Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Podium
PD57: Prostate Cancer: Detection & Screening VI
PD57-11: Impact of Contact Surface Area and PI-RADS Category on the Capsular Invasion of Localized Cancer with Serum Prostate-Specific Antigen Levels &[le]20 ng/mL and Tumor-Capsule Contact
Monday, May 16, 2022
11:10 AM – 11:20 AM
Location: Room 245
TAKAHIRO OGAWA*, SUNAO SHOJI, Isehara, Japan, KAZUMA TAKEDA, Hiratsuka, Japan, TAKAHITO UCHIDA, SOICHIRO YUZURIHA, IZUMI HANADA, SATOSHI KURODA, Isehara, Japan, KENTARO NAGAO, Okayama, Japan, TARO HIGURE, Chichibu, Japan, MASAYOSHI KAWAKAMI, MAYURA NAKANO, MASAHIRO NITTA, YOSHIAKI KAWAMURA, MASANORI HASEGAWA, AKIRA MIYAJIMA, Isehara, Japan
- TO
Podium Presenter(s)
Introduction: To analyze clinical factors related to pathological capsular invasion in patients with localized prostate cancer treated with robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP).
Methods: Consecutive patient with localized prostate cancer, serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels =20 ng/mL, tumor-capsule contact on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and had undergone RARP were enrolled retrospectively. The relationship between the clinical factors and pathological capsular invasion was investigated. The contact surface area of the prostate cancer on the capsule was calculated using three-dimensional reconstructed MRI.
Results: Of the 89 patients, 30 had capsular invasion. The mean PSA level was 8.21 ng/mL, and the mean prostate volume was 27 cc. In multivariate logistic regression analyses to predict capsular invasion of prostate cancer with Gleason score = 3+4 (n=41), capsular contact surface area (cm2) (odds ratio [OR], 29.624; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.783–492.149, P=0.018) was found to be a significant factor. Areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUCs) based on the contact surface area (AUC, 0.713; P=0.045) were significantly greater than non-discrimination for the prediction of capsular invasion. In multivariate logistic regression analyses to predict capsular invasion of prostate cancer with Gleason score = 4+3 (n=48), the Prostate Imaging–Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) category of prostate cancer with tumor-capsule contact (OR, 11.504; 95% CI: 2.072–63.874, P=0.005) and D’Amico risk group (OR, 6.665; 95% CI: 1.130–39.310, P=0.036) were found to be significant factors. In the pathological analysis, there was a significant difference in invasion types (protruding vs. infiltrating) between lesions with Gleason scores = 3+4 and those with Gleason scores = 4+3 in patients with capsular invasion (P=0.001).
Conclusions: In patients with localized prostate cancer with serum prostate-specific antigen levels = 20 ng/mL, contact surface area was considered a significant risk factor for those with Gleason scores = 3+4 and PI-RADS category of prostate cancer with tumor-capsule contact was considered a significant risk factor for those with Gleason scores = 4+3.
Source of Funding: None.
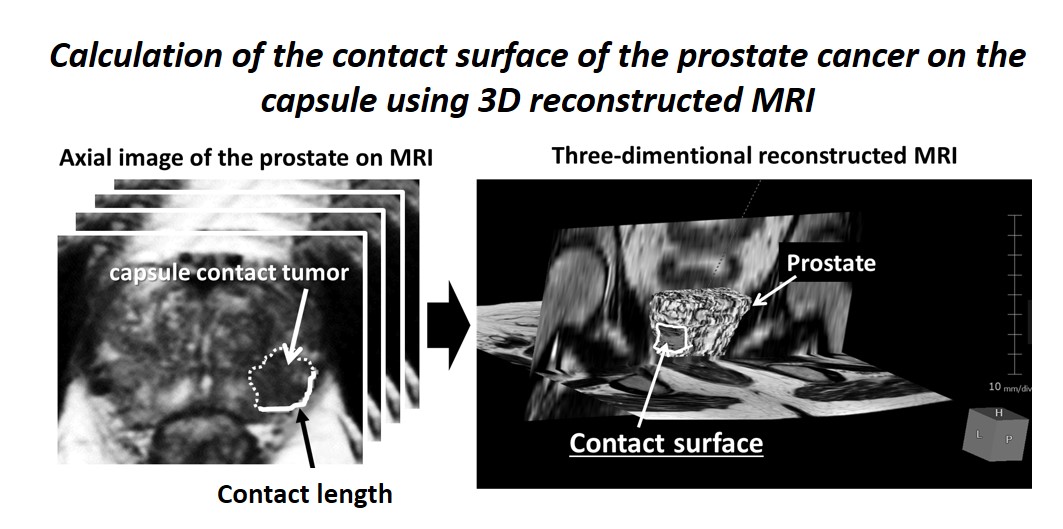
Methods: Consecutive patient with localized prostate cancer, serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels =20 ng/mL, tumor-capsule contact on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and had undergone RARP were enrolled retrospectively. The relationship between the clinical factors and pathological capsular invasion was investigated. The contact surface area of the prostate cancer on the capsule was calculated using three-dimensional reconstructed MRI.
Results: Of the 89 patients, 30 had capsular invasion. The mean PSA level was 8.21 ng/mL, and the mean prostate volume was 27 cc. In multivariate logistic regression analyses to predict capsular invasion of prostate cancer with Gleason score = 3+4 (n=41), capsular contact surface area (cm2) (odds ratio [OR], 29.624; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.783–492.149, P=0.018) was found to be a significant factor. Areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUCs) based on the contact surface area (AUC, 0.713; P=0.045) were significantly greater than non-discrimination for the prediction of capsular invasion. In multivariate logistic regression analyses to predict capsular invasion of prostate cancer with Gleason score = 4+3 (n=48), the Prostate Imaging–Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) category of prostate cancer with tumor-capsule contact (OR, 11.504; 95% CI: 2.072–63.874, P=0.005) and D’Amico risk group (OR, 6.665; 95% CI: 1.130–39.310, P=0.036) were found to be significant factors. In the pathological analysis, there was a significant difference in invasion types (protruding vs. infiltrating) between lesions with Gleason scores = 3+4 and those with Gleason scores = 4+3 in patients with capsular invasion (P=0.001).
Conclusions: In patients with localized prostate cancer with serum prostate-specific antigen levels = 20 ng/mL, contact surface area was considered a significant risk factor for those with Gleason scores = 3+4 and PI-RADS category of prostate cancer with tumor-capsule contact was considered a significant risk factor for those with Gleason scores = 4+3.
Source of Funding: None.


.jpg)
.jpg)