Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD43: Kidney Cancer: Basic Research & Pathophysiology II
PD43-02: Therapeutic efficacy of YM155 to repress an epigenetic enzyme and everolimus resistance in RCC.
Sunday, May 15, 2022
9:40 AM – 9:50 AM
Location: Room 244
Seong Hwi Hong, Hyun Ji Hwang*, Na Gyeong Ha, Sung Yul Park, Hong Sang Moon, Young Eun Yoon, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
- HH
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer accounting for approximately 85% of cases. Because clear cell RCC (ccRCC) accounts for more than 75% of RCC, most RCC studies were focused on ccRCC. Everolimus is an mTOR inhibitor and is one of the option for metastatic ccRCC treatment. However, because everolimus resistance limits the therapeutic effect, new strategy has been needed to overcome resistance. So we conducted this research to identify a target for all subtype RCC and everolimus resistant RCC treatment.
Methods: We analyzed the TCGA databases of ccRCC, pRCC, and chRCC to find genetic targets of all subtype RCCs. Additionally, we treated the everolimus gradually from 1 to 10 µM for 3 months to produce everolimus-resistant RCC cell lines. In order to investigate the effect of YM155 as a BIRC5 inhibitor in RCC, we checked cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis using ccRCC, pRCC, chRCC, everolimus resistant cell lines. To confirm in vitro experiment, we were generated xenograft animal models.
Results: In the analysis of the TCGA database, BIRC5 was discovered as a key oncogene for three types of RCCs. For the RCC cell lines and xenograft model, we observed the anti-tumorigenic effect of YM155. In ChIP assay, H3K27Ac was decreased by YM155. Also, everolimus resistant Caki1 and ACHN showed anti-tumorigenic effects of YM155. We screened for genes that induce everolimus resistance, and we selected AURKA, a kinase that is very important for cell cycle regulation. In the everolimus-resistant RCC cell line, there was no change in mRNA expression of AURKA by everolimus treatment but decreased when YM155 was treated.
Conclusions: This study indicated BIRC5 as a key factor that can target pRCC and chRCC, and showed the anti-tumorigenic effect and epigenetic switching mechanism of YM155 through in vitro and in vivo experiments. Also, we suggested YM155 as a novel drug to overcome everolimus resistance. Therefore, this study will shed light on the therapy of various cancers that have everolimus resistance as well as RCCs.
Source of Funding: This work was supported by the research fund of Hanyang University (HY-2021)
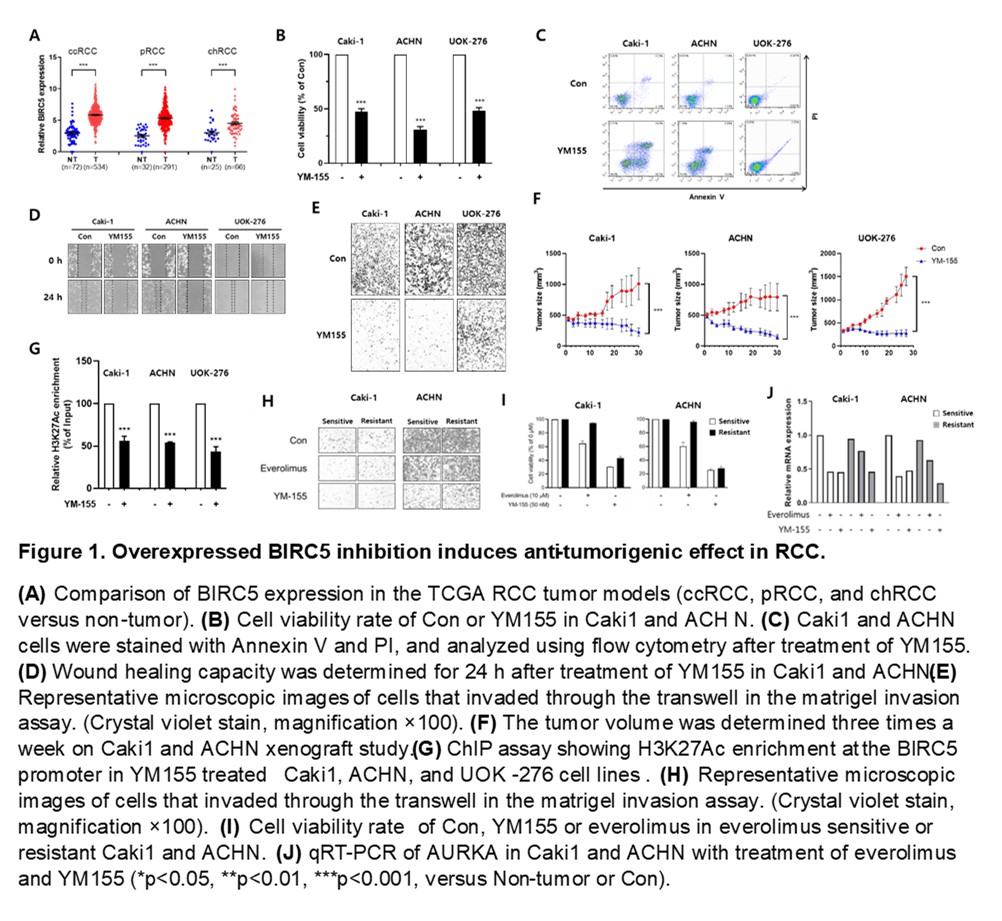

Methods: We analyzed the TCGA databases of ccRCC, pRCC, and chRCC to find genetic targets of all subtype RCCs. Additionally, we treated the everolimus gradually from 1 to 10 µM for 3 months to produce everolimus-resistant RCC cell lines. In order to investigate the effect of YM155 as a BIRC5 inhibitor in RCC, we checked cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis using ccRCC, pRCC, chRCC, everolimus resistant cell lines. To confirm in vitro experiment, we were generated xenograft animal models.
Results: In the analysis of the TCGA database, BIRC5 was discovered as a key oncogene for three types of RCCs. For the RCC cell lines and xenograft model, we observed the anti-tumorigenic effect of YM155. In ChIP assay, H3K27Ac was decreased by YM155. Also, everolimus resistant Caki1 and ACHN showed anti-tumorigenic effects of YM155. We screened for genes that induce everolimus resistance, and we selected AURKA, a kinase that is very important for cell cycle regulation. In the everolimus-resistant RCC cell line, there was no change in mRNA expression of AURKA by everolimus treatment but decreased when YM155 was treated.
Conclusions: This study indicated BIRC5 as a key factor that can target pRCC and chRCC, and showed the anti-tumorigenic effect and epigenetic switching mechanism of YM155 through in vitro and in vivo experiments. Also, we suggested YM155 as a novel drug to overcome everolimus resistance. Therefore, this study will shed light on the therapy of various cancers that have everolimus resistance as well as RCCs.
Source of Funding: This work was supported by the research fund of Hanyang University (HY-2021)



.jpg)
.jpg)