Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD07: Prostate Cancer: Basic Research & Pathophysiology I
PD07-03: An oral first-in-class small molecule RSK inhibitor suppresses AR variants and tumor growth in prostate cancer
Friday, May 13, 2022
9:50 AM – 10:00 AM
Location: Room 245
Masaki Shiota*, Miho Ushijima, Takashi Matsumoto, Eiji Kashiwagi, Junichi Inokuchi, Masatoshi Eto, Fukuoka, Japan
- MS
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Ribosomal S6 kinase has been shown to play a key role in the cellular resistance to endocrine therapy in prostate cancer through its regulation of YB-1/androgen receptor (AR) signaling. PMD-026, an oral first-in-class small molecule kinase inhibitor, is the first identified ribosomal S6 kinase inhibitor. This study investigated the effect of PMD-026 on YB-1/AR signaling and its antitumor effect in prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: Castration-resistant prostate cancer 22Rv1 cells that express high levels AR variants were used in this study. The effect of PMD-026 on YB-1/AR signaling was investigated by quantitative real-time PCR and western blot analysis. The effects of PMD-026 on prostate cancer cells were investigated by cytotoxicity analysis, apoptosis assay, and cell cycle assay in vitro and a mouse castration model in vivo.
Results: PMD-026 decreased YB-1 phosphorylation as well as AR V7 mRNA and AR variants expressions in 22Rv1 cells. PMD-026 suppressed cell proliferation alone and in combination with the second-generation antiandrogens enzalutamide and darolutamide by inducing cellular apoptosis and G2/M arrest. In a mouse xenograft model, PMD-026 suppressed tumor growth, and the combination of PMD-026 and enzalutamide inhibited tumor growth more prominently than single treatments.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate an excellent antitumor effect of the novel ribosomal S6 kinase inhibitor PMD-026 and the combination effect with the antiandrogen enzalutamide in castration-resistant prostate cancer. These findings warrant a clinical trial of PMD-026 in prostate cancer patients.
Source of Funding: None
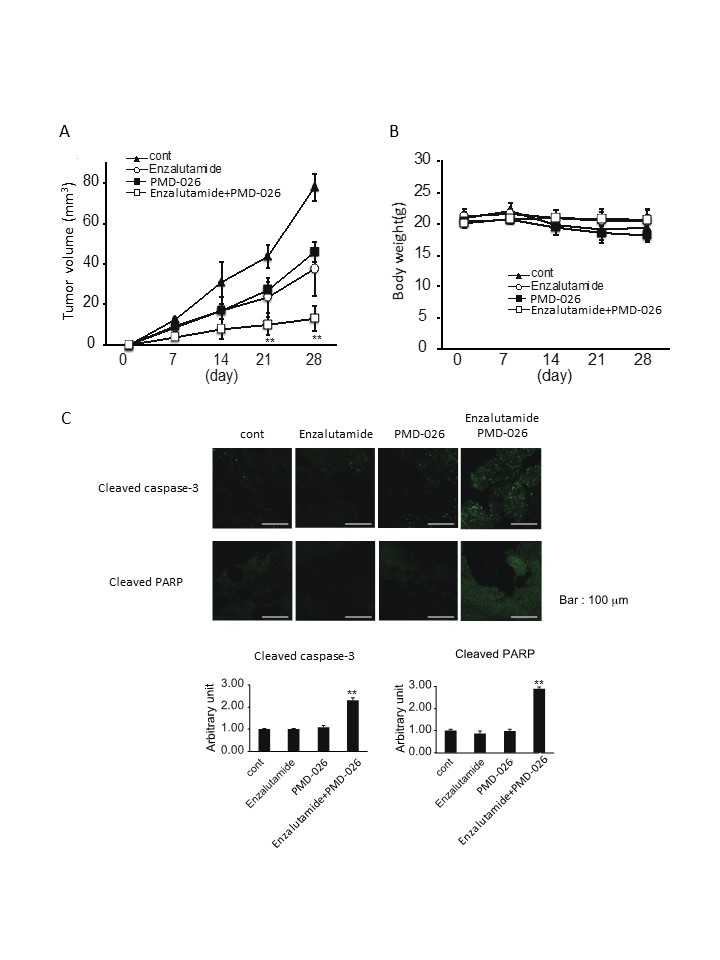
Methods: Castration-resistant prostate cancer 22Rv1 cells that express high levels AR variants were used in this study. The effect of PMD-026 on YB-1/AR signaling was investigated by quantitative real-time PCR and western blot analysis. The effects of PMD-026 on prostate cancer cells were investigated by cytotoxicity analysis, apoptosis assay, and cell cycle assay in vitro and a mouse castration model in vivo.
Results: PMD-026 decreased YB-1 phosphorylation as well as AR V7 mRNA and AR variants expressions in 22Rv1 cells. PMD-026 suppressed cell proliferation alone and in combination with the second-generation antiandrogens enzalutamide and darolutamide by inducing cellular apoptosis and G2/M arrest. In a mouse xenograft model, PMD-026 suppressed tumor growth, and the combination of PMD-026 and enzalutamide inhibited tumor growth more prominently than single treatments.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate an excellent antitumor effect of the novel ribosomal S6 kinase inhibitor PMD-026 and the combination effect with the antiandrogen enzalutamide in castration-resistant prostate cancer. These findings warrant a clinical trial of PMD-026 in prostate cancer patients.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)