Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD18: Kidney Cancer: Epidemiology & Evaluation/Staging/Surveillance II
PD18-07: Performance of GFR calculators: CKD-EPI 2021, CKD-EPI 2009, and MDRD in estimation of kidney function prior to nephrectomy
Saturday, May 14, 2022
8:00 AM – 8:10 AM
Location: Room 255
Maria Antony*, Aditi Chaurasia, Nikhil Gopal, Pouria Yazdian, Zach Kozel, Sandeep Gurram, Marston Linehan, Mark Ball, Bethesda, MD

Maria B. Antony, BS
University of Connecticut School of Medicine
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Patients with hereditary kidney cancer can have multifocal, recurrent tumors. They are at high risk of loss of renal function and parenchymal volume from repeated surgeries. Accurate staging of preoperative kidney disease is essential for assessing functional risk before surgery.
Our study compares gold standard measures of preoperative renal function to three eGFR calculators: MDRD (race-based), CKD-EPI 2009 (race-based), and the new CKD-EPI 2021 (non-race based).
Methods: Retrospective analysis was conducted on a surgical database of 554 nephrectomies (91% PN, 9% RN) from 2006-2021 conducted at the National Cancer Institute.
Serum creatinine, urinalysis, and creatinine clearance was assessed from patient charts within a week of surgery. KDIGO classification of CKD risk was determined based on degree of proteinuria and creatinine clearance by 24-hour urine collection.
Serum creatinine was used to calculate eGFR using 3 calculators: MDRD, CKD-EPI 2009, and CKD-EPI 2021. Net reclassification index (NRI) was determined for each calculator for prediction of KDIGO prognosis of “moderately increased” or higher (McNemar test for correlated proportions). Analysis was done on RStudio.v.4.1.1.
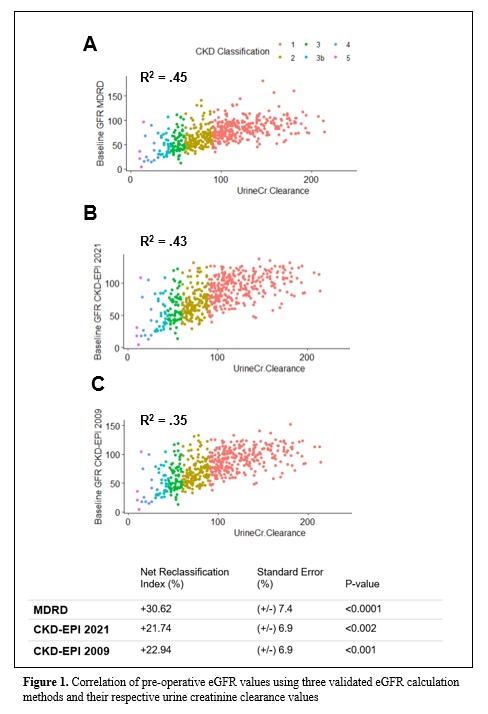
Results: Cohort was 62% male, with mean age at surgery of 45. Proportion of patients with preop eGFR <60 differed when using MDRD (34.1%) vs. CKD-EPI 2009 (27.6%) vs. CKD-EPI 2021 (24.9%) equations (p < 0.05).
MDRD equation reclassified the highest proportion of patients as having better renal function than their KDIGO classification (RCI: 30.62%, p <0.001). Reclassification indices for CKD-EPI 2021 and CKD-EPI 2009 were 21.74% and 22.94% respectively—both overestimating GFR compared to KDIGO class.
45 (8%) of the study population were Black. Out of the two race-based calculators, only CKD-EPI 2009 demonstrated significant difference in preoperative eGFR between Black and non-Black patients (p=0.032), while MDRD and CKD-EPI 2021 did not differ based on race.
Conclusions: Both CKD-EPI calculators outperformed MDRD in CKD risk estimation for the preoperative assessment of renal function. Since CKD-EPI 2009 (race-based) and the new CKD-EPI 2021 (non-race based) estimated risk similarly, CKD-EPI 2021 may offer additional benefit in reducing racial biases.
Source of Funding: NIH MRSP
Our study compares gold standard measures of preoperative renal function to three eGFR calculators: MDRD (race-based), CKD-EPI 2009 (race-based), and the new CKD-EPI 2021 (non-race based).
Methods: Retrospective analysis was conducted on a surgical database of 554 nephrectomies (91% PN, 9% RN) from 2006-2021 conducted at the National Cancer Institute.
Serum creatinine, urinalysis, and creatinine clearance was assessed from patient charts within a week of surgery. KDIGO classification of CKD risk was determined based on degree of proteinuria and creatinine clearance by 24-hour urine collection.
Serum creatinine was used to calculate eGFR using 3 calculators: MDRD, CKD-EPI 2009, and CKD-EPI 2021. Net reclassification index (NRI) was determined for each calculator for prediction of KDIGO prognosis of “moderately increased” or higher (McNemar test for correlated proportions). Analysis was done on RStudio.v.4.1.1.
Results: Cohort was 62% male, with mean age at surgery of 45. Proportion of patients with preop eGFR <60 differed when using MDRD (34.1%) vs. CKD-EPI 2009 (27.6%) vs. CKD-EPI 2021 (24.9%) equations (p < 0.05).
MDRD equation reclassified the highest proportion of patients as having better renal function than their KDIGO classification (RCI: 30.62%, p <0.001). Reclassification indices for CKD-EPI 2021 and CKD-EPI 2009 were 21.74% and 22.94% respectively—both overestimating GFR compared to KDIGO class.
45 (8%) of the study population were Black. Out of the two race-based calculators, only CKD-EPI 2009 demonstrated significant difference in preoperative eGFR between Black and non-Black patients (p=0.032), while MDRD and CKD-EPI 2021 did not differ based on race.
Conclusions: Both CKD-EPI calculators outperformed MDRD in CKD risk estimation for the preoperative assessment of renal function. Since CKD-EPI 2009 (race-based) and the new CKD-EPI 2021 (non-race based) estimated risk similarly, CKD-EPI 2021 may offer additional benefit in reducing racial biases.
Source of Funding: NIH MRSP

.jpg)
.jpg)