Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD36: Infertility: Basic Research & Pathophysiology
PD36-05: Loss-of-function in PHF7 Cause Male Infertility by Impairing Histone-to-Protamine Exchange during Spermiogenesis
Sunday, May 15, 2022
7:40 AM – 7:50 AM
Location: Room 255
Jianxing Cheng*, Mengyang Cao, Zhongjie Zheng, Haocheng Lin, BEIJING, China, People's Republic of
- JC
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction:
Introduction: Recently, studies shows that PHF7 is specifically expressed in elongating spermatid during spermiogenesis, however whether it results infertility in human are still unclear as well as the mechanism.
Objective: To investigate the role of PHF7 on male infertility and explore its mechanism.
Methods: The blood and testicular samples from azoospermia patients were collected and used for genome sequencing and immunohistology. The PHF7 knockout mice model were established and used for animal study. RT-PCR, Immunohistology, GST-pulldown and western blotting were used for mechanism exploring.
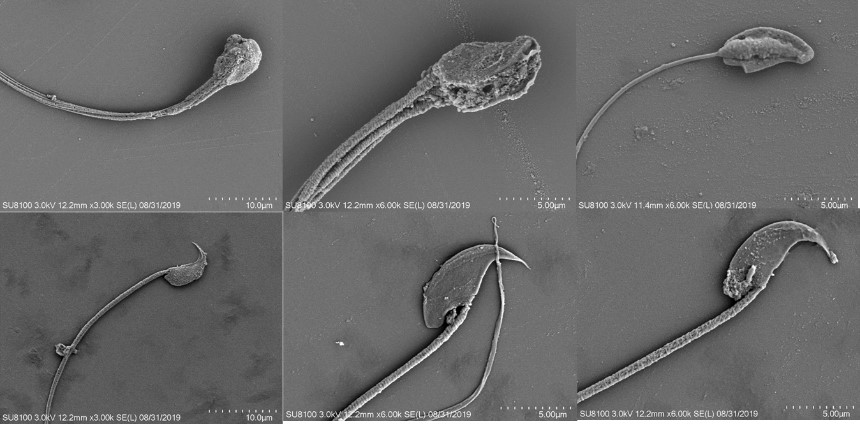
Results: Our results revealed that expression level of PHF7 in patients with male infertility was significant less than control. Two heterozygous mutations were also identified in azoospemia patients. PHF7 knockout mice show defective spermatogenesis at a later spermiogenic stage with abnormal sperm morphology with histone retention.
Conclusions: Our study identified PHF7 mutations as etiological factors in male infertility and reveal its mechanism for regulating the histone-to-protamine exchange during spermiogenesis.
Source of Funding: Peking University Clinical Medicine +X Youth Special Program (PKU2018LCXQ019)
Introduction: Recently, studies shows that PHF7 is specifically expressed in elongating spermatid during spermiogenesis, however whether it results infertility in human are still unclear as well as the mechanism.
Objective: To investigate the role of PHF7 on male infertility and explore its mechanism.
Methods: The blood and testicular samples from azoospermia patients were collected and used for genome sequencing and immunohistology. The PHF7 knockout mice model were established and used for animal study. RT-PCR, Immunohistology, GST-pulldown and western blotting were used for mechanism exploring.
Results: Our results revealed that expression level of PHF7 in patients with male infertility was significant less than control. Two heterozygous mutations were also identified in azoospemia patients. PHF7 knockout mice show defective spermatogenesis at a later spermiogenic stage with abnormal sperm morphology with histone retention.
Conclusions: Our study identified PHF7 mutations as etiological factors in male infertility and reveal its mechanism for regulating the histone-to-protamine exchange during spermiogenesis.
Source of Funding: Peking University Clinical Medicine +X Youth Special Program (PKU2018LCXQ019)


.jpg)
.jpg)