Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP15: Prostate Cancer: Localized: Surgical Therapy I
MP15-11: Outcomes of Salvage Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy ( S-RARP) post focal ablation for prostate cancer in comparison with primary Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy (RARP); A matched analysis
Friday, May 13, 2022
2:45 PM – 4:00 PM
Location: Room 222
Seetharam Bhat, Celebration, FL, Marcio Covas Moschovas*, kissimee, FL, Jonathan Noel, Travis Rogers, Roshane Pereira, Sunil Reddy, Vipul Patel, Celebration, FL, Marco Sandri, Milan, Italy
- MC
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: To evaluate the impact of focal therapy on functional and oncological outcomes
following RARP.
Methods: 53 patients who had prostatectomy following the failure of focal ablation were selected and labeled group I. The patients who had whole gland ablation and external beam therapy were excluded. They were then compared to a matched control sample of the ratio of 1:1, 1:2,1:3 with the RARP cohort. Age, PSA, PSA density, BMI, SHIM, AUA, Charlson Comorbidity Index, Prostate weight, Preoperative Gleason score, and history of Smoking were used to perform matching. The oncological and functional outcomes between these groups were compared.SRARP following focal therapy was performed in all cases using a standardized technique developed at our institute with the da Vinci Xi Surgical System.
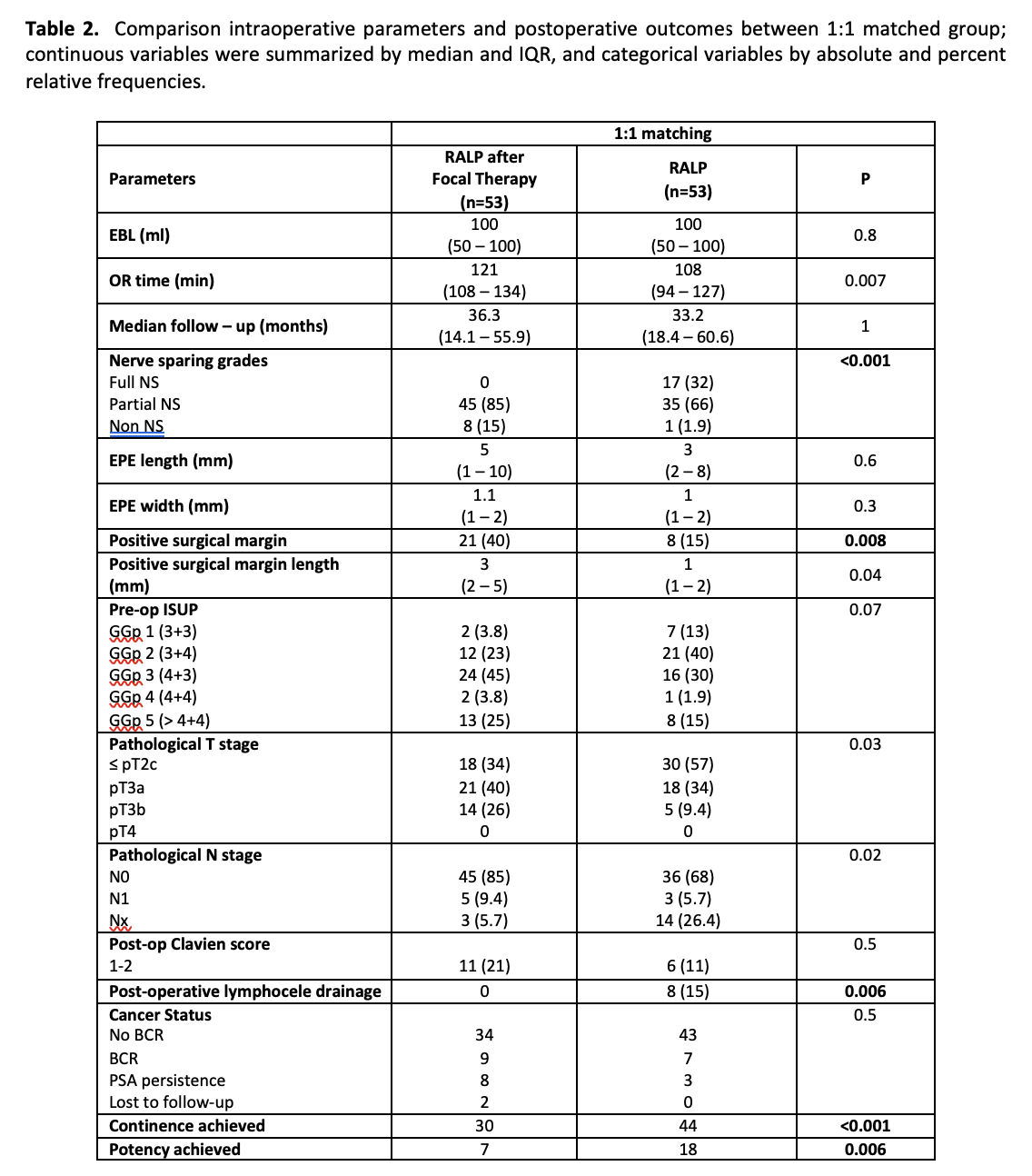
Results: No difference in EBL and OR time was noted between the focal and control group. More full NS was performed in the control group compared to the focal group. The focal therapy group had a higher incidence of the positive surgical margin. Also, the focal therapy group had a higher incidence of GS >= 8 and positive lymph node status. The focal therapy group had a higher incidence of lymphocele drainage post-surgery.
Conclusions: Salvage robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy after focal therapy failure is feasible
however, surgery following focal therapy leads to poorer oncological and functional outcomes.
Despite the targeted nature of FT, significant non-focal collateral damage is seen to tissues
surrounding the prostate, which in turn translates to poorer functional outcomes post salvage
RARP.
Source of Funding: None
following RARP.
Methods: 53 patients who had prostatectomy following the failure of focal ablation were selected and labeled group I. The patients who had whole gland ablation and external beam therapy were excluded. They were then compared to a matched control sample of the ratio of 1:1, 1:2,1:3 with the RARP cohort. Age, PSA, PSA density, BMI, SHIM, AUA, Charlson Comorbidity Index, Prostate weight, Preoperative Gleason score, and history of Smoking were used to perform matching. The oncological and functional outcomes between these groups were compared.SRARP following focal therapy was performed in all cases using a standardized technique developed at our institute with the da Vinci Xi Surgical System.
Results: No difference in EBL and OR time was noted between the focal and control group. More full NS was performed in the control group compared to the focal group. The focal therapy group had a higher incidence of the positive surgical margin. Also, the focal therapy group had a higher incidence of GS >= 8 and positive lymph node status. The focal therapy group had a higher incidence of lymphocele drainage post-surgery.
Conclusions: Salvage robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy after focal therapy failure is feasible
however, surgery following focal therapy leads to poorer oncological and functional outcomes.
Despite the targeted nature of FT, significant non-focal collateral damage is seen to tissues
surrounding the prostate, which in turn translates to poorer functional outcomes post salvage
RARP.
Source of Funding: None


.jpg)
.jpg)