Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD30: Education Research III
PD30-06: Trends in PubMed-Indexed Research in Matched Urology Applicants: Yearly Analysis of the 2017-2021 Match Cycles
Saturday, May 14, 2022
1:50 PM – 2:00 PM
Location: Room 243
David E. Hinojosa-Gonzalez*, Dimitar V. Zlatev, Anton Wintner, Boston, MA, Wesley A. Mayer, Houston, TX, Ruslan Korets, Brian H. Eisner, Boston, MA

David Eugenio Hinojosa Gonzalez, MD
Massachusetts General Hospital
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Research experience and authorship of peer-reviewed publications are important components of the residency application. This study aims to determine indexed research output of matched urology applicants and examine yearly trends between match-cycles.
Methods: The resident rosters of 145 urology programs were screened for matched applicants. PubMed-indexed publications prior to starting residency were recorded and further analyzed to determine authorship role, relation to urology and journal ranking. Journal ranking was extracted from scimagojr, with the top 25% journals of the index considered Q1. Gathered data was analyzed in RStudio.
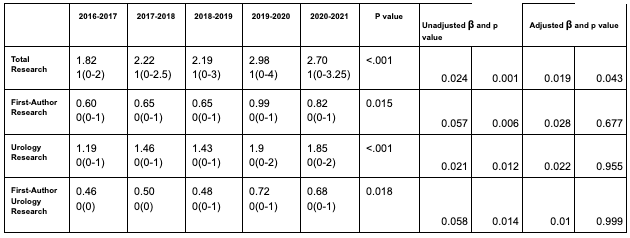
Results: Data was successfully extracted from 131 out of 145 urology residency programs (90%) for a total of 1,655 matched applicants spanning the 2017-2021 match cycles. Mean and median total publications were 2.39 and 1 respectively (range 0-60). Mean and median first-authored publications were 0.75 and 0 (range 0-19), while mean and median urology publications were 1.57 and 0 (range 0-52). First-authored urology research had a mean of 0.57 and a median of 0 (0-18). There has been a significant trend of increased publications among matched urology applicants from 2017 to 2021. Linear regression modelling of research productivity and match years revealed a significant increase in publications per year (adjusted ß 0.019, p=0.043). Mean and median total publications for 2017 were 1.82 and 1 (0-36) respectively, 2.22 and 1 (0-52) for 2018, 2.19 and 1 (0-38) for 2019, 2.98 and 1 (0-40) for 2020 and 2.70 and 2 (0-32) for 2021 (p= <.001). Findings are summarized in Table 1.
Conclusions: Research productivity has increased from 2017 to 2021. However, there is still a wide range of urology research productivity amongst successful urology applicants.
Source of Funding: No funding was received
Methods: The resident rosters of 145 urology programs were screened for matched applicants. PubMed-indexed publications prior to starting residency were recorded and further analyzed to determine authorship role, relation to urology and journal ranking. Journal ranking was extracted from scimagojr, with the top 25% journals of the index considered Q1. Gathered data was analyzed in RStudio.
Results: Data was successfully extracted from 131 out of 145 urology residency programs (90%) for a total of 1,655 matched applicants spanning the 2017-2021 match cycles. Mean and median total publications were 2.39 and 1 respectively (range 0-60). Mean and median first-authored publications were 0.75 and 0 (range 0-19), while mean and median urology publications were 1.57 and 0 (range 0-52). First-authored urology research had a mean of 0.57 and a median of 0 (0-18). There has been a significant trend of increased publications among matched urology applicants from 2017 to 2021. Linear regression modelling of research productivity and match years revealed a significant increase in publications per year (adjusted ß 0.019, p=0.043). Mean and median total publications for 2017 were 1.82 and 1 (0-36) respectively, 2.22 and 1 (0-52) for 2018, 2.19 and 1 (0-38) for 2019, 2.98 and 1 (0-40) for 2020 and 2.70 and 2 (0-32) for 2021 (p= <.001). Findings are summarized in Table 1.
Conclusions: Research productivity has increased from 2017 to 2021. However, there is still a wide range of urology research productivity amongst successful urology applicants.
Source of Funding: No funding was received


.jpg)
.jpg)