Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD32: Infections/Inflammation/Cystic Disease of the Genitourinary Tract: Kidney & Bladder III
PD32-09: Comparison of Guidance UTI&[reg] and standard urine culture for rates of sepsis, hospitalization and other adverse outcomes in complicated urinary tract infections
Saturday, May 14, 2022
4:50 PM – 5:00 PM
Location: Room 255
Aparna Ashok*, Dicken Ko, Providence, RI, Emily Lukacz, La Jolla, CA, Annah Vollstedt, Iowa City, IA, Iver Juster, San Rafael, CA, Timothy Niecko, Tierra Verde, FL, David Baunoch, Trabuco Canyon, CA, Mohit Mathur, Irvine, CA

Aparna Ashok, MD, M. Eng (she/her/hers)
Reconstructive Urologist
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI) are a significant burden on individual health and healthcare resources. They are often caused by polymicrobial infections where interactions between bacteria can change the antibiotic resistance of the pool of organisms. Guidance UTI® is a urine-based test that combines PCR and Pooled Antibiotic Susceptibility (P-AST), which tests for antibiotic susceptibility against the combined pool of organisms. This study sought to determine rates of adverse outcomes, medical resource utilization, and costs with Guidance UTI compared to standard urine culture (SUC).
Methods: Using a randomized 5% sample of Medicare Parts A+B beneficiaries enrolled in 2017-19 (n ~1.5M in each year), we compared 2 cohorts matched on sex, diabetes, and propensity score, based on whether outpatient UTI diagnosis was made with SUC (N=678) or Guidance UTI (N=69) initially, and for the year following their first cUTI after a 12-month baseline. UTI-related utilization and Medicare-allowed cost was acquired from professional and facility claims.
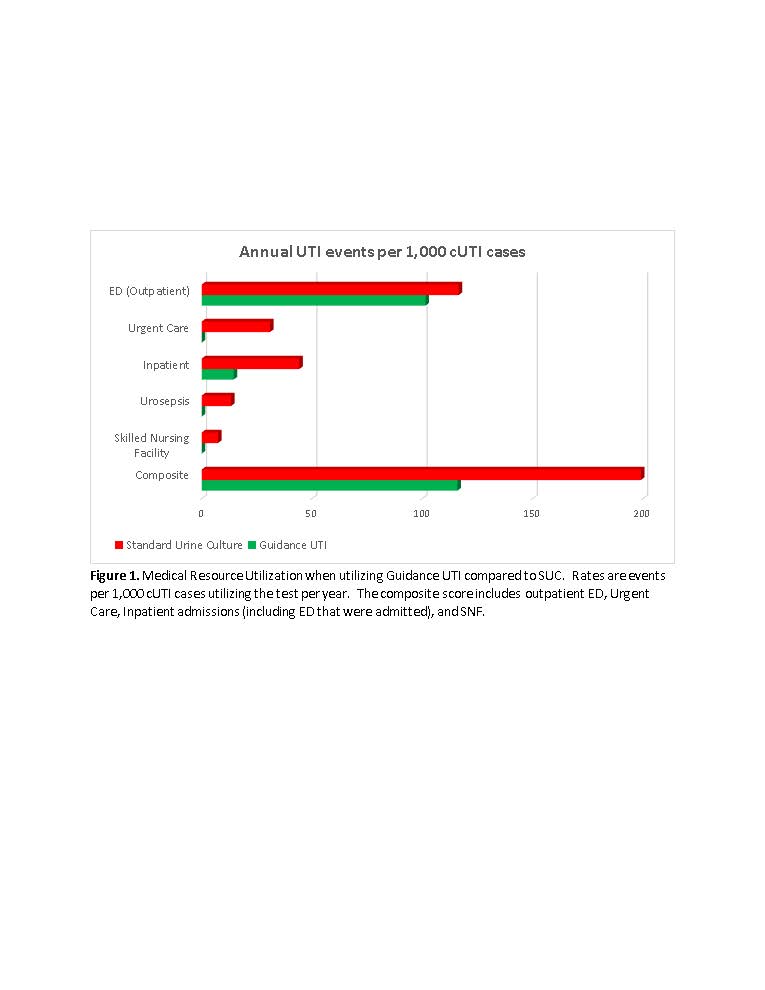
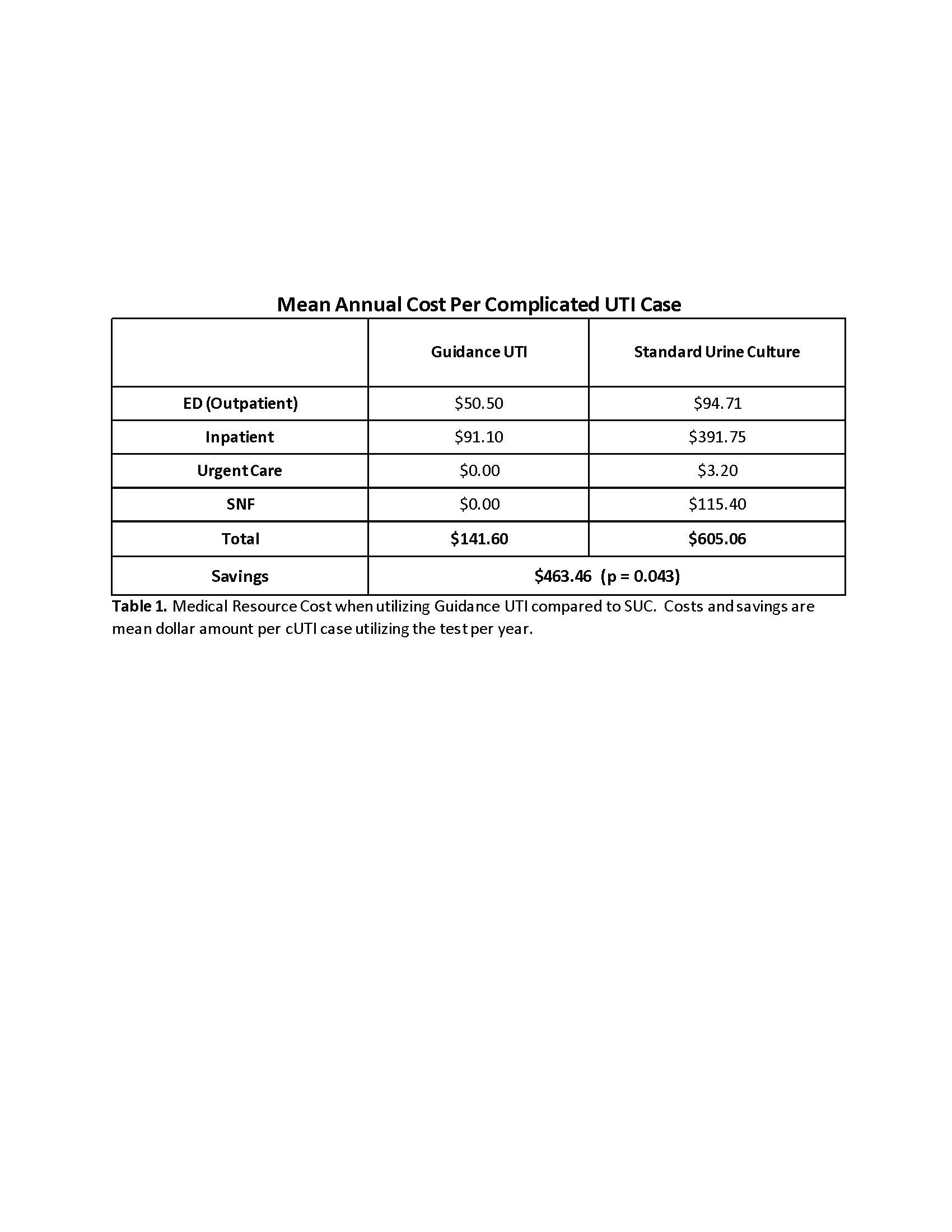
Results: The rate of outpatient emergency visits was 13% lower and inpatient admissions was 67% lower when using Guidance UTI compared to SUC. For every 1,000 patients there were zero urosepsis, urgent care and skilled nursing facility admissions with Guidance UTI vs 13, 31 and 7 events respectively with SUC. For the composite outcome, Guidance UTI testing was associated with a 42% reduction compared to SUC (Figure 1). These reductions translate to $463.46 saving per cUTI patient tested with Guidance UTI (p=0.043), a saving of $11.6 million for 25,000 cUTI cases (Table 1).
Conclusions: Guidance UTI testing is associated with reductions in critical adverse outcomes, healthcare resource utilization and cost for cUTI cases as compared to standard urine culture. cUTI cases may benefit from Guidance UTI’s combination of increased sensitivity, reduced time to results, and P-AST results.
Source of Funding: Pathnostics
Methods: Using a randomized 5% sample of Medicare Parts A+B beneficiaries enrolled in 2017-19 (n ~1.5M in each year), we compared 2 cohorts matched on sex, diabetes, and propensity score, based on whether outpatient UTI diagnosis was made with SUC (N=678) or Guidance UTI (N=69) initially, and for the year following their first cUTI after a 12-month baseline. UTI-related utilization and Medicare-allowed cost was acquired from professional and facility claims.
Results: The rate of outpatient emergency visits was 13% lower and inpatient admissions was 67% lower when using Guidance UTI compared to SUC. For every 1,000 patients there were zero urosepsis, urgent care and skilled nursing facility admissions with Guidance UTI vs 13, 31 and 7 events respectively with SUC. For the composite outcome, Guidance UTI testing was associated with a 42% reduction compared to SUC (Figure 1). These reductions translate to $463.46 saving per cUTI patient tested with Guidance UTI (p=0.043), a saving of $11.6 million for 25,000 cUTI cases (Table 1).
Conclusions: Guidance UTI testing is associated with reductions in critical adverse outcomes, healthcare resource utilization and cost for cUTI cases as compared to standard urine culture. cUTI cases may benefit from Guidance UTI’s combination of increased sensitivity, reduced time to results, and P-AST results.
Source of Funding: Pathnostics



.jpg)
.jpg)