Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD11: Prostate Cancer: Detection & Screening II
PD11-12: Associations of Serum-based and Urine-based Molecular Diagnostics with Histologic Subtyping on Prostate Biopsy
Friday, May 13, 2022
2:50 PM – 3:00 PM
Location: Room 245
Claire de la Calle*, Nancy Greenland, Janet Cowan, Vittorio Fasulo, Martina Maggi, Emily Chan, Bradley Stohr, Jeffry Simko, Katsuto Shinohara, Matthew Cooperberg, Peter Carroll, Hao Nguyen, San Francisco, CA
- CD
Claire M. De La Calle, MD
Johns Hopkins Univeristy
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Serum kallikrein proteins (4Kscore) and urine exosome transcripts (ExosomeDx) biomarkers are increasingly used in the pre-biopsy setting as they have higher specificity than Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA). However, their real-world performance in predicting Gleason score at biopsy is unknown. We hypothesized that these biomarkers would be associated with increasing pathology severity at biopsy.
Methods: We included men who underwent prostate biopsy after 4Kscore and/or ExosomeDx testing, had no prior biopsy with cancer, and had pre-test PSA <20 ng/mL. Prostate biopsies with prostatic adenocarcinoma were re-reviewed in a blinded manner for Gleason Grade (GG), type of Gleason pattern 4, and intraductal carcinoma. Associations between GG group and test score were tested using ANOVA with linear trend test. Comparisons between biopsies with no cancer, GG1, and GG=2 were tested by Kruskal-Wallis test. Comparison of types of pattern 4 and presence of intraductal carcinoma were tested by Mann-Whitney test.
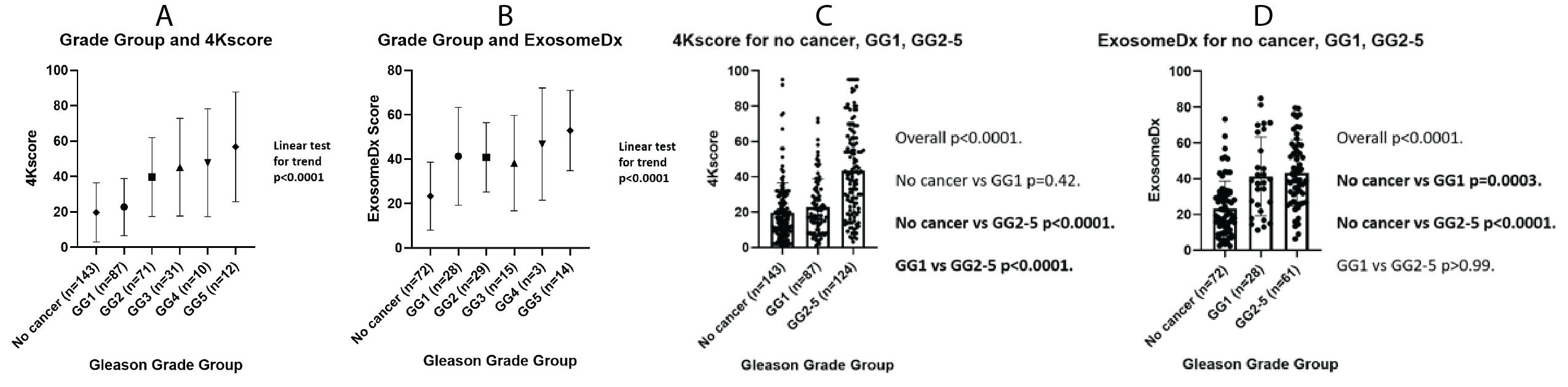
Results: Within 460 men who met inclusion criteria, both test scores were positively associated with increasing Gleason GG (Figure 1A-B). 4Kscores were higher in men who had GG=2 versus GG1 and no cancer, but there was no difference between men with GG1 versus benign biopsies (Figure 1C). ExosomeDx scores were higher in men with biopsies showing GG1 or GG=2 cancer. However, there was no significant difference in ExosomeDx scores between men with GG1 and GG=2 pathology (Figure 1D). While numerous studies have shown the cribriform subtype to be the Gleason pattern 4 subtype associated with the worst outcomes, there was no difference in either score based on the presence of this pattern (P>0.27). Higher 4Kscores were observed with fused glands (P=0.03) and poorly formed glands (P=0.005), while high ExosomeDx scores were observed with poorly formed glands (P=0.03) and intraductal carcinoma (P=0.005).
Conclusions: Both tests were increased in men with prostate cancer. The 4Kscores were higher in men who had GG=2 versus GG1 and no cancer. ExosomeDx scores were higher in men with biopsies showing GG1 or GG=2 cancer. The differential performance and histology patterns associated with these test values may reflect differences in tumor behavior.
Source of Funding: UCSF Goldberg-Benioff Program in Cancer Translational Biology
Methods: We included men who underwent prostate biopsy after 4Kscore and/or ExosomeDx testing, had no prior biopsy with cancer, and had pre-test PSA <20 ng/mL. Prostate biopsies with prostatic adenocarcinoma were re-reviewed in a blinded manner for Gleason Grade (GG), type of Gleason pattern 4, and intraductal carcinoma. Associations between GG group and test score were tested using ANOVA with linear trend test. Comparisons between biopsies with no cancer, GG1, and GG=2 were tested by Kruskal-Wallis test. Comparison of types of pattern 4 and presence of intraductal carcinoma were tested by Mann-Whitney test.
Results: Within 460 men who met inclusion criteria, both test scores were positively associated with increasing Gleason GG (Figure 1A-B). 4Kscores were higher in men who had GG=2 versus GG1 and no cancer, but there was no difference between men with GG1 versus benign biopsies (Figure 1C). ExosomeDx scores were higher in men with biopsies showing GG1 or GG=2 cancer. However, there was no significant difference in ExosomeDx scores between men with GG1 and GG=2 pathology (Figure 1D). While numerous studies have shown the cribriform subtype to be the Gleason pattern 4 subtype associated with the worst outcomes, there was no difference in either score based on the presence of this pattern (P>0.27). Higher 4Kscores were observed with fused glands (P=0.03) and poorly formed glands (P=0.005), while high ExosomeDx scores were observed with poorly formed glands (P=0.03) and intraductal carcinoma (P=0.005).
Conclusions: Both tests were increased in men with prostate cancer. The 4Kscores were higher in men who had GG=2 versus GG1 and no cancer. ExosomeDx scores were higher in men with biopsies showing GG1 or GG=2 cancer. The differential performance and histology patterns associated with these test values may reflect differences in tumor behavior.
Source of Funding: UCSF Goldberg-Benioff Program in Cancer Translational Biology


.jpg)
.jpg)