Podium
PD08: Infections/Inflammation/Cystic Disease of the Genitourinary Tract: Interstitial Cystitis
-

Che Hsueh Yang, MD
resident trainee
Tungs' Taichung MetroHarbor Hospital
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Interstitial cystitis (IC) is characterized by urothelial dysfunction allowing potassium permeability and mast cells infiltration secreting excessive vasoactive and inflammatory mediators. Dehydrated human amnion-chorion membranes (dHACM) belongs to bioactive substances extracted from maternal placenta and possesses immense sources of growth factors and anti-inflammatory proteins. It is applied in treating burns and non-healing diabetic ulcers and results are promising. This study is to evaluate the treating effect of dHACM in rats with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced IC.
Methods: A total of 30 eight-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats were used in this experiment and there were 10 rats in each group (control group; LPS group; LPS/dHACM group). LPS (750 µg; 30 minutes) was instilled via instrumented catheters from bladder to induced IC while LPS was replaced with phosphate-buffered saline in control group. The induction of IC was repeated two times with interval of one week. In LPS/dHACM group, solution of dHACM was prepared by adding 15-mg dHACM into 7.5 ml distilled water and evenly instilled into bladder of 10 rats at 24 hours after induction of IC. Every induction of IC would be accompanied by dHACM instillation and instilled dHACM would stay in bladder for two hours. One and two-way ANOVA were applied in analysis.
Results: Compared with LPS group, there were remarkably decrease of mast cells infiltration and fibrosis in LPS/dHACM group under Toludine blue and Masson's Trichrome stains, respectively. Meanwhile, cytokeratin was restored in LPS/dHACM group under immunostaining. In protein coding genes about proliferation, TGFß-2, TGFß-3, SMAD 2 and SMAD 3 were all (p < 0.001) significantly reduced in LPS/dHACM group, compared with those in LPS group. In inflammatory cytokines, TNF-a (p < 0.001), IL-6 (p < 0.05), IL-8 (p < 0.001) and IL-1ß (p < 0.05) were also significantly down-regulated, compared with those in LPS group.
Conclusions: Instillation of dHACM could ameliorate LPS-induced IC in rats by decreasing fibrosis, reducing mast cells infiltration, restoring cytokeratin, down-regulating inflammatory response and promoting cell proliferation via TGFß/SMAD pathway. Its practical utility in human IC is deserved to be explored.
Source of Funding: None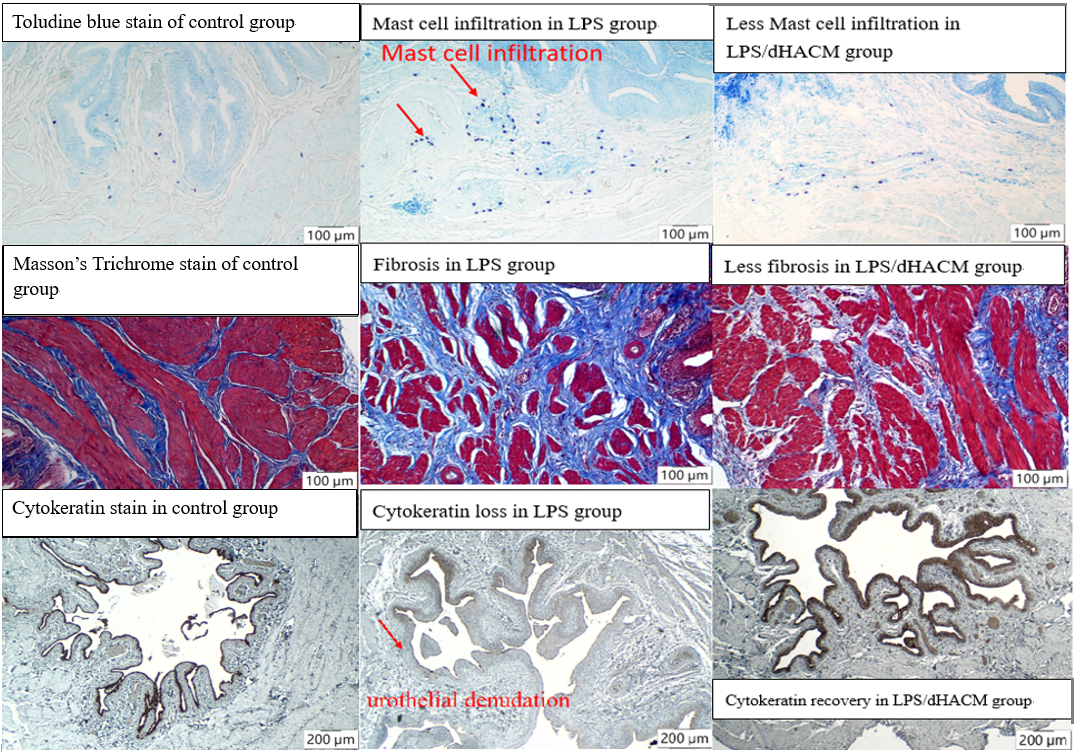

.jpg)
.jpg)