Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD10: Bladder Cancer: Invasive II
PD10-03: HRQOL After Robotic-Assisted Versus Open Radical Cystectomy: Analysis of a RCT
Friday, May 13, 2022
1:20 PM – 1:30 PM
Location: Room 255
Matthew Clements*, Benjamin Beech, Thomas Atkionson, Guido Dalbagni, Yuelin Li, Andrew Vickers, Harry Herr, S. Machele Donat, Jaspreet Sandhu, Daniel Sjoberg, Amy Tin, Jonathan Coleman, Bruce Rapkin, Vincent Laudone, Bernard Bochner, New York, NY
- MC
Matthew B. Clements, MD,MS
Fellow
Lahey Hospital & Medical Center
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Prior randomized-controlled trials (RCTs) comparing RARC to open radical cystectomy (ORC) have evaluated a limited breadth of health-related quality of life (HRQOL) domains. Our objective was to compare the effectiveness of RARC and ORC over a broad range of HRQOL domains longitudinally over two years following surgery.
Methods: We analyzed HRQOL in patients enrolled in a RCT of RARC vs ORC (2010-2013), who also enrolled in a prospective study of HRQOL in RC patients (2008-2014). Both studies enrolled patients receiving surgery and follow up care for non-metastatic disease at MSKCC. The urinary diversion was performed via an open approach in both arms. The prospective study of cystectomy QOL collected 14 patient-reported outcomes measures preoperatively, and at 3-, 6-, 12-, 18-, and 24-months postoperatively. Our primary outcome was differences between arms within each domain. Linear mixed effects models were used to test for changes in mean scores over 24-months, adjusting for baseline scores, with an interaction term for study arm×time.
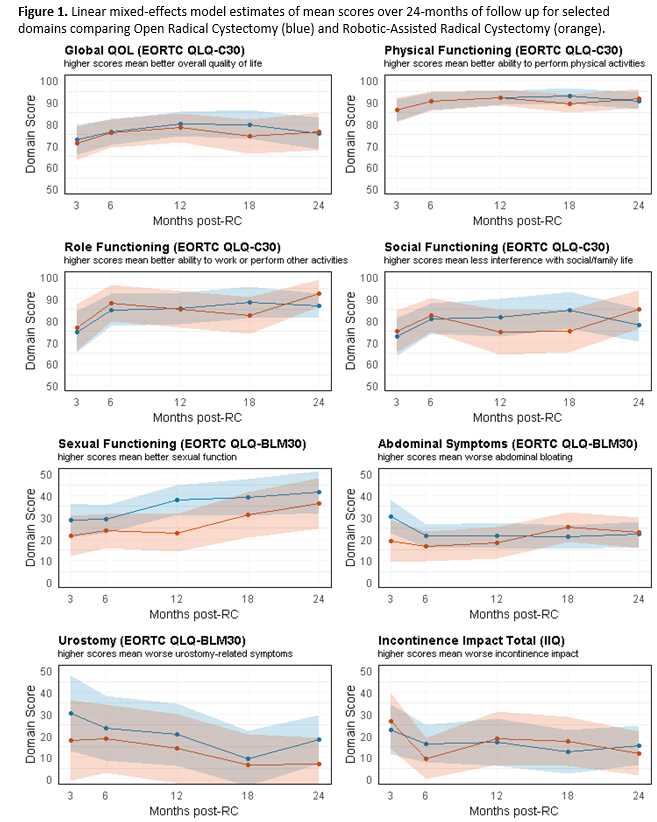
Results: The RCT enrolled 118 subjects, of which 88 also consented to participate in the prospective HRQOL protocol. After excluding 16 ineligible patients, 72 were analyzed (n=32 RARC, n=40 ORC). The rate of continent diversion was similar (66% RARC, 70% ORC). No differences were detected in EORTC QLQ-C30 (scale 0-100, Figure 1) domains such as Global QOL (mean difference -1.1, 95% CI -8.4-6.2, p=0.8), Physical Functioning (mean diff. -0.4, 95% CI -5.8-5.0, p=0.9), or Social Functioning (mean diff. -0.3, 95% CI 9.2-8.7, p>0.9) and with no time interactions (all p>0.05). We did not detect significant differences in bladder cancer-specific domains (EORTC QLQ-BLM30, scale 0-100) including Body Image (mean diff. 2.9, 95% CI -7.2-13.1, p=0.6), Urinary Symptoms (mean diff. 8.0, 95% CI -3.0-19.0, p=0.2), and Sexual Functioning (mean diff. -8.5, 95% CI -17.2-0.19, p=0.052), and without a significant time interaction (all p>0.3).
Conclusions: This analysis of a broad range of HRQOL domains in RCT patients did not detect significant differences between RARC and ORC. While the sample size was relatively small, the randomized design, large number of domains studied, and the longitudinal nature of the study can exclude a strong signal for differences based on surgical approach in the first 2-years postop.
Source of Funding: This work was supported by the Sidney Kimmel Center for Prostate and Urologic Cancers,the National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Core grant number P30-CA008748, and the Pin Down Bladder Cancer Fund.
Methods: We analyzed HRQOL in patients enrolled in a RCT of RARC vs ORC (2010-2013), who also enrolled in a prospective study of HRQOL in RC patients (2008-2014). Both studies enrolled patients receiving surgery and follow up care for non-metastatic disease at MSKCC. The urinary diversion was performed via an open approach in both arms. The prospective study of cystectomy QOL collected 14 patient-reported outcomes measures preoperatively, and at 3-, 6-, 12-, 18-, and 24-months postoperatively. Our primary outcome was differences between arms within each domain. Linear mixed effects models were used to test for changes in mean scores over 24-months, adjusting for baseline scores, with an interaction term for study arm×time.
Results: The RCT enrolled 118 subjects, of which 88 also consented to participate in the prospective HRQOL protocol. After excluding 16 ineligible patients, 72 were analyzed (n=32 RARC, n=40 ORC). The rate of continent diversion was similar (66% RARC, 70% ORC). No differences were detected in EORTC QLQ-C30 (scale 0-100, Figure 1) domains such as Global QOL (mean difference -1.1, 95% CI -8.4-6.2, p=0.8), Physical Functioning (mean diff. -0.4, 95% CI -5.8-5.0, p=0.9), or Social Functioning (mean diff. -0.3, 95% CI 9.2-8.7, p>0.9) and with no time interactions (all p>0.05). We did not detect significant differences in bladder cancer-specific domains (EORTC QLQ-BLM30, scale 0-100) including Body Image (mean diff. 2.9, 95% CI -7.2-13.1, p=0.6), Urinary Symptoms (mean diff. 8.0, 95% CI -3.0-19.0, p=0.2), and Sexual Functioning (mean diff. -8.5, 95% CI -17.2-0.19, p=0.052), and without a significant time interaction (all p>0.3).
Conclusions: This analysis of a broad range of HRQOL domains in RCT patients did not detect significant differences between RARC and ORC. While the sample size was relatively small, the randomized design, large number of domains studied, and the longitudinal nature of the study can exclude a strong signal for differences based on surgical approach in the first 2-years postop.
Source of Funding: This work was supported by the Sidney Kimmel Center for Prostate and Urologic Cancers,the National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Core grant number P30-CA008748, and the Pin Down Bladder Cancer Fund.


.jpg)
.jpg)