Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD35: Prostate Cancer: Advanced (including Drug Therapy) II
PD35-09: Homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) score in Chinese aggressive prostatic adenocarcinoma with or without intraductal carcinoma of the prostate
Sunday, May 15, 2022
8:20 AM – 8:30 AM
Location: Room 252
Sha Zhu*, Hao Zeng, Chengdu, China, People's Republic of
- SZ
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) score manifests tumors’ genomic instability. Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate (IDC-P) is reported to be exceptionally genomically unstable.
Methods: This study investigates the landscape of HRD score distribution in a Chinese prostate cancer (PCa) cohort with a particular interest in IDC-P. This study included 123 PCa patients. HRD score is calculated based on over 10,000 single-nucleotide polymorphisms distributed across the human genome. We explored the association between HRD scores and clinicopathological characteristics, genomic alterations, and patients' prognoses using rank-sum tests, chi-square tests, Kaplan-Meier curves, and Cox proportional hazards method.
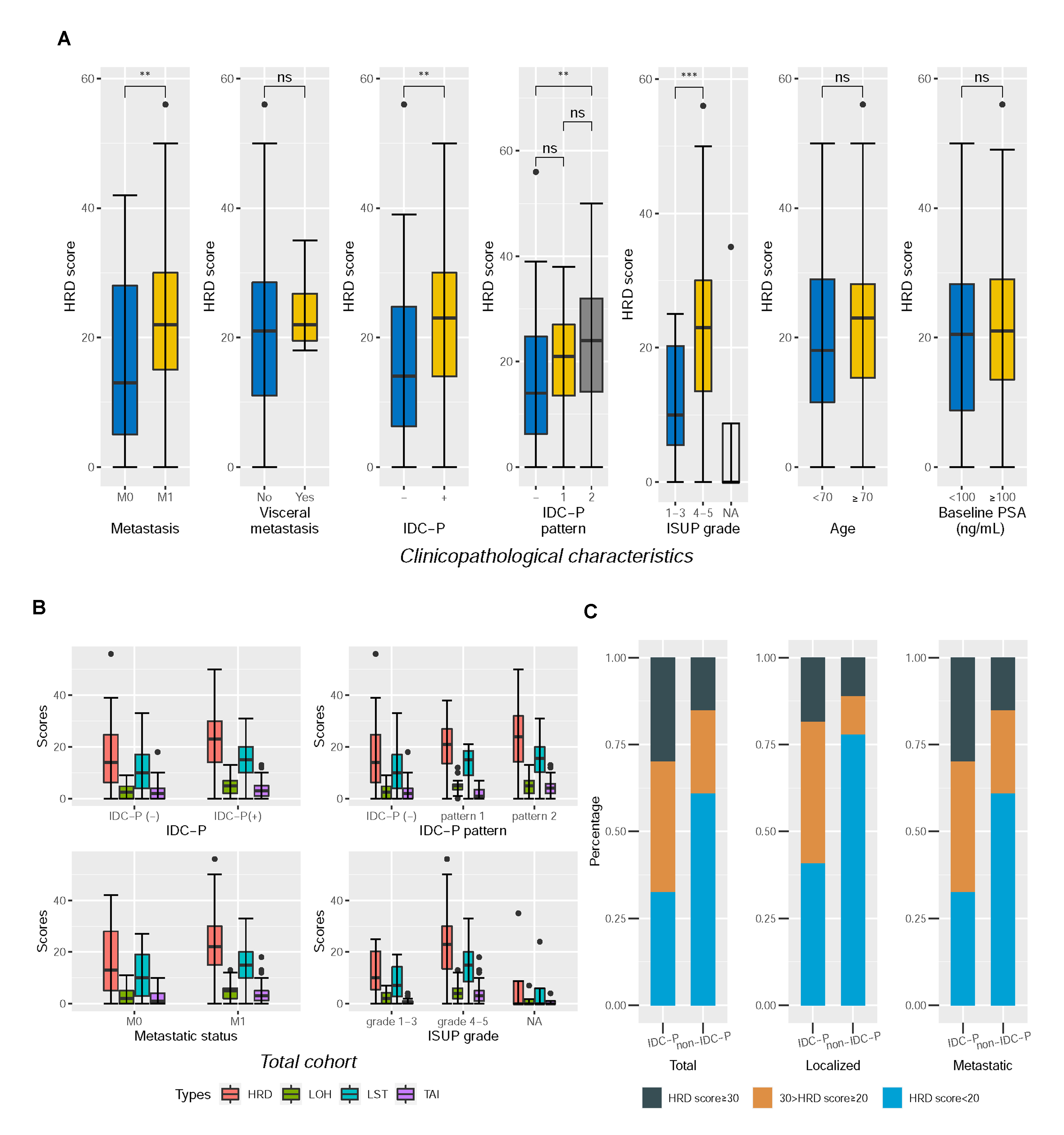
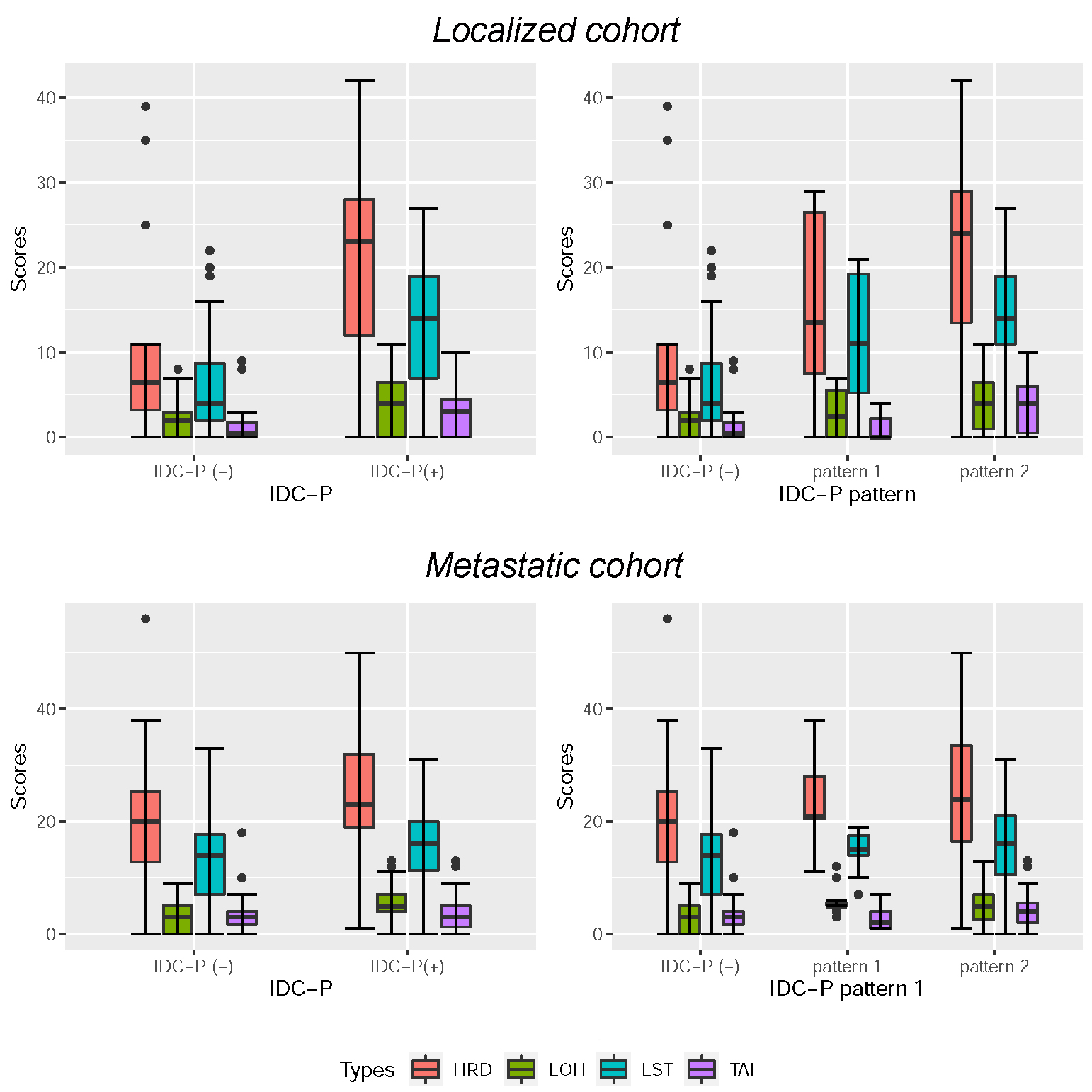
Results: The Median HRD score of this cohort is 21.0, with 70 (56.9%) patients showing HRD score=20. De novo metastatic (M1) (P =0.008), high ISUP grades (4-5) (P=0.001), and IDC-P (P=0.002) all correlated to high HRD scores. BRCA-mutated tumors displayed higher HRD scores than BRCA-wild type (wt) tumors (P=0.019). Nevertheless, the BRCA-wt group also showed a considerable amount of high (=20) HRD score tumors (54.7%), and within this group, patients with IDC-P showed significantly higher HRD score (P=0.002). MYC mutations were associated with high HRD scores (P <0.001) in the total cohort. TP53 mutations (P=0.010) and HRR pathway mutations (P=0.028) corresponded to high HRD scores in IDC-P positive and non-IDC-P patients, respectively, but not vise versa. Patients with higher HRD scores seemed to progress faster with standard treatment (11.3 months vs. 28.0 months, P=0.077). M1, high Gleason score, and IDC-P pathology represent higher HRD scores in PCa.
Conclusions: Tumors with IDC-P might have different driven mechanisms for high HRD scores than non-IDC-P. Alternative treatment should be considered for PCa patients with high HRD scores.
Source of Funding: The Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 81902577);
China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M673239);
The Research Foundation for the Postdoctoral Program of Sichuan University (2021SCU12014);
Post-Doctor Research Project, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (20HXBH026).
Methods: This study investigates the landscape of HRD score distribution in a Chinese prostate cancer (PCa) cohort with a particular interest in IDC-P. This study included 123 PCa patients. HRD score is calculated based on over 10,000 single-nucleotide polymorphisms distributed across the human genome. We explored the association between HRD scores and clinicopathological characteristics, genomic alterations, and patients' prognoses using rank-sum tests, chi-square tests, Kaplan-Meier curves, and Cox proportional hazards method.
Results: The Median HRD score of this cohort is 21.0, with 70 (56.9%) patients showing HRD score=20. De novo metastatic (M1) (P =0.008), high ISUP grades (4-5) (P=0.001), and IDC-P (P=0.002) all correlated to high HRD scores. BRCA-mutated tumors displayed higher HRD scores than BRCA-wild type (wt) tumors (P=0.019). Nevertheless, the BRCA-wt group also showed a considerable amount of high (=20) HRD score tumors (54.7%), and within this group, patients with IDC-P showed significantly higher HRD score (P=0.002). MYC mutations were associated with high HRD scores (P <0.001) in the total cohort. TP53 mutations (P=0.010) and HRR pathway mutations (P=0.028) corresponded to high HRD scores in IDC-P positive and non-IDC-P patients, respectively, but not vise versa. Patients with higher HRD scores seemed to progress faster with standard treatment (11.3 months vs. 28.0 months, P=0.077). M1, high Gleason score, and IDC-P pathology represent higher HRD scores in PCa.
Conclusions: Tumors with IDC-P might have different driven mechanisms for high HRD scores than non-IDC-P. Alternative treatment should be considered for PCa patients with high HRD scores.
Source of Funding: The Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 81902577);
China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M673239);
The Research Foundation for the Postdoctoral Program of Sichuan University (2021SCU12014);
Post-Doctor Research Project, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (20HXBH026).



.jpg)
.jpg)