Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD28: Sexual Function/Dysfunction: Surgical Therapy I
PD28-09: Single Perineal Incision in Simultaneously Placed Penile Implant and Artificial Sphincter: A Comparison of Complications and Device Longevity
Saturday, May 14, 2022
2:20 PM – 2:30 PM
Location: Room 245
Kirema Macharia, Kyle Blum*, Travis Green, Justin Mehr, Leyla Akhverdiyeva, Alex Leonard, Run Wang, Houston, TX
- KB
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Inflatable penile prosthesis (IPP) is commonly implanted via a penoscrotal or infrapubic incision. It is known that artificial urinary sphincters (AUS) are more effective when placed through a perineal approach. The most common approach for the synchronous implantation of an IPP and AUS has been through dual incisions (penoscrotal/infrapubic and perineal) or a single penoscrotal approach. We have developed a technique to simultaneously implant an IPP and AUS through a single perineal incision. Presently, no data is available that compares the complications and device longevity of a single perineal approach versus a penoscrotal approach for dual implants.
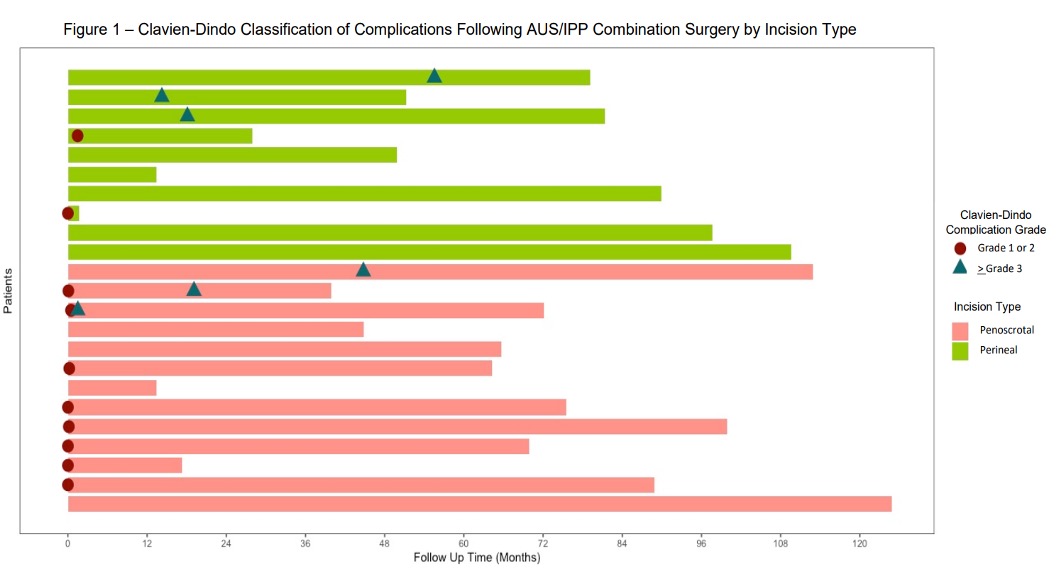
Methods: We retrospectively identified 45 patients who underwent an AUS/IPP synchronous dual implantation at a large single-institution tertiary referral center between 2011 to 2019. These patients were surveyed regarding their AUS/IPP devices using a series of questions. Out of these patients, a total of 23 patients had responses available for analysis; 13 with penoscrotal incision and 10 via perineal incision. Device malfunction, infection, and Clavien-Dindo classification (CD) for complications were analyzed. Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables was used and p<0.05 was considered to be significant. Follow up ranged from 1.6 to 124.9 months.
Results: A difference was observed between the two groups when comparing for total CD Grade 1-2 postoperative complications (p=0.028). Notably, 61.5% (n=8) in the penoscrotal group experienced a CD Grade 1-2 complication in the first 30 days postoperatively vs 10% (n=1) in the perineal group, most commonly surgical site pain. There was no statistically significant difference in CD Grade >3 postoperative complications between the two groups (p=0.617). There was also no significant difference found between the two groups when comparing for infection rates (p=0.603), AUS malfunction (p=1.00), or IPP malfunction (p=1.00).
Conclusions: A single perineal incision for the placement of AUS/IPP synchronous implantation is a viable and effective option with similar device longevity compared to a penoscrotal approach. Low grade complications were found to be significantly improved with the perineal approach.
Source of Funding: N/A
Methods: We retrospectively identified 45 patients who underwent an AUS/IPP synchronous dual implantation at a large single-institution tertiary referral center between 2011 to 2019. These patients were surveyed regarding their AUS/IPP devices using a series of questions. Out of these patients, a total of 23 patients had responses available for analysis; 13 with penoscrotal incision and 10 via perineal incision. Device malfunction, infection, and Clavien-Dindo classification (CD) for complications were analyzed. Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables was used and p<0.05 was considered to be significant. Follow up ranged from 1.6 to 124.9 months.
Results: A difference was observed between the two groups when comparing for total CD Grade 1-2 postoperative complications (p=0.028). Notably, 61.5% (n=8) in the penoscrotal group experienced a CD Grade 1-2 complication in the first 30 days postoperatively vs 10% (n=1) in the perineal group, most commonly surgical site pain. There was no statistically significant difference in CD Grade >3 postoperative complications between the two groups (p=0.617). There was also no significant difference found between the two groups when comparing for infection rates (p=0.603), AUS malfunction (p=1.00), or IPP malfunction (p=1.00).
Conclusions: A single perineal incision for the placement of AUS/IPP synchronous implantation is a viable and effective option with similar device longevity compared to a penoscrotal approach. Low grade complications were found to be significantly improved with the perineal approach.
Source of Funding: N/A


.jpg)
.jpg)