Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD22: Prostate Cancer: Localized: Radiation Therapy
PD22-12: Comparative study of RARP and carbon ion radiotherapy sexual functional changes for prostate cancer using the propensity score matching method
Saturday, May 14, 2022
11:20 AM – 11:30 AM
Location: Room 252
Yoshiyuki Miyazawa*, Daisuke Oka, Hidekazu Koike, Hidemasa Kawamura, Yuhei Miyasaka, Seiji Arai, Yoshitaka Sekine, Masashi Nomura, Hiroshi Matsui, Kazuhiro Suzuki, Maebashi, Japan

Yoshiyuki Miyazawa, MD, PHD
Gunma University Department of Urology
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: We mainly perform Robotic-Assisted laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy (RARP) and Carbon Ion Radiotherapy (CIRT) as curative treatment for prostate cancer. Several factors such as cancer control and quality of life after treatment are considered to be important, but there are few reports comparing sexual function changes before and after treatment between RARP and CIRT. We performed retrospective study comparing the evaluation of sexual function after RARP and CIRT cases using the propensity score matching method.
Methods: 127 patients treated by RARP from 2014 to 2018 and 190 patients treated by CIRT monotherapy from 2010 to 2019 were evaluated. We evaluated Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC) score before and after treatment. The EPIC was compared before, 12 months, and 24 months after treatment. Propensity score matching was performed using the age at treatment, PSA value, T stage, and pretreatment EPIC comprehensive score of sexual function as covariates. A cohort of 101 patients in each group was prepared and examined. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Gunma University Hospital (No. IRB2020-050, 1839).
Results: The mean ± standard deviation of each of the RARP and CIRT groups were age; 65.1 ± 5.9, 65.3 ± 6.5 years, PSA value; 6.31 ± 2.07, 6.34 ± 2.46 ng / ml, pretreatment EPIC sexual function overall score; 46.4 ± 15.6, 48.2 ± 16.2. In both groups, T1N0M0 was 16%, T2N0M0 was 83%, and T3N0M0 was 1%. The total EPIC sexual function scores before, 12 months, and 24 months after treatment were 46.4, 27.9, 28.2 in the RARP group, and 48.2, 41.4, 41.6 in the CIRT group, respectively. In both groups, there was a significant decrease in score after 12 months and 24 months compared to before treatment (p <0.05). At 12 and 24 months, the total EPIC sexual function score in the CIRT group was significantly higher than RARP group (p <0.001).
Conclusions: In prostate cancer cases adjusted by propensity score matching, the decrease in EPIC sexual function score was significantly smaller in the CIRT group than RARP group. The results of this study seemed to be useful information for decision making with patients.
Source of Funding: None.
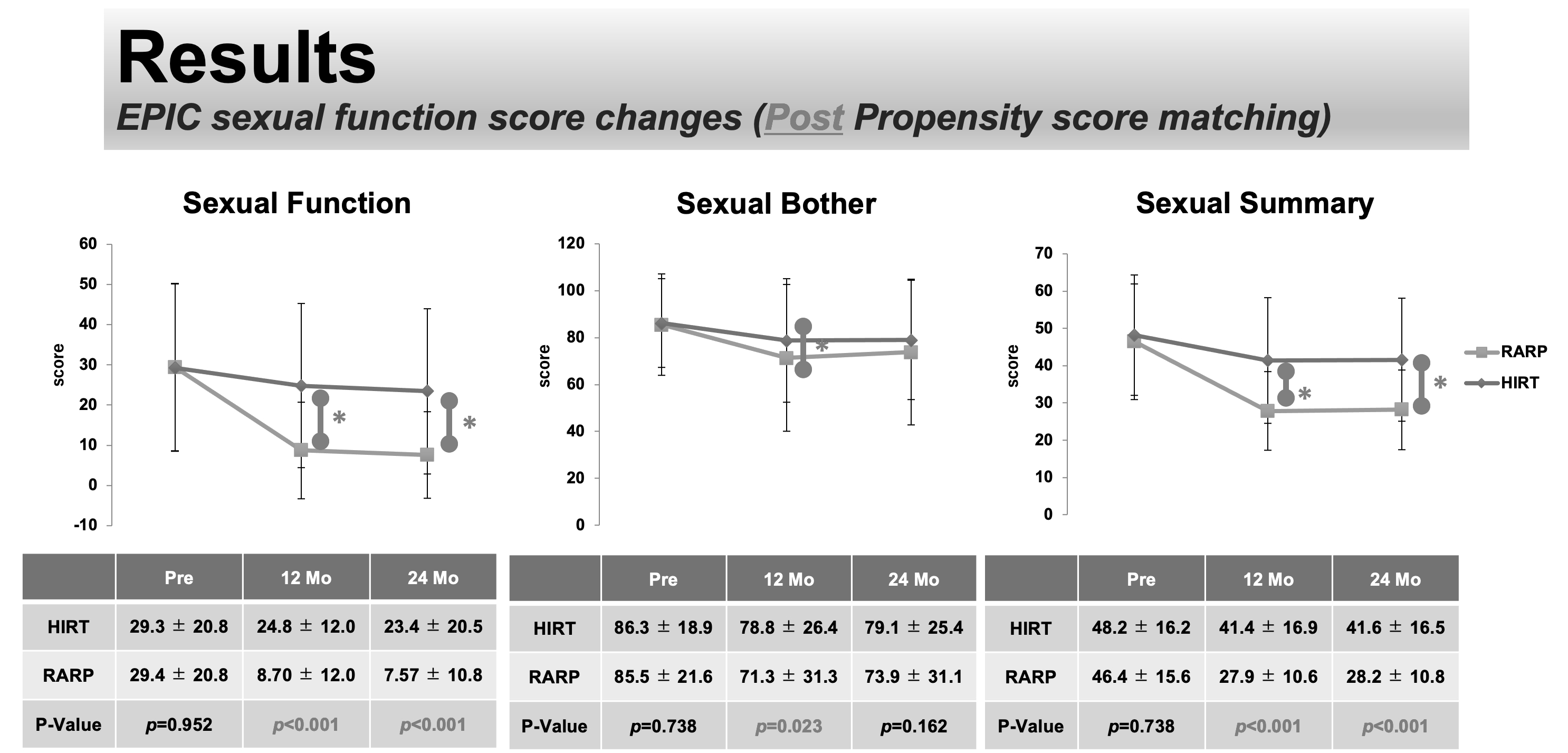
Methods: 127 patients treated by RARP from 2014 to 2018 and 190 patients treated by CIRT monotherapy from 2010 to 2019 were evaluated. We evaluated Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC) score before and after treatment. The EPIC was compared before, 12 months, and 24 months after treatment. Propensity score matching was performed using the age at treatment, PSA value, T stage, and pretreatment EPIC comprehensive score of sexual function as covariates. A cohort of 101 patients in each group was prepared and examined. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Gunma University Hospital (No. IRB2020-050, 1839).
Results: The mean ± standard deviation of each of the RARP and CIRT groups were age; 65.1 ± 5.9, 65.3 ± 6.5 years, PSA value; 6.31 ± 2.07, 6.34 ± 2.46 ng / ml, pretreatment EPIC sexual function overall score; 46.4 ± 15.6, 48.2 ± 16.2. In both groups, T1N0M0 was 16%, T2N0M0 was 83%, and T3N0M0 was 1%. The total EPIC sexual function scores before, 12 months, and 24 months after treatment were 46.4, 27.9, 28.2 in the RARP group, and 48.2, 41.4, 41.6 in the CIRT group, respectively. In both groups, there was a significant decrease in score after 12 months and 24 months compared to before treatment (p <0.05). At 12 and 24 months, the total EPIC sexual function score in the CIRT group was significantly higher than RARP group (p <0.001).
Conclusions: In prostate cancer cases adjusted by propensity score matching, the decrease in EPIC sexual function score was significantly smaller in the CIRT group than RARP group. The results of this study seemed to be useful information for decision making with patients.
Source of Funding: None.


.jpg)
.jpg)