Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD48: Pediatic Urology: Genitalia, Upper & Lower Urinary Tract
PD48-09: Is There an Optimal Way to Measure Renal Function in Prune Belly Syndrome?
Sunday, May 15, 2022
2:20 PM – 2:30 PM
Location: Room 244
Shane Batie*, Samuel Gold, Shaheer Ali, Daniel Wong, Niccolo Passoni, Steven Harrison, Nida Karra, Nathalia Amado, Jyothsna Gattineni, Linda Baker, Dallas, TX

Shane Forest Batie, MD
University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Thirty percent of Prune Belly Syndrome (PBS) patients progress to renal failure, making reliable measures of PBS renal function critical. While serum creatinine (sCr) is a clinical surrogate for renal function, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is calculated via formulas using sCr (eGFRcr aka “Bedside Schwartz”), cystatin C (eGFRcys), or both combined (CKiD). We hypothesized sCr alone poorly predicts renal function and there would be a difference in eGFRcr compared to eGFRcys and CKiD in PBS patients.
Methods: From 2014-2021, PBS patients without neuromuscular disorders, renal transplantation, or dialysis were retrospectively reviewed for outpatient labs performed at our hospital. eGFRcr, eGFRcys, and CKiD were calculated. Patients were categorized for chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage using the eGFRcr Bedside Schwartz equation. A paired-sample t-test was used to compare mean eGFR values within CKD groups between different eGFR calculators.
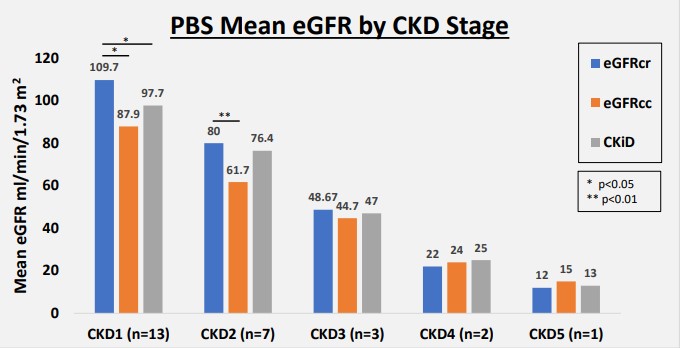
Results: 26 PBS patients (25M:1F; median age 10.7 [range 0.5-18.8 years]; 11Caus:10Black:5Hisp) had paired sCr and cystatin C. Overall, 13, 7, 3, 2, and 1 were CKD 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 respectively. 20/26 had normal range sCr. Of these, 5/20(25%) had an eGFRcr consistent with CKD2. Similarly, 21/26 had normal serum cystatin C but 6/21(29%) had an eGFRcr consistent with CKD2. Using all GFR calculators to classify each patient by CKD level relative to the eGFRcr, 9/26 were classified 1-2 CKD stages higher using eGFRcys and 4/26 were classified higher using CKiD. No patient was lower staged for CKD. Mean eGFRcys was lower than eGFRcr for CKD1 (p=0.02) and CKD2 (p=0.003). Mean CKiD was lower than eGFRcr for CKD1 (p=0.03), but not CKD2 (p=0.18). For CKD stages 3, 4, and 5 with low group sizes, there was no difference between mean eGFRcr, eGFRcys and CKiD.
Conclusions: Normal for age and sex sCr or cystatin C values alone are not a reliable measure of renal function in PBS patients, falsely suggesting normalcy in 25-29% who instead have CKD2. In PBS patients categorized as CKD 1 and 2 by the classically used eGFRcr calculator, there was a significant CKD understaging compared to eGFRcys and CKiD. While this data was cross-sectional, it stresses the importance of obtaining paired sCr and cystatin C for use in eGFR calculators, permitting more accurate monitoring of renal function trends in PBS pediatric patients.
Source of Funding: This study was supported in part by NIH grant R01 DK105068 (PI: L. Baker)
Methods: From 2014-2021, PBS patients without neuromuscular disorders, renal transplantation, or dialysis were retrospectively reviewed for outpatient labs performed at our hospital. eGFRcr, eGFRcys, and CKiD were calculated. Patients were categorized for chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage using the eGFRcr Bedside Schwartz equation. A paired-sample t-test was used to compare mean eGFR values within CKD groups between different eGFR calculators.
Results: 26 PBS patients (25M:1F; median age 10.7 [range 0.5-18.8 years]; 11Caus:10Black:5Hisp) had paired sCr and cystatin C. Overall, 13, 7, 3, 2, and 1 were CKD 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 respectively. 20/26 had normal range sCr. Of these, 5/20(25%) had an eGFRcr consistent with CKD2. Similarly, 21/26 had normal serum cystatin C but 6/21(29%) had an eGFRcr consistent with CKD2. Using all GFR calculators to classify each patient by CKD level relative to the eGFRcr, 9/26 were classified 1-2 CKD stages higher using eGFRcys and 4/26 were classified higher using CKiD. No patient was lower staged for CKD. Mean eGFRcys was lower than eGFRcr for CKD1 (p=0.02) and CKD2 (p=0.003). Mean CKiD was lower than eGFRcr for CKD1 (p=0.03), but not CKD2 (p=0.18). For CKD stages 3, 4, and 5 with low group sizes, there was no difference between mean eGFRcr, eGFRcys and CKiD.
Conclusions: Normal for age and sex sCr or cystatin C values alone are not a reliable measure of renal function in PBS patients, falsely suggesting normalcy in 25-29% who instead have CKD2. In PBS patients categorized as CKD 1 and 2 by the classically used eGFRcr calculator, there was a significant CKD understaging compared to eGFRcys and CKiD. While this data was cross-sectional, it stresses the importance of obtaining paired sCr and cystatin C for use in eGFR calculators, permitting more accurate monitoring of renal function trends in PBS pediatric patients.
Source of Funding: This study was supported in part by NIH grant R01 DK105068 (PI: L. Baker)


.jpg)
.jpg)