Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD12: Bladder Cancer: Basic Research & Pathophysiology II
PD12-09: Elevated Semaphorin-6A facilitates FLT4-meditated tumor migration and associates with immune suppression in bladder cancer.
Friday, May 13, 2022
2:20 PM – 2:30 PM
Location: Room 244
Wenjie Luo*, Yiping Zhu, Hailiang Zhang, Yuanyuan Qu, Dingwei Ye, Shanghai, China, People's Republic of
- WL
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Bladder cancer (BLCA) is one of the most heterogeneous malignancies and effective potential targets remain largely undetermined. Semaphorin-6A (SEMA6A) is a single-pass transmembrane protein involved in the epithelia cell migration and only a few studies have examined the role of SEMA6A in cancer biology and immunity. Our research observed the upregulation of SEMA6A in BLCA tissues and aimed to further investigate the underlying mechanism of SEMA6A in tumor migration and immune dysregulation of BLCA.
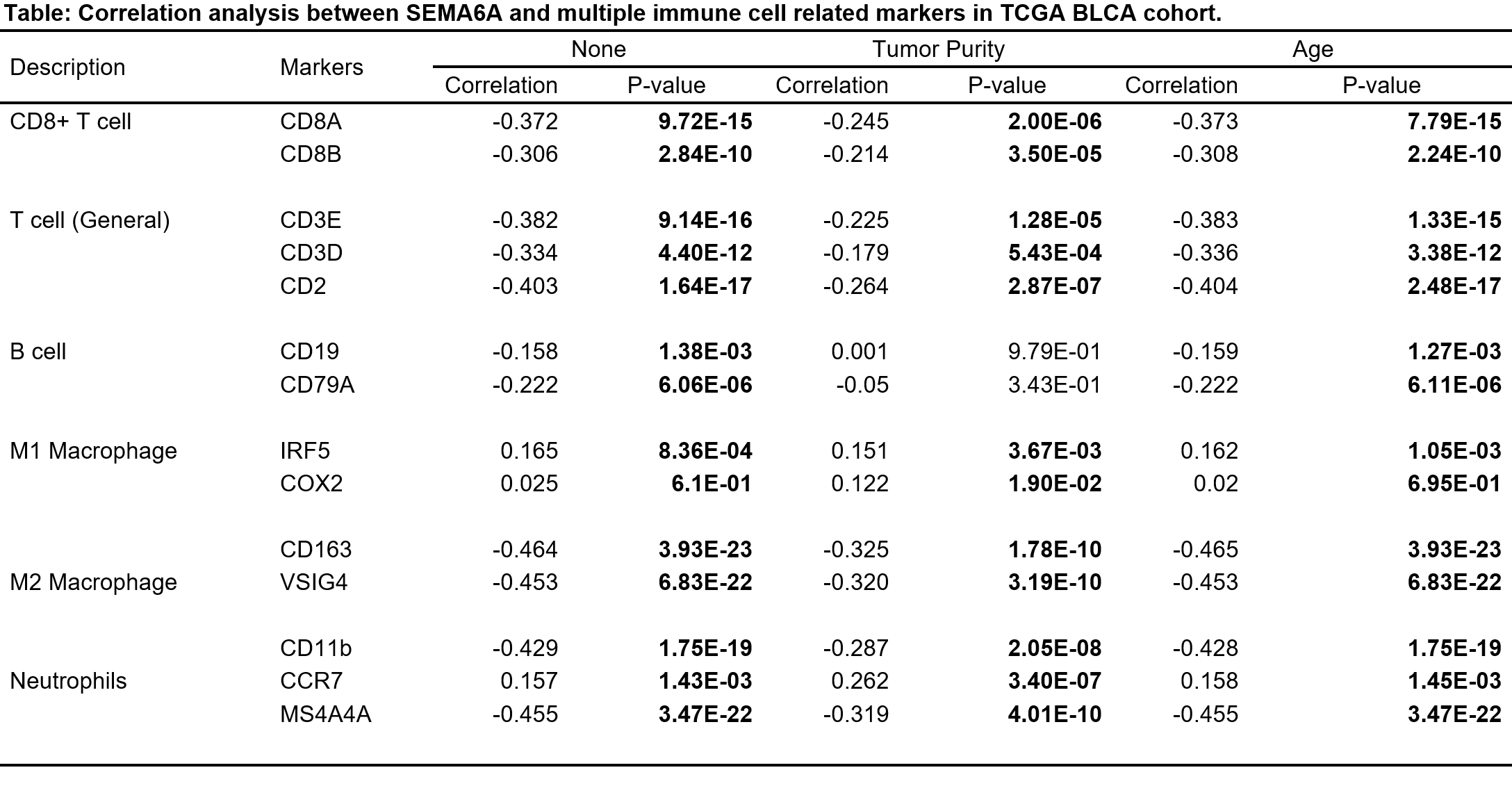
Methods: Multiple cohorts were enrolled for analysis including TCGA cohort, IMvigor 210 Cohort and Fudan University Shanghai Cancer cohort (FUSCC). The potential mechanism was explored using Protein–protein interactions, Chromatin immunoprecipitation and Dual luciferase reporter assay. Rescue assays were performed using in-vitro and in-vivo models. The correlation between SEMA6A expression and immune response was analyzed using Tumor Immune Estimation Resource database. Immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry were performed to determine the proportion of immune cells in fresh BLCA tissues compared with normal tissues.
Results: SEMA6A was demonstrated highly expressed in BLCA tissues compared with normal tissues. In addition, rescue assays revealed downregulated SEMA6A suppressed BLCA cells in vitro and in vivo via meditating FLT4 expression. Besides, the expression of SEMA6A was correlated with infiltration of multiple immune cells. The enrichment of CD8+ T Cell was observed in patients with lower level of SEMA6A. And higher level of SEMA6A predicted suppressed immunotherapeutic responses in IMvigor 210 Cohort.
Conclusions: Our study first revealed that elevated SEMA6A enhanced the migration of BLCA cells via regulating FLT4 and suppressed the infiltration of CD8+ T cell. Furthermore, SEMA6A served as a novel biomarker for predicting patient outcomes after immunotherapeutic treatments, which may improve the development of individualized therapy for BLCA.
Source of Funding: This work is supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.81772706 and No.81802525).
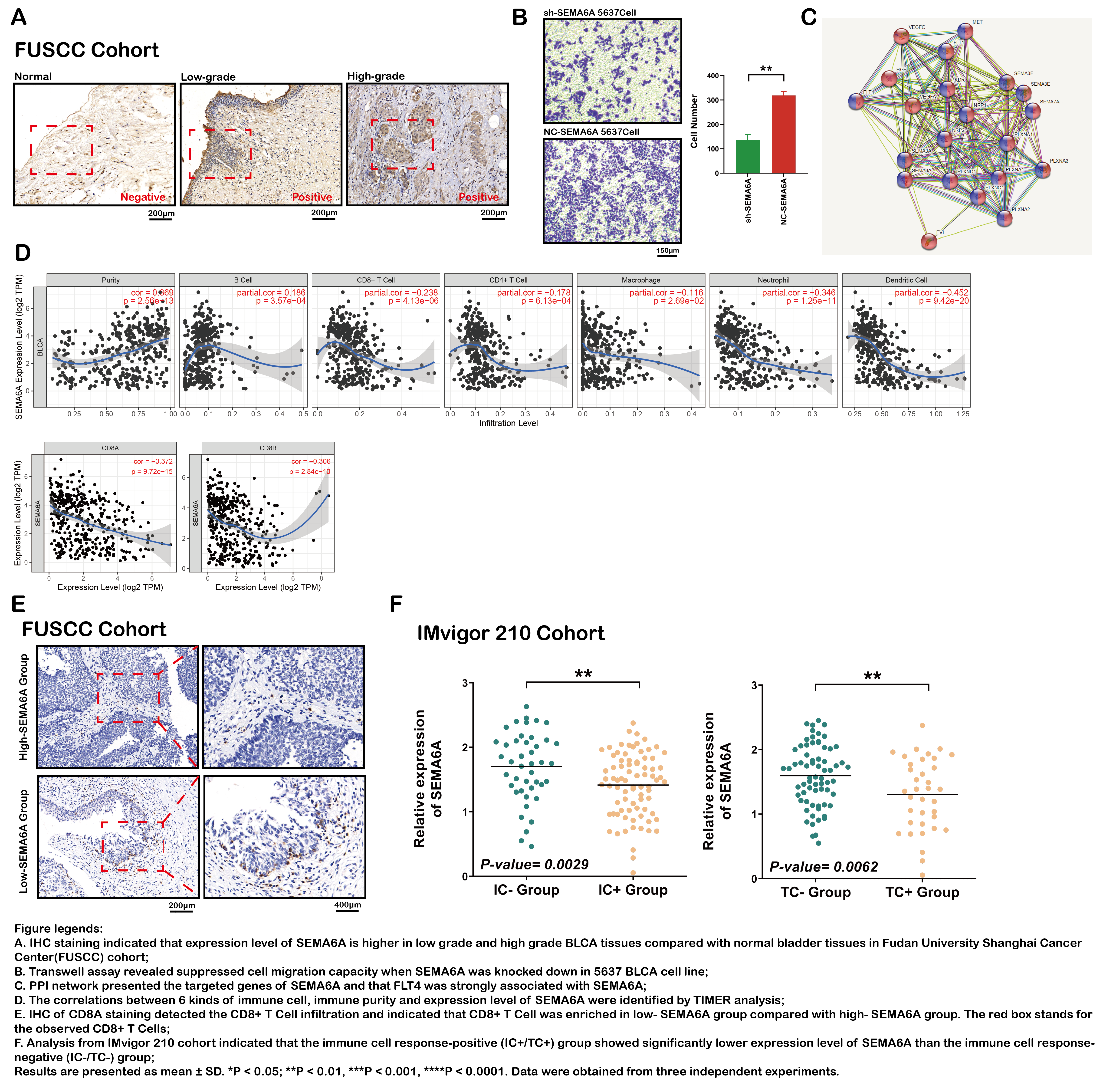
Methods: Multiple cohorts were enrolled for analysis including TCGA cohort, IMvigor 210 Cohort and Fudan University Shanghai Cancer cohort (FUSCC). The potential mechanism was explored using Protein–protein interactions, Chromatin immunoprecipitation and Dual luciferase reporter assay. Rescue assays were performed using in-vitro and in-vivo models. The correlation between SEMA6A expression and immune response was analyzed using Tumor Immune Estimation Resource database. Immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry were performed to determine the proportion of immune cells in fresh BLCA tissues compared with normal tissues.
Results: SEMA6A was demonstrated highly expressed in BLCA tissues compared with normal tissues. In addition, rescue assays revealed downregulated SEMA6A suppressed BLCA cells in vitro and in vivo via meditating FLT4 expression. Besides, the expression of SEMA6A was correlated with infiltration of multiple immune cells. The enrichment of CD8+ T Cell was observed in patients with lower level of SEMA6A. And higher level of SEMA6A predicted suppressed immunotherapeutic responses in IMvigor 210 Cohort.
Conclusions: Our study first revealed that elevated SEMA6A enhanced the migration of BLCA cells via regulating FLT4 and suppressed the infiltration of CD8+ T cell. Furthermore, SEMA6A served as a novel biomarker for predicting patient outcomes after immunotherapeutic treatments, which may improve the development of individualized therapy for BLCA.
Source of Funding: This work is supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.81772706 and No.81802525).


.jpg)
.jpg)