Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD53: Bladder Cancer: Basic Research & Pathophysiology III
PD53-01: Molecular subtyping of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU) rat model of urothelial carcinoma reveals both luminal and basal signatures
Monday, May 16, 2022
7:00 AM – 7:10 AM
Location: Room 255
Kara Lombardo*, Takahiro Yoshida, Kate Fitzgerald, Kate Johnson, David McConkey, Alok Singh, Ridwan Alam, Max Kates, Alex Baras, Baltimore, MD, Trinity Bivalacqua, Philadelphia, PA

Kara Lombardo, BS
Johns Hopkins Urology
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: Intrinsic subtypes of urothelial carcinoma have been identified with relevant genetic alterations and distinct clinical behavior. Carcinogen induced rodent models are clinically relevant to study urothelial carcinogenesis. In the present study, we sought to identify molecular profiles of the MNU-tumor induced rat model of urothelial carcinoma and provide additional insight into how experimental pre-clinical models may parallel human non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC).
Methods: Intravesical MNU instillations were administered in 16 Fisher female rats every other week for a total of 4 instillations. Rats were sacrificed at either 16 (n=10) or 30 (n=6) weeks after initial instillation and bladders were harvested for analysis. Pathologic staging was assessed on H&E, and IHC was performed for basal (KRT5, KRT14, p63) and luminal (CK20, FOXA1, Pparg, Gata3) markers. Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on fresh whole bladders using an Illumina Sequencing platform and cluster analyses were performed for luminal and basal markers using Rstudio.
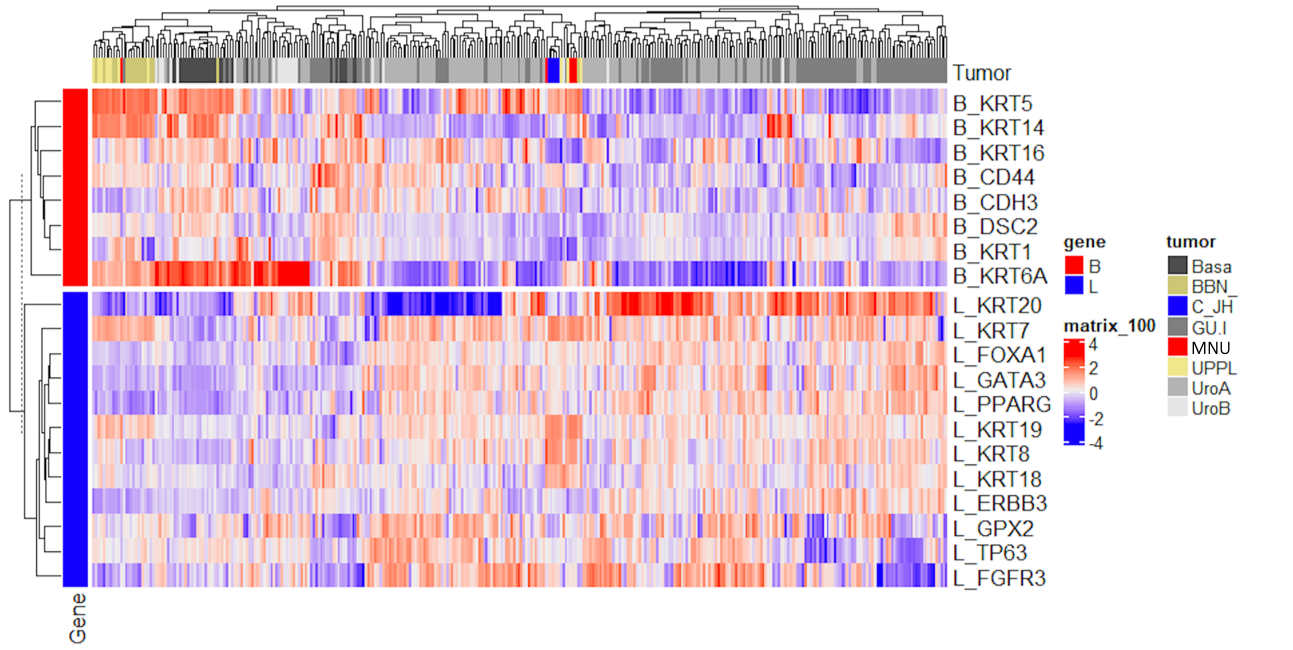
Results: MNU induced development of non-invasive tumors in 10/10 (100%,3 CIS, 3 Ta, 4 T1) bladders at week 16 and 3/6 (50%,3 T1) at week 30, while 3/6 (50%, 3 T2) progressed to muscle invasive disease at week 30. IHC analysis showed retention of luminal markers CK20, FOXA1, Pparg, and Gata3 in CIS, Ta and T1 tumor cells but loss of CDK20, Pparg and Gata3 expression in T2 disease. Basal IHC markers KRT5, KRT14 and p63 were highly expressed in all stages of MNU tumors. Sequencing data show MNU tumors cluster separately from basal-like BBN murine tumors and are more closely clustered with luminal-like UPPL mice tumors when looking at luminal signature markers KRT8 and KRT18 as well as with BASE47 subtype classifier. Cluster analysis including human tumors show MNU clusters more closely with urobasal A and B subtypes which have features including elevated expression of FGFR3, CCND1, and TP63 as well as KRT5 expression (Figure 1).
Conclusions: This study is the first to characterize molecular subtype of the MNU-carcinogen induced rat model of urothelial cancer revealing a complex signature of both basal and luminal markers and provides insight into guiding clinically relevant investigations aimed at improving therapies for urothelial carcinoma.
Source of Funding: None
Methods: Intravesical MNU instillations were administered in 16 Fisher female rats every other week for a total of 4 instillations. Rats were sacrificed at either 16 (n=10) or 30 (n=6) weeks after initial instillation and bladders were harvested for analysis. Pathologic staging was assessed on H&E, and IHC was performed for basal (KRT5, KRT14, p63) and luminal (CK20, FOXA1, Pparg, Gata3) markers. Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on fresh whole bladders using an Illumina Sequencing platform and cluster analyses were performed for luminal and basal markers using Rstudio.
Results: MNU induced development of non-invasive tumors in 10/10 (100%,3 CIS, 3 Ta, 4 T1) bladders at week 16 and 3/6 (50%,3 T1) at week 30, while 3/6 (50%, 3 T2) progressed to muscle invasive disease at week 30. IHC analysis showed retention of luminal markers CK20, FOXA1, Pparg, and Gata3 in CIS, Ta and T1 tumor cells but loss of CDK20, Pparg and Gata3 expression in T2 disease. Basal IHC markers KRT5, KRT14 and p63 were highly expressed in all stages of MNU tumors. Sequencing data show MNU tumors cluster separately from basal-like BBN murine tumors and are more closely clustered with luminal-like UPPL mice tumors when looking at luminal signature markers KRT8 and KRT18 as well as with BASE47 subtype classifier. Cluster analysis including human tumors show MNU clusters more closely with urobasal A and B subtypes which have features including elevated expression of FGFR3, CCND1, and TP63 as well as KRT5 expression (Figure 1).
Conclusions: This study is the first to characterize molecular subtype of the MNU-carcinogen induced rat model of urothelial cancer revealing a complex signature of both basal and luminal markers and provides insight into guiding clinically relevant investigations aimed at improving therapies for urothelial carcinoma.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)