Back
Poster, Podium & Video Sessions
Moderated Poster
MP16: Health Services Research: Quality Improvement & Patient Safety I
MP16-04: Practice-level variation in rates positive surgical margins at partial nephrectomy: a MUSIC-KIDNEY analysis
Friday, May 13, 2022
4:30 PM – 5:45 PM
Location: Room 228
Mohit Butaney, Detroit, MI, Sonia Bhayani, St. Louis, MO, Ji Qi, Anna Johnson, Ann Arbor, MI, Sara Perkins*, Detroit, MI, Sabrina Noyes, Grand Rapids, MI, Alon Weizer, Ann Arbor, MI, Lewis Johnson, Kalamazoo, MI, Amit Patel, Detroit, MI, Alice Semerjian, Ypsilanti, MI, Brian Lane, Grand Rapids, MI, Craig Rogers, Detroit, MI, for the Michigan Urological Surgery Improvement Collaborative, Ann Arbor, MI
- SP
Sara Q. Perkins, MD
Vattikuti Urology Institute, Henry Ford Hospital
Poster Presenter(s)
Introduction: The aim of partial nephrectomy (PN) is to completely excise the small renal mass while optimizing renal parenchymal preservation and minimizing morbidity to the patient. While focal PSM have not conclusively been associated with local recurrence in published series, they lead to increased patient anxiety and intensity of surveillance. MUSIC-KIDNEY is a state-wide quality improvement collaborative focused on reducing the burden of care for patients with clinical T1 renal masses (cT1RM). PSM rate represents a surrogate of surgical quality in this patient population. As part of a quality improvement initiative to improve rates of PSM, we evaluated the influence of practice-level variation, patient, and tumor factors on PSM rates in the MUSIC-KIDNEY cohort.
Methods: MUSIC-KIDNEY commenced data collection in June 2017 and now includes >3500 patients with newly diagnosed cT1RM. Data abstractors record clinical data for patients at 16 MUSIC practices including >90 physicians 120 days after initial consultation. We evaluated PSM rates across the registry and their associations with patient and perioperative factors. Practice variation was also assessed.
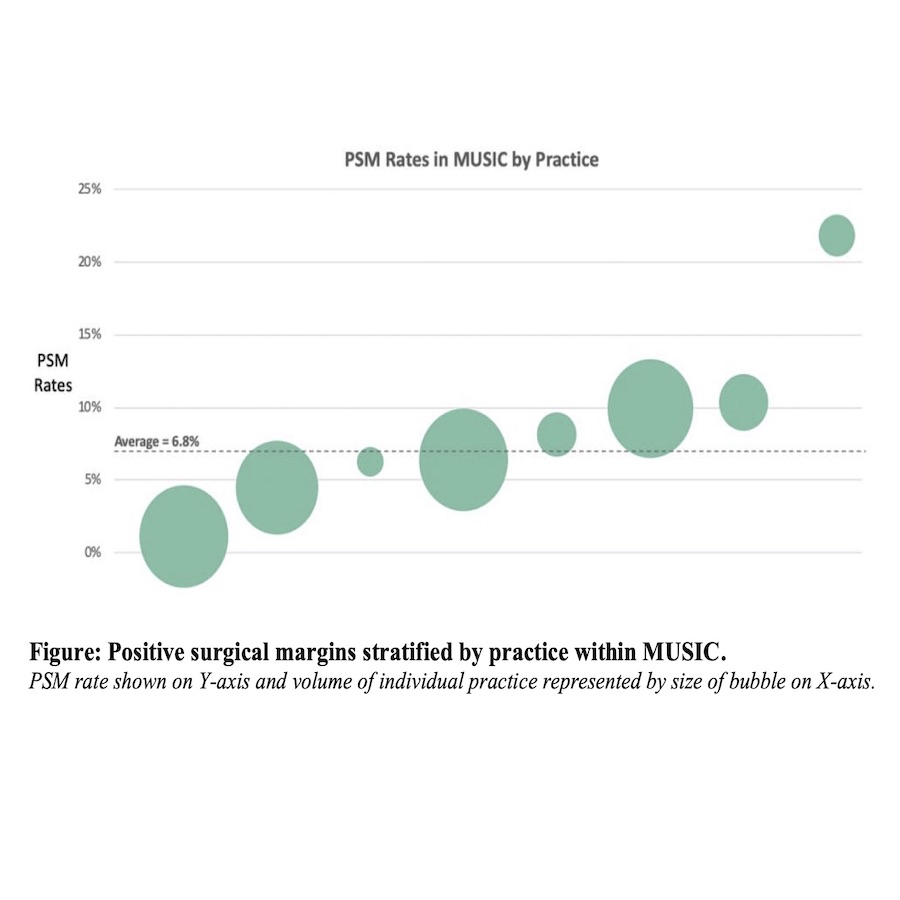
Results: A total of 873 underwent PN. Median patient age was 59 years (IQR 49-67), tumor size 2.8 cm (22% T1b tumors), and RENL scores were 4-6 in 44%, 7-9 in 48%, and >=10 in 8.3%. A PSM was noted in 6.8% of patients. Clinical factors associated with PSM included BMI>=25 (p=0.049) and the endophytic component of the RENL score (p < 0.01) There was a wide variation with regards to rates of PSM between practices (Figure).
Conclusions: PSM rates for PN was associated with an increased BMI, and endophytic component of RENL score. There exists a wide practice variation in rates of PSM across the state of Michigan. Given this variation, there is a potential to learn technique from practices that are performing well in this metric. An international virtual workshop on techniques for avoiding PSM was conducted in October 2021. Factors driving this variation, including surgeon-specific factors and institutional factors (pathology protocols), need further investigation. Future QI projects planned include a video library of PN videos, and live peer-to-peer skills sessions.
Source of Funding: Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan
Methods: MUSIC-KIDNEY commenced data collection in June 2017 and now includes >3500 patients with newly diagnosed cT1RM. Data abstractors record clinical data for patients at 16 MUSIC practices including >90 physicians 120 days after initial consultation. We evaluated PSM rates across the registry and their associations with patient and perioperative factors. Practice variation was also assessed.
Results: A total of 873 underwent PN. Median patient age was 59 years (IQR 49-67), tumor size 2.8 cm (22% T1b tumors), and RENL scores were 4-6 in 44%, 7-9 in 48%, and >=10 in 8.3%. A PSM was noted in 6.8% of patients. Clinical factors associated with PSM included BMI>=25 (p=0.049) and the endophytic component of the RENL score (p < 0.01) There was a wide variation with regards to rates of PSM between practices (Figure).
Conclusions: PSM rates for PN was associated with an increased BMI, and endophytic component of RENL score. There exists a wide practice variation in rates of PSM across the state of Michigan. Given this variation, there is a potential to learn technique from practices that are performing well in this metric. An international virtual workshop on techniques for avoiding PSM was conducted in October 2021. Factors driving this variation, including surgeon-specific factors and institutional factors (pathology protocols), need further investigation. Future QI projects planned include a video library of PN videos, and live peer-to-peer skills sessions.
Source of Funding: Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan


.jpg)
.jpg)