Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD50: Stone Disease: Epidemiology & Evaluation II
PD50-04: Electronic Health Record-Based Risk Stratification for Recurrence of Kidney Stones: A Feasibility Implementation
Sunday, May 15, 2022
4:00 PM – 4:10 PM
Location: Room 255
Ryan Hsi*, Tatsuki Koyama, Allison McCoy, Nashville, TN

Ryan S. Hsi, MD,FACS
Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Clinical nomograms for kidney stone recurrence risk prediction exist, however a major barrier is their high burden of work and the need for external applications. We present a feasibility implementation of the ROKS nomogram integrated into the electronic health record (EHR), which we term EHR-ROKS, to improve provider risk stratification for patients with kidney stone disease.
Methods: Questions from the 2018 ROKS nomogram were converted into the Epic EHR flowsheet activity. The nomogram sums total points based on 10 questions (or 14 if imaging was performed at the last stone event), then calculates risk as 1-ae^(-1.84089+pointsx0.019) with defined values for a by stone episode and number of years since the last stone episode. Calculations were performed using both automated and queried values to calculate the predicted risk of kidney stone recurrence at 5 and 10 years. Accuracy of the EHR-ROKS was compared to the web-based 2018 ROKS nomogram predicted risk.
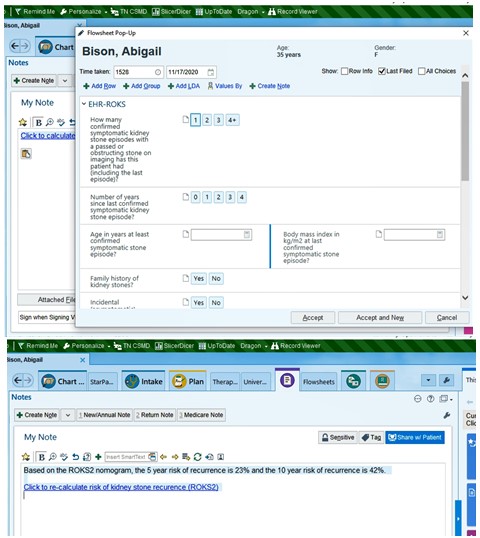
Results: EHR-ROKS is accessed from within the progress note using a text shortcut (i.e., SmartPhrase) that inserts a hyperlink into the note, as well as the predicted risk of recurrence (see Figure). Clicking the hyperlink opens the ROKS questionnaire in a flowsheet activity that allows clinicians to answer questions about the patient and prior stone episodes. Within Epic, calculations for EHR-ROKS are performed using a combination of 18 logic rules that return numeric values. Two rules impute age and BMI, and one rule determines whether the patient is pregnant. Another rule determines the total number of points based on the three prior rules and the manually entered flowsheet values. To determine the a, five rules return the a for 5-year risk, and five rules return the a for 10-year risk based on the manually entered episode number and number of years since the last stone episode. Two rules calculate the 5- and 10-year risk, respectively. We found the EHR-ROKS completely matched web-based calculations after simulations.
Conclusions: Our feasibility implementation indicates that the ROKS nomogram can be integrated into our commercial EHR into existing workflows, improving the likelihood of adoption in future work towards improving provider risk stratification and delivery of appropriate preventive treatment based on risk.
Source of Funding: Supported UL1 TR002243.
Methods: Questions from the 2018 ROKS nomogram were converted into the Epic EHR flowsheet activity. The nomogram sums total points based on 10 questions (or 14 if imaging was performed at the last stone event), then calculates risk as 1-ae^(-1.84089+pointsx0.019) with defined values for a by stone episode and number of years since the last stone episode. Calculations were performed using both automated and queried values to calculate the predicted risk of kidney stone recurrence at 5 and 10 years. Accuracy of the EHR-ROKS was compared to the web-based 2018 ROKS nomogram predicted risk.
Results: EHR-ROKS is accessed from within the progress note using a text shortcut (i.e., SmartPhrase) that inserts a hyperlink into the note, as well as the predicted risk of recurrence (see Figure). Clicking the hyperlink opens the ROKS questionnaire in a flowsheet activity that allows clinicians to answer questions about the patient and prior stone episodes. Within Epic, calculations for EHR-ROKS are performed using a combination of 18 logic rules that return numeric values. Two rules impute age and BMI, and one rule determines whether the patient is pregnant. Another rule determines the total number of points based on the three prior rules and the manually entered flowsheet values. To determine the a, five rules return the a for 5-year risk, and five rules return the a for 10-year risk based on the manually entered episode number and number of years since the last stone episode. Two rules calculate the 5- and 10-year risk, respectively. We found the EHR-ROKS completely matched web-based calculations after simulations.
Conclusions: Our feasibility implementation indicates that the ROKS nomogram can be integrated into our commercial EHR into existing workflows, improving the likelihood of adoption in future work towards improving provider risk stratification and delivery of appropriate preventive treatment based on risk.
Source of Funding: Supported UL1 TR002243.


.jpg)
.jpg)