Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD33: Kidney Cancer: Localized: Surgical Therapy II
PD33-05: Incidence and significance of 20% decrease from new baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate after radical and partial nephrectomy
Saturday, May 14, 2022
4:00 PM – 4:10 PM
Location: Room 245
Bo Fan*, Minato Yokoyama, Yosuke Yasuda, Yuki Nakamura, Yusuke Uchida, Shohei Fukuda, Sho Uehara, Hajime Tanaka, Soichiro Yoshida, Yoh Matsuoka, Yasuhisa Fujii, Tokyo, Japan
- BF
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: New baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (NBeGFR) after radical or partial nephrectomy (RN or PN) was shown to be associated with non-renal cancer mortality. In general population, 20% eGFR decrease from the baseline within 2 years was reported to have impact on the overall mortality and development of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Here, we investigated the incidences and risk factors of 20% decrease from NBeGFR within 2 years and its impact on the development of ESRD.
Methods: 607 Japanese patients with non-metastatic renal masses undergoing RN (n = 238) or PN (n = 369) between 2007 and 2018 and followed for longer than 2 years were enrolled in this retrospective study. NBeGFR was defined as eGFR at 1 month after RN/PN. The primary endpoint of this study was 20% decrease from NBeGFR within 2 years. Potential risk factors including surgery type for 20% decrease from NBeGFR within 2 years were assessed by logistic regression analysis. The secondary endpoint was ESRD defined as eGFR <15 ml/min/1.73 m2. The development of ESRD was compared according to the presence or absence of the 20% decrease from NBeGFR.
Results: The median preoperative eGFR and NBeGFRs after RN and PN were 69, 44 and 67 ml/min/1.73 m2, respectively. The 20% decrease from NBeGFR within 2 years was observed in 37 patients (6.1%), showing no significant differences between patients undergoing RN and PN (4.2% vs 7.3%) . Diabetes mellitus, proteinuria, and perioperative complications were shown to be independent risk factors for the 20% decrease, while surgery type was not associated.
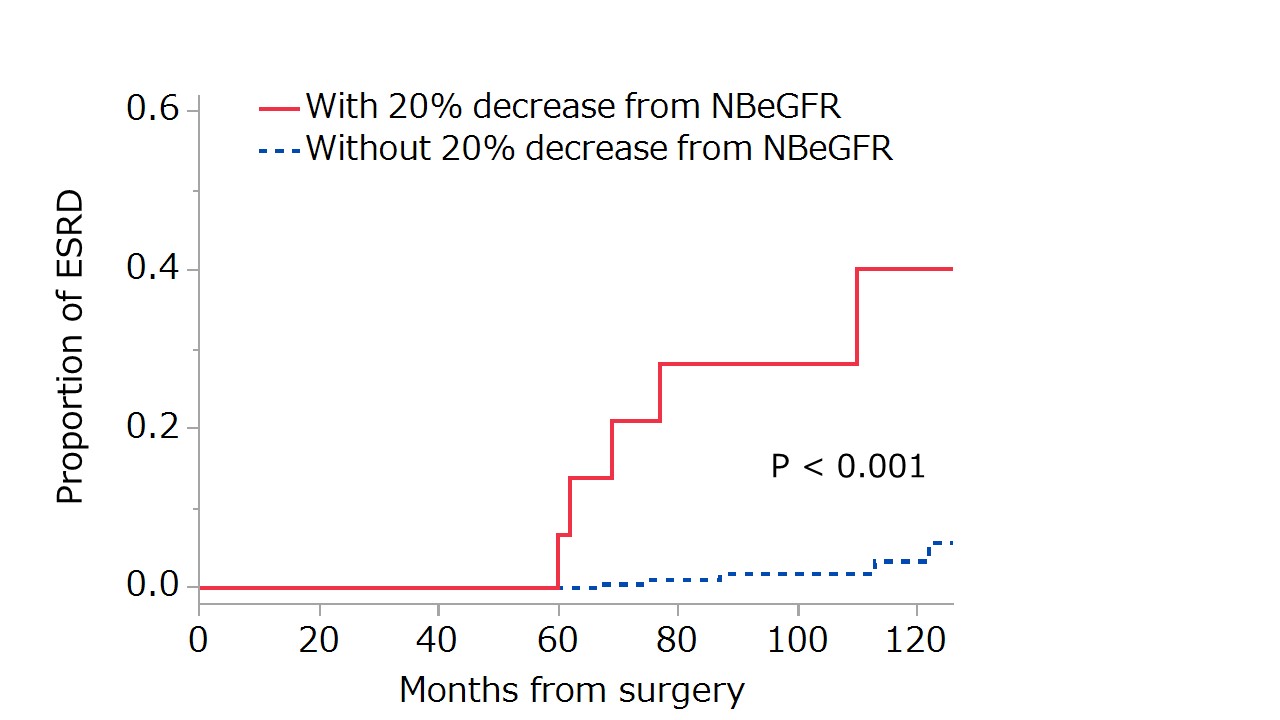
During the median follow-up of 5 years, ESRD was observed in 10 patients (1.6%), including 5 (2.1%) and 5 (1.4%) managed with RN and PN, respectively. 5 (13.5%) of the 37 patients with the 20% decrease from NBeGFR eventually developed ESRD, while 5 (0.9%) of the 570 without the 20% decrease did. The incidence of ESRD at 6 years was 21.0% and 0.4% in patients with and without 20% decrease from NBeGFR (figure, p <0.001).
Conclusions: Approximately 5% of patients undergoing RN or PN experienced 20% decrease from NBeGFR with 2 years irrespective of surgery type. Because the incidence of ESRD after the 20% decrease from NBeGFR was considerably high, such patients should be followed with maximal care.
Source of Funding: none
Methods: 607 Japanese patients with non-metastatic renal masses undergoing RN (n = 238) or PN (n = 369) between 2007 and 2018 and followed for longer than 2 years were enrolled in this retrospective study. NBeGFR was defined as eGFR at 1 month after RN/PN. The primary endpoint of this study was 20% decrease from NBeGFR within 2 years. Potential risk factors including surgery type for 20% decrease from NBeGFR within 2 years were assessed by logistic regression analysis. The secondary endpoint was ESRD defined as eGFR <15 ml/min/1.73 m2. The development of ESRD was compared according to the presence or absence of the 20% decrease from NBeGFR.
Results: The median preoperative eGFR and NBeGFRs after RN and PN were 69, 44 and 67 ml/min/1.73 m2, respectively. The 20% decrease from NBeGFR within 2 years was observed in 37 patients (6.1%), showing no significant differences between patients undergoing RN and PN (4.2% vs 7.3%) . Diabetes mellitus, proteinuria, and perioperative complications were shown to be independent risk factors for the 20% decrease, while surgery type was not associated.
During the median follow-up of 5 years, ESRD was observed in 10 patients (1.6%), including 5 (2.1%) and 5 (1.4%) managed with RN and PN, respectively. 5 (13.5%) of the 37 patients with the 20% decrease from NBeGFR eventually developed ESRD, while 5 (0.9%) of the 570 without the 20% decrease did. The incidence of ESRD at 6 years was 21.0% and 0.4% in patients with and without 20% decrease from NBeGFR (figure, p <0.001).
Conclusions: Approximately 5% of patients undergoing RN or PN experienced 20% decrease from NBeGFR with 2 years irrespective of surgery type. Because the incidence of ESRD after the 20% decrease from NBeGFR was considerably high, such patients should be followed with maximal care.
Source of Funding: none


.jpg)
.jpg)