Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD38: Urodynamics/Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction/Female Pelvic Medicine: Non-neurogenic Voiding Dysfunction II
PD38-03: Role of post-voided residual ratio in patients with detrusor underactivity: a pressure-flow study analysis
Sunday, May 15, 2022
7:20 AM – 7:30 AM
Location: Room 244
Cosimo De Nunzio, Riccardo Lombardo, Rome, Italy, Antonio Nacchia*, Rionero in Vulture, Italy, Antonio Maria Cicione, Rome, Italy, Simon Carter, London, United Kingdom, Carlo Vicentini, L'Aquila, Italy, Beatrice Turchi, Carmen Gravina, Jordi Stira, Alessandro Guercio, Giacomo Gallo, Valeria Baldassarri, Olivia Alessandra Voglino, Antonio Franco, Lorenzo Maria Rivesti, Sara Riolo, Simone D'Annunzio, Elisa Mancini, Giorgio Guarnotta, Andrea Tubaro, Rome, Italy
- AN
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Recently some authors have suggested a possible role of post-void residual ratio to predict detrusor underactivity (DU). Aim of our study is to confirm the correlation between post-void residual urine ratio (PVR-R) and DU diagnosed by pressure-flow studies (PFS) in males with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and to develop a clinical nomogram.
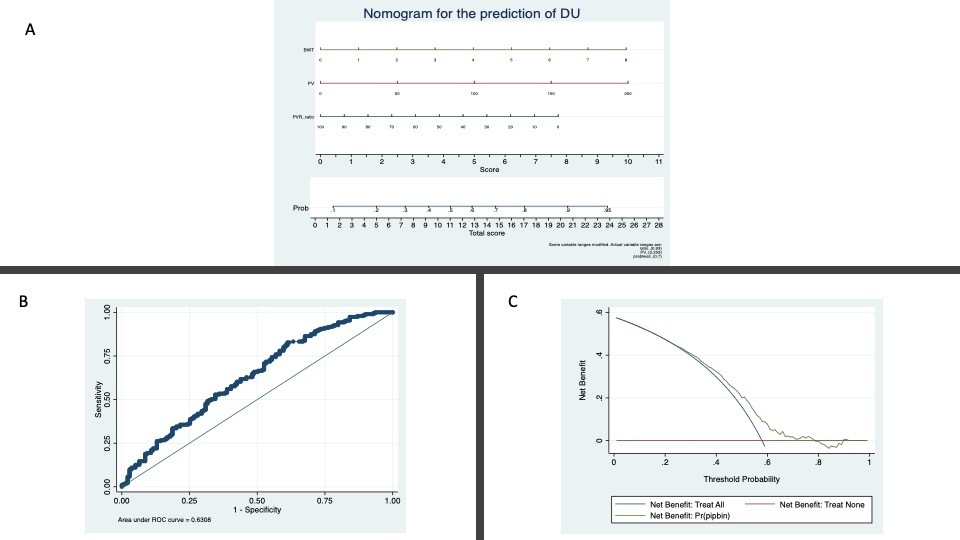
Methods: A consecutive series of patients aged 45 years or older with non-neurogenic LUTS were prospectively enrolled. Patients underwent standard diagnostic assessment for DU including International Prostatic Symptoms Score, uroflowmetry, urodynamic studies (cystometry and pressure-flow studies), suprapubic ultrasound of the prostate and ultrasound measurements of the bladder wall thickness (BTW). PVR urine and the percentage of PVR to bladder volume (voided volume+PVR) (PVR-R) were evaluated. Logistic regression analysis was used to investigate predictors of DU defined as bladder contractility index (BCI) <100. A nomogram to predict DU based on the multivariable logistic regression model was then developed. Discrimination and net benefit of the model was evaluated.
Results: Overall 335 patients with a mean age of 66 ± 11 years were enrolled. Overall, 195/335 (58%) presented DU on PFS. In a multivariable logistic age-adjusted regression model BWT (odds ratio [OR]: 1,33 per mm; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1,01- 1,75; p=0.043), PVR-R (OR: 0,98 per mL/s; 95% CI, 0,97-0,99; p=0.004) and prostate volume (OR: 1,01 per mL/s; 95% CI, 1,00-1,02; p =0.008) were significant predictors for DU. The model presented an accuracy of 0,63 and a clinical net benefit in the range of 25-80%.
Figure: A Nomogram, B: ROC curve, C: Decision Curve Analysis
Conclusions: The present study confirms the important role of PVR-ratio in the prediction of DU For the first time we present a clinical nomogram including PVR-ratio for the prediction of DU. External validation is needed before clinical implementation.
Source of Funding: None.
Methods: A consecutive series of patients aged 45 years or older with non-neurogenic LUTS were prospectively enrolled. Patients underwent standard diagnostic assessment for DU including International Prostatic Symptoms Score, uroflowmetry, urodynamic studies (cystometry and pressure-flow studies), suprapubic ultrasound of the prostate and ultrasound measurements of the bladder wall thickness (BTW). PVR urine and the percentage of PVR to bladder volume (voided volume+PVR) (PVR-R) were evaluated. Logistic regression analysis was used to investigate predictors of DU defined as bladder contractility index (BCI) <100. A nomogram to predict DU based on the multivariable logistic regression model was then developed. Discrimination and net benefit of the model was evaluated.
Results: Overall 335 patients with a mean age of 66 ± 11 years were enrolled. Overall, 195/335 (58%) presented DU on PFS. In a multivariable logistic age-adjusted regression model BWT (odds ratio [OR]: 1,33 per mm; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1,01- 1,75; p=0.043), PVR-R (OR: 0,98 per mL/s; 95% CI, 0,97-0,99; p=0.004) and prostate volume (OR: 1,01 per mL/s; 95% CI, 1,00-1,02; p =0.008) were significant predictors for DU. The model presented an accuracy of 0,63 and a clinical net benefit in the range of 25-80%.
Figure: A Nomogram, B: ROC curve, C: Decision Curve Analysis
Conclusions: The present study confirms the important role of PVR-ratio in the prediction of DU For the first time we present a clinical nomogram including PVR-ratio for the prediction of DU. External validation is needed before clinical implementation.
Source of Funding: None.


.jpg)
.jpg)