Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD35: Prostate Cancer: Advanced (including Drug Therapy) II
PD35-03: The significance of De-Ritis ratio in patients with radiation-recurrent prostate cancer undergoing salvage radical prostatectomy
Sunday, May 15, 2022
7:20 AM – 7:30 AM
Location: Room 252
Fahad Quhal*, Ekaterina Laukhtina, Benjamin Pradere, Pawel Rajwa, Vienna, Austria, Axel Heidenreich, Cologne, Germany, Shahrokh F. Shariat, Vienna, Austria

Fahad Quhal, MD
Medical University of Vienna
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: To evaluate the clinical prognostic value of preoperative serum De Ritis Ratio (Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)/ Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)) on postoperative survival outcomes in patients with radiation-recurrent prostate cancer who underwent salvage radical prostatectomy (SRP).
Methods: A retrospective review was conducted of patients with radiation-recurrent prostate cancer who underwent SRP in five tertiary referral centers from 2007 to 2015. An increased pre-operative serum De Ritis ratio was defined as =1.35. The association between De Ritis Ratio and postoperative outcomes was tested. Multivariate Cox analyses were performed to identify the independent predictors of Biochemical recurrence free survival (BCRFS), metastases free survival (MFS), overall survival (OS) and cancer specific survival (CSS).
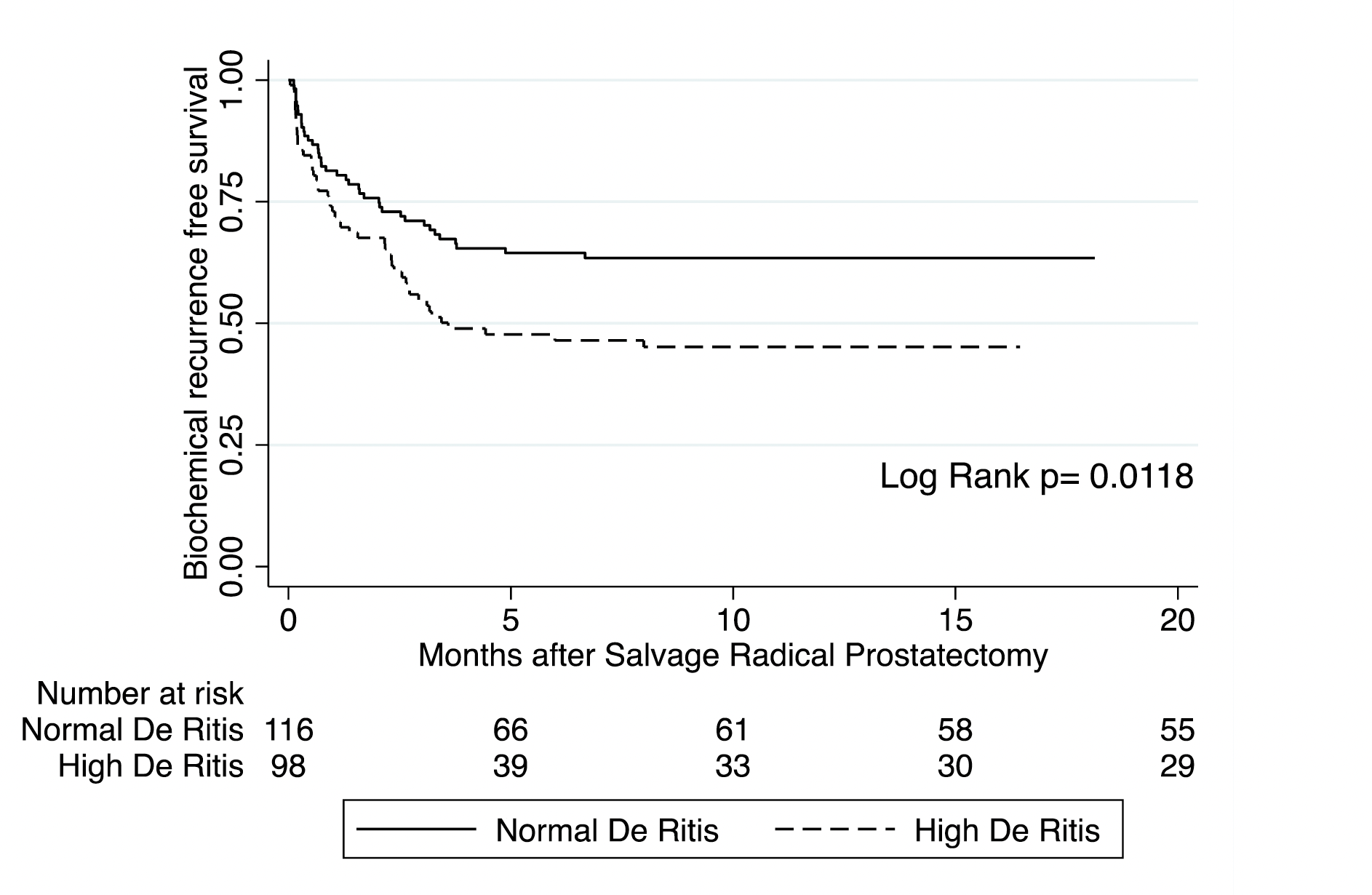
Results: Overall 214 patients underwent SRP, out of them 98 (45.8%) patients with high serum De Ritis Ratio, were included in the study. In a multivariate analysis high De Ritis Ratio was an independent predictor of Biochemical Recurrence (BCR) (hazard ratio (HR) 1.79, 95% Confidence Interval (CI) 1.16-2.78, p-value 0.009) (Figure 1). No significant association was found between pre-operative DRR and MFS (HR 1.32, 95% CI 0.53-3.30, P=0.55), OS (HR 2.35, 95% CI 0.84-6.57, P=0.10) and CSS (HR 3.36, 95%CI 0.65-17.35, P=0.15).
Conclusions: Increased preoperative serum DRR is associated with the development of BCR in patients with radiation-recurrent prostate cancer who underwent SRP. DRR might serve as an early indicator for BCR, which may facilitate recognition of potential relapse and could translate into more intense follow-up and even salvage therapy in selected patients.
Source of Funding: no funding
Methods: A retrospective review was conducted of patients with radiation-recurrent prostate cancer who underwent SRP in five tertiary referral centers from 2007 to 2015. An increased pre-operative serum De Ritis ratio was defined as =1.35. The association between De Ritis Ratio and postoperative outcomes was tested. Multivariate Cox analyses were performed to identify the independent predictors of Biochemical recurrence free survival (BCRFS), metastases free survival (MFS), overall survival (OS) and cancer specific survival (CSS).
Results: Overall 214 patients underwent SRP, out of them 98 (45.8%) patients with high serum De Ritis Ratio, were included in the study. In a multivariate analysis high De Ritis Ratio was an independent predictor of Biochemical Recurrence (BCR) (hazard ratio (HR) 1.79, 95% Confidence Interval (CI) 1.16-2.78, p-value 0.009) (Figure 1). No significant association was found between pre-operative DRR and MFS (HR 1.32, 95% CI 0.53-3.30, P=0.55), OS (HR 2.35, 95% CI 0.84-6.57, P=0.10) and CSS (HR 3.36, 95%CI 0.65-17.35, P=0.15).
Conclusions: Increased preoperative serum DRR is associated with the development of BCR in patients with radiation-recurrent prostate cancer who underwent SRP. DRR might serve as an early indicator for BCR, which may facilitate recognition of potential relapse and could translate into more intense follow-up and even salvage therapy in selected patients.
Source of Funding: no funding


.jpg)
.jpg)