Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD40: Uroradiology II
PD40-06: Usefulness of Prostate Specific Antigen–Glycosylation Isomer for Significant Cancer Detection and Pathological Findings of Index Prostate Cancers on Magnetic Resonance Imaging–Transrectal Ultrasound Fusion Image-Guided Biopsy: A Prospective Multicenter Study
Sunday, May 15, 2022
10:20 AM – 10:30 AM
Location: Room 252
SUNAO SHOJI*, MAYURA NAKANO, Isehara, Japan, KOHEI UEMURA, Bunkyo-ku, Japan, KUMPEI TAKAHASHI, TATSUO KANO, SOICHIRO YUZURIHA, IZUMI HANADA, TAKAHIRO OGAWA, TATSUYA UMEMOTO, MASAYOSHI KAWAKAMI, MASAHIRO NITTA, MASANORI HASEGAWA, Isehara, Japan, TERUMITSU HASEBE, Hachioji, Japan, AKIRA MIYAJIMA, Isehara, Japan

Sunao Shoji, MD, PHD, MBA
Tokai University School of Medicine
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: This study aimed to evaluate the ability of prostate specific antigen–glycosylation isomer (PSA-Gi) to predict the pathological findings of biopsy-proven index prostate cancer (PC).
Methods: Patients with serum PSA levels = 20 ng/mL who underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)–transrectal ultrasound fusion image-guided target biopsy were included. PSA-Gi was measured by an automated two-step Wisteria Floribunda Agglutinin lectin–anti-PSA antibody sandwich immunoassay using a highly sensitive surface plasmon field-enhanced fluorescence spectrometry system. Target biopsies were performed of cancer-suspicious lesions and analyzed by a Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) v.2.0.
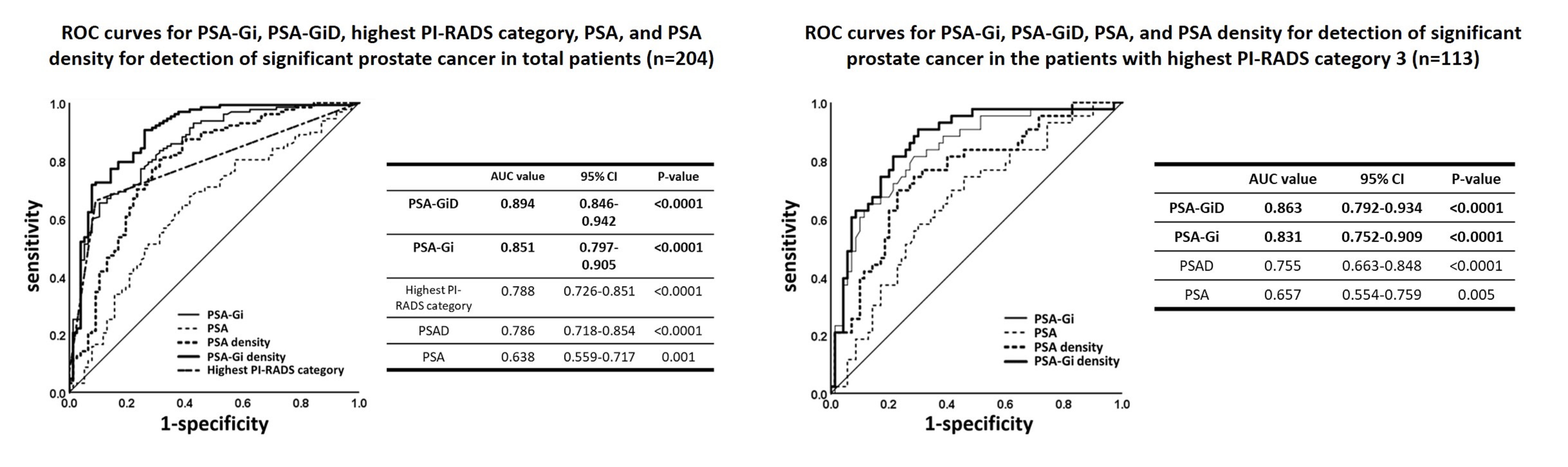
Results: Two hundred four patients were included. Patients’ median values were age, 70 years; PSA, 6.71 ng/mL; PSA-Gi, 40.2 mU/mL; and prostate volume, 35 cc. Their categories were PI-RADS 3 (n=113), PI-RADS 4 (n=82), and PI-RADS 5 (n=9). Median PSA-Gi (65.4 mU/mL vs. 25.3 mU/mL, P<0.0001) and PSA-Gi density (PSA-GiD) (0.232 mU/mL/cc vs. 0.0578 mU/mL/cc, p<0.0001) levels significantly differed between patients with and those without detected biopsy-proven significant cancer (SC). Areas under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for PSA-Gi (AUC 0.851, 95%CI: 0.797-0.905, P<0.0001) and PSA-GiD (AUC 0.894, 95%CI: 0.846-0.942, P<0.0001) were significantly greater than non-discrimination for SC detection in all patients. Among patients with the highest PI-RADS category 3, ROC curves for PSA-Gi (AUC 0.831, P<0.0001) and PSA-GiD (AUC 0.863, P<0.0001) were significantly greater than non-discrimination for detecting clinically SC. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive, and negative predictive values of a PSA-GiD of 0.812 mU/mL/cc were 85%, 84%, 91.3%, and 72.7%, respectively. The highest Gleason score was positively correlated with PSA-Gi MRI-measured tumor volume density (PSA-GiTVD) (r=0.557, p<0.0001).
Conclusions: PSA-Gi, PSA-GiD, and PSA-GiTVD may predict pathological findings of biopsy-proven index PC. PSA-GiD may predict SC detection in patients with the highest PI-RADS category.
Source of Funding: None.
Methods: Patients with serum PSA levels = 20 ng/mL who underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)–transrectal ultrasound fusion image-guided target biopsy were included. PSA-Gi was measured by an automated two-step Wisteria Floribunda Agglutinin lectin–anti-PSA antibody sandwich immunoassay using a highly sensitive surface plasmon field-enhanced fluorescence spectrometry system. Target biopsies were performed of cancer-suspicious lesions and analyzed by a Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) v.2.0.
Results: Two hundred four patients were included. Patients’ median values were age, 70 years; PSA, 6.71 ng/mL; PSA-Gi, 40.2 mU/mL; and prostate volume, 35 cc. Their categories were PI-RADS 3 (n=113), PI-RADS 4 (n=82), and PI-RADS 5 (n=9). Median PSA-Gi (65.4 mU/mL vs. 25.3 mU/mL, P<0.0001) and PSA-Gi density (PSA-GiD) (0.232 mU/mL/cc vs. 0.0578 mU/mL/cc, p<0.0001) levels significantly differed between patients with and those without detected biopsy-proven significant cancer (SC). Areas under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for PSA-Gi (AUC 0.851, 95%CI: 0.797-0.905, P<0.0001) and PSA-GiD (AUC 0.894, 95%CI: 0.846-0.942, P<0.0001) were significantly greater than non-discrimination for SC detection in all patients. Among patients with the highest PI-RADS category 3, ROC curves for PSA-Gi (AUC 0.831, P<0.0001) and PSA-GiD (AUC 0.863, P<0.0001) were significantly greater than non-discrimination for detecting clinically SC. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive, and negative predictive values of a PSA-GiD of 0.812 mU/mL/cc were 85%, 84%, 91.3%, and 72.7%, respectively. The highest Gleason score was positively correlated with PSA-Gi MRI-measured tumor volume density (PSA-GiTVD) (r=0.557, p<0.0001).
Conclusions: PSA-Gi, PSA-GiD, and PSA-GiTVD may predict pathological findings of biopsy-proven index PC. PSA-GiD may predict SC detection in patients with the highest PI-RADS category.
Source of Funding: None.


.jpg)
.jpg)