Back
Poster Session C
Genetics, genomics and proteomics
Session: (1118–1149) Genetics, Genomics and Proteomics Poster
1134: Genome-wide Association Study Identifies Novel Loci for Leukopenia Among TPMT and NUDT15 Normal Metabolizers Taking Azathioprine
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall

Cecilia Chung, MD, MPH
Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Nashville, TN, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Jacy Zanussi, Puran Nepal, Alyson Dickson, Laura Daniel, Peter Straub, Tyne Miller-Fleming, Wei-Qi Wei, Adriana Hung, Nancy Cox, Vivian Kawai, Jonathan Mosley, Michael Stein, QiPing Feng, Ge Liu, Ran Tao and Cecilia Chung, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN
Background/Purpose: Azathioprine is a thiopurine drug used for the treatment of several inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. However, its use is limited due to side effects, in particular hematopoietic toxicity. While variants in both TPMT and NUDT15 are associated with leukopenia, they only explain 25% of the risk. Little is known about the genetic factors associated with azathioprine-associated leukopenia among TPMT and NUDT15 normal metabolizers.
Methods: We conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) among 1,184 new users of azathioprine with race reported as White in the electronic health record who were TPMT and NUDT15 normal metabolizers, did not receive an organ transplant, and who received azathioprine for an autoimmune or inflammatory condition. Leukopenia was defined as a white blood cell count less than 3,000 cells/mm3 while taking azathioprine and all cases were adjudicated by review of clinical records. A total of 7,363,955 genotyped and imputed single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) passed quality control. We used PLINK2 to test the association between the SNPs and azathioprine-associated leukopenia among 125 cases and 1,059 control subjects. Results were adjusted by demographic characteristics, indication for azathioprine, concurrent medications, last recorded azathioprine dose, and 10 genetic principal components.
Results: Cohort patients had an average age of 44.1+/-17.7 years at baseline and were predominantly female (n=772, 65.2%). The main indications for azathioprine were rheumatic conditions (n = 609; 51.4%) and inflammatory bowel disease/ulcerative colitis (n = 411; 34.7%); 134 were taking concurrent immunosuppressants. The mean last recorded azathioprine dose was 107.5+/- 55.4 mg/d. Two SNPs were associated with leukopenia at a GWAS level of significance (p< 5x10-8) after adjustment for clinical variables (Fig); rs11664064 (OR = 3.61; CI = [2.31, 5.66]; risk allele = C) is an intronic variant in PTPN2 (a gene that encodes protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2 and regulates T-cell responses), and rs45566135 (OR = 3.65; 95% CI = [2.33, 5.72]; risk allele = C) lies downstream from PTPN2 and is in strong linkage disequilibrium with the PTPN2 intronic variant (r2 = 0.98). The minor allele frequency for both alleles is 0.0527872.
Conclusion: We describe novel variants in the PTPN2 locus associated with leukopenia among TPMT and NUDT15 normal metabolizers taking azathioprine for inflammatory or autoimmune conditions.
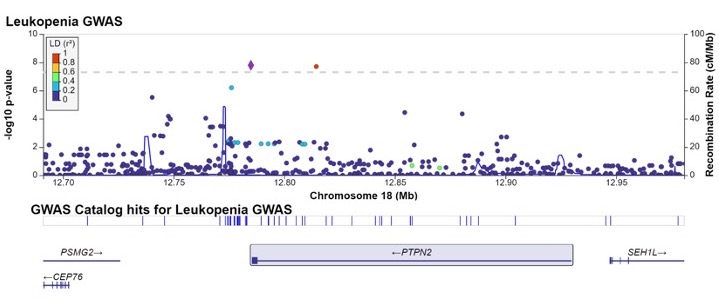 PTPN2 region and the associations with leukopenia (cases = 125; controls = 1059; total = 1184)
PTPN2 region and the associations with leukopenia (cases = 125; controls = 1059; total = 1184)
Disclosures: J. Zanussi, None; P. Nepal, None; A. Dickson, None; L. Daniel, None; P. Straub, None; T. Miller-Fleming, None; W. Wei, None; A. Hung, None; N. Cox, None; V. Kawai, None; J. Mosley, None; M. Stein, None; Q. Feng, None; G. Liu, None; R. Tao, None; C. Chung, None.
Background/Purpose: Azathioprine is a thiopurine drug used for the treatment of several inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. However, its use is limited due to side effects, in particular hematopoietic toxicity. While variants in both TPMT and NUDT15 are associated with leukopenia, they only explain 25% of the risk. Little is known about the genetic factors associated with azathioprine-associated leukopenia among TPMT and NUDT15 normal metabolizers.
Methods: We conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) among 1,184 new users of azathioprine with race reported as White in the electronic health record who were TPMT and NUDT15 normal metabolizers, did not receive an organ transplant, and who received azathioprine for an autoimmune or inflammatory condition. Leukopenia was defined as a white blood cell count less than 3,000 cells/mm3 while taking azathioprine and all cases were adjudicated by review of clinical records. A total of 7,363,955 genotyped and imputed single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) passed quality control. We used PLINK2 to test the association between the SNPs and azathioprine-associated leukopenia among 125 cases and 1,059 control subjects. Results were adjusted by demographic characteristics, indication for azathioprine, concurrent medications, last recorded azathioprine dose, and 10 genetic principal components.
Results: Cohort patients had an average age of 44.1+/-17.7 years at baseline and were predominantly female (n=772, 65.2%). The main indications for azathioprine were rheumatic conditions (n = 609; 51.4%) and inflammatory bowel disease/ulcerative colitis (n = 411; 34.7%); 134 were taking concurrent immunosuppressants. The mean last recorded azathioprine dose was 107.5+/- 55.4 mg/d. Two SNPs were associated with leukopenia at a GWAS level of significance (p< 5x10-8) after adjustment for clinical variables (Fig); rs11664064 (OR = 3.61; CI = [2.31, 5.66]; risk allele = C) is an intronic variant in PTPN2 (a gene that encodes protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2 and regulates T-cell responses), and rs45566135 (OR = 3.65; 95% CI = [2.33, 5.72]; risk allele = C) lies downstream from PTPN2 and is in strong linkage disequilibrium with the PTPN2 intronic variant (r2 = 0.98). The minor allele frequency for both alleles is 0.0527872.
Conclusion: We describe novel variants in the PTPN2 locus associated with leukopenia among TPMT and NUDT15 normal metabolizers taking azathioprine for inflammatory or autoimmune conditions.
 PTPN2 region and the associations with leukopenia (cases = 125; controls = 1059; total = 1184)
PTPN2 region and the associations with leukopenia (cases = 125; controls = 1059; total = 1184)Disclosures: J. Zanussi, None; P. Nepal, None; A. Dickson, None; L. Daniel, None; P. Straub, None; T. Miller-Fleming, None; W. Wei, None; A. Hung, None; N. Cox, None; V. Kawai, None; J. Mosley, None; M. Stein, None; Q. Feng, None; G. Liu, None; R. Tao, None; C. Chung, None.

