Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD28: Sexual Function/Dysfunction: Surgical Therapy I
PD28-04: Reservoir Distance from Critical Pelvic Structures: Radiographic Comparison of High Submuscular and Space of Retzius Inflatable Penile Prosthesis Placement Techniques
Saturday, May 14, 2022
1:30 PM – 1:40 PM
Location: Room 245
Mehraban Kavoussi*, Grayden Cook, Shaun Nordeck, Shervin Badkhshan, Samantha Nealon, Benjamin Dropkin, Gregory Joice, Sarah Sanders, Jeffrey Pruitt, Steven Hudak, Allen Morey, Dallas, TX
- MK
Mehraban Kavoussi
UT Southwestern Medical Center
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Inflatable penile prosthesis (IPP) reservoir placement into the High Submuscular space (HSM) has been proposed as a strategy to prevent injury to organs adjacent to the Space of Retzius (SOR). SOR reservoir proximity to critical pelvic structures (CPS) has been previously established in a cadaver study. We sought to evaluate reservoir distance from CPS for SOR and HSM placements using cross-sectional imaging obtained following IPP insertion.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed our institutional database and identified men who underwent IPP insertion between 2007 and 2020. Men who underwent subsequent cross-sectional abdominopelvic imaging following IPP insertion until October 2020 were included in this study. Two radiologists blinded to IPP surgical technique evaluated reservoir position to determine (a) mass effect on the bladder and iliac vessels and (b) the shortest distance between each of these structures and the reservoir. Men were grouped based on reservoir placement technique (SOR vs. HSM) as documented in the operative notes. Variables were analyzed using chi-squared, fisher’s exact, and student’s T-tests as indicated.
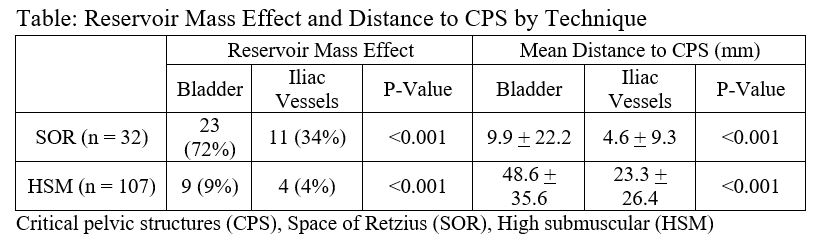
Results: Among 1010 IPP cases performed during the study interval, 139 (13.7%) met our inclusion criteria with imaging obtained an average of 827 (+ 785) days after IPP insertion. Oncologic follow-up (46%) was the most common indication for imaging. Compared with SOR reservoirs (n = 32), HSM reservoirs (n =107) were significantly less likely to induce a mass effect on the bladder (72 vs. 9%) or iliac vessels (34 vs. 4%) and were located roughly 5x further from the bladder (10 + 22 vs. 49 + 36 mm) and iliac vessels (5 + 9 vs. 23 + 26 mm, Table).
Conclusions: This study radiographically confirms that IPP reservoirs are located significantly further away from CPS following HSM placement compared to SOR placement. These findings suggest a potential patient safety benefit via avoidance of bladder and iliac vessel related IPP reservoir complications.
Source of Funding: N/A
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed our institutional database and identified men who underwent IPP insertion between 2007 and 2020. Men who underwent subsequent cross-sectional abdominopelvic imaging following IPP insertion until October 2020 were included in this study. Two radiologists blinded to IPP surgical technique evaluated reservoir position to determine (a) mass effect on the bladder and iliac vessels and (b) the shortest distance between each of these structures and the reservoir. Men were grouped based on reservoir placement technique (SOR vs. HSM) as documented in the operative notes. Variables were analyzed using chi-squared, fisher’s exact, and student’s T-tests as indicated.
Results: Among 1010 IPP cases performed during the study interval, 139 (13.7%) met our inclusion criteria with imaging obtained an average of 827 (+ 785) days after IPP insertion. Oncologic follow-up (46%) was the most common indication for imaging. Compared with SOR reservoirs (n = 32), HSM reservoirs (n =107) were significantly less likely to induce a mass effect on the bladder (72 vs. 9%) or iliac vessels (34 vs. 4%) and were located roughly 5x further from the bladder (10 + 22 vs. 49 + 36 mm) and iliac vessels (5 + 9 vs. 23 + 26 mm, Table).
Conclusions: This study radiographically confirms that IPP reservoirs are located significantly further away from CPS following HSM placement compared to SOR placement. These findings suggest a potential patient safety benefit via avoidance of bladder and iliac vessel related IPP reservoir complications.
Source of Funding: N/A

.jpg)
.jpg)