Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD49: Sexual Function/Dysfunction: Medical, Hormonal & Non-surgical Therapy II
PD49-02: Medications Most Commonly Associated with Erectile Dysfunction: Evaluation of the Food and Drug Administration National Pharmacovigilance Database
Sunday, May 15, 2022
3:40 PM – 3:50 PM
Location: Room 252
Elie Kaplan-Marans*, Mariela Martinez, Arshia Sandozi, Jeffrey Lee, Jacob Khurgin, Ariel Schulman, New York, NY
- EK
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a side effect of many medications. We used a national pharmacovigilance database to assess which medications had the highest frequency of ED.
Methods: The Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) was queried to identify medications with the highest frequency of ED adverse event reports from 2010-2020. Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors and testosterone were excluded because these medications are treatments for ED. Proportional Reporting Ratios (PRRs) and their 95% confidence intervals were calculated. The top 20 medications with the highest frequency of ED were included in the disproportionality analysis.
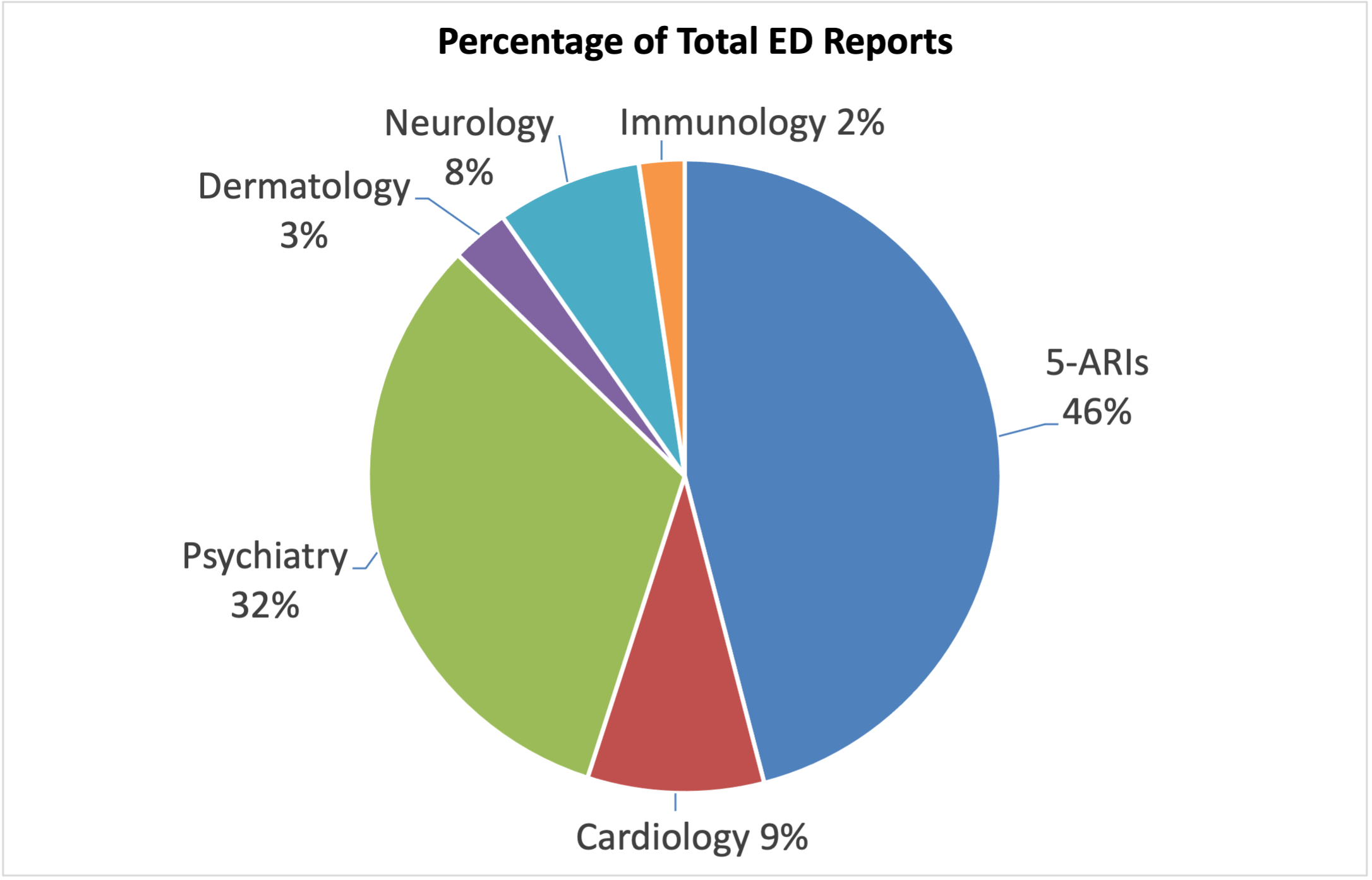
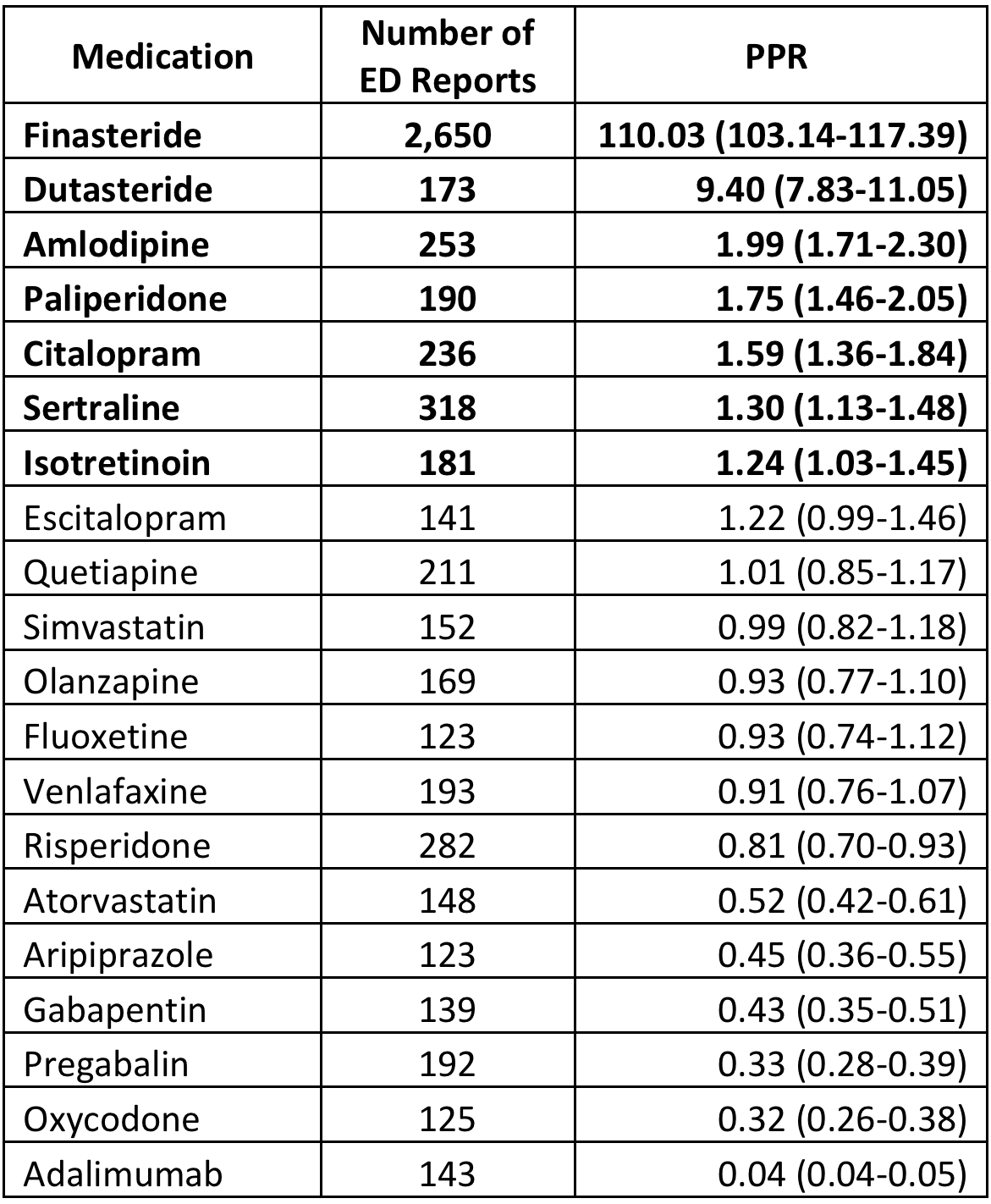
Results: Of these 20 medications, there were 6,142 reports of ED and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (5-ARIs) accounted for 2,823 (46%) of these reports (Figure 1). Seven medications showed significant levels of disproportionate reporting but finasteride and dutasteride had the highest PRRs: 110.03 (103.14-117.39) and 9.40 (7.83-11.05) respectively (Table 1). The other medications are used in a wide variety of medical fields such as psychiatry, neurology, cardiology, dermatology, and immunology.
Conclusions: In a national pharmacovigilance database, 5-ARIs had the highest number of reports and proportional reporting ratios of ED side effects. There were many other medications used in a variety of medical fields that were also associated with ED. Physicians and patients should be familiar with medications that are associated with ED.
Source of Funding: None.
Methods: The Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) was queried to identify medications with the highest frequency of ED adverse event reports from 2010-2020. Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors and testosterone were excluded because these medications are treatments for ED. Proportional Reporting Ratios (PRRs) and their 95% confidence intervals were calculated. The top 20 medications with the highest frequency of ED were included in the disproportionality analysis.
Results: Of these 20 medications, there were 6,142 reports of ED and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (5-ARIs) accounted for 2,823 (46%) of these reports (Figure 1). Seven medications showed significant levels of disproportionate reporting but finasteride and dutasteride had the highest PRRs: 110.03 (103.14-117.39) and 9.40 (7.83-11.05) respectively (Table 1). The other medications are used in a wide variety of medical fields such as psychiatry, neurology, cardiology, dermatology, and immunology.
Conclusions: In a national pharmacovigilance database, 5-ARIs had the highest number of reports and proportional reporting ratios of ED side effects. There were many other medications used in a variety of medical fields that were also associated with ED. Physicians and patients should be familiar with medications that are associated with ED.
Source of Funding: None.



.jpg)
.jpg)