Ureteral stents (US) are commonly used for the treatment of ureteral obstruction, most often urolithiasis. Their use may be associated with significant bothersome symptoms and discomfort. Prior studies have examined the effects of various medication regimens on ureteral stent symptoms. This study utilized Bayesian network meta-analysis to analyze all available evidence on the pharmacological management of ureteral stent-related symptoms.
Methods: In August 2021 a systematic review was conducted following PRISMA guidelines on randomized prospective studies on pharmacological management of USRS reporting outcomes using the USSQ score on urinary symptoms and pain. Data was analyzed in Review Manager 5.3 and R Studio where a Bayesian network meta-analysis was performed. Treatments were ranked using surface under the cumulative ranking curve(SUCRA) and mean difference(MD) vs placebo with 95% Credible Intervals(CrI).
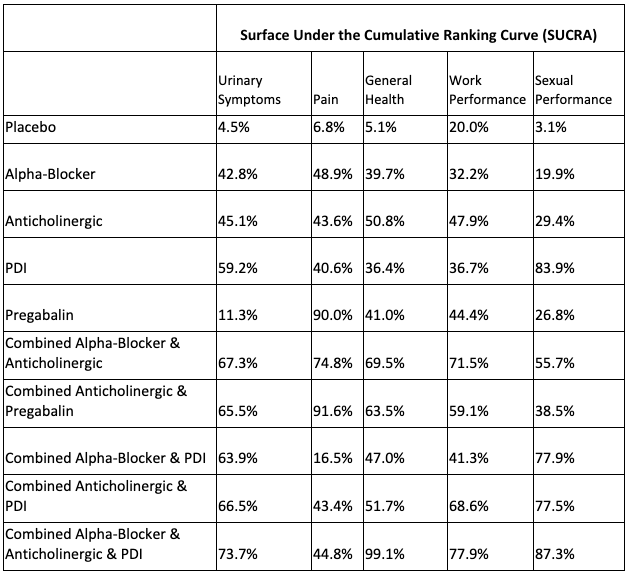
Results: 22 studies were analyzed. These were used to build networks which were modelled to run 100,000 Markov Chain Montecarlo simulations each. Drug-class analysis revealed the most effective class for each domain: for urinary symptoms, sexual performance, general health and work performance - combined Alpha-Blocker & Anticholinergic & PDI; for pain - combined Anticholinergic & Pregabalin. The following were the most effective drugs and dosages for specific symptoms: for urinary symptoms - combined Silodosin 8mg + Solifenacin 10mg; for pain - combined Silodosin 8mg + Solifenacin 10mg; for sexual performance - Tadalafil 5mg. Combined Silodosin 8mg + Solifenacin 10mg + Tadalafil 5mg has the best general health scores while Solifenacin 10mg had the best work experience scores.
Conclusions: This network meta-analysis demonstrated the most effective therapy is different for each symptom domain. It is important to consider patient chief complaints and domains in order to ascertain the optimal medication regimen for each patient.
Source of Funding: No funding was received
Methods: In August 2021 a systematic review was conducted following PRISMA guidelines on randomized prospective studies on pharmacological management of USRS reporting outcomes using the USSQ score on urinary symptoms and pain. Data was analyzed in Review Manager 5.3 and R Studio where a Bayesian network meta-analysis was performed. Treatments were ranked using surface under the cumulative ranking curve(SUCRA) and mean difference(MD) vs placebo with 95% Credible Intervals(CrI).
Results: 22 studies were analyzed. These were used to build networks which were modelled to run 100,000 Markov Chain Montecarlo simulations each. Drug-class analysis revealed the most effective class for each domain: for urinary symptoms, sexual performance, general health and work performance - combined Alpha-Blocker & Anticholinergic & PDI; for pain - combined Anticholinergic & Pregabalin. The following were the most effective drugs and dosages for specific symptoms: for urinary symptoms - combined Silodosin 8mg + Solifenacin 10mg; for pain - combined Silodosin 8mg + Solifenacin 10mg; for sexual performance - Tadalafil 5mg. Combined Silodosin 8mg + Solifenacin 10mg + Tadalafil 5mg has the best general health scores while Solifenacin 10mg had the best work experience scores.
Conclusions: This network meta-analysis demonstrated the most effective therapy is different for each symptom domain. It is important to consider patient chief complaints and domains in order to ascertain the optimal medication regimen for each patient.
Source of Funding: No funding was received


.jpg)
.jpg)