Back
Poster Session C
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (1387–1416) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
1405: In Contrast to Anti-CCP, Then MMP Degraded and Citrullinated Vimentin (VICM) Is Both a Diagnostic and Treatment Response Biomarker
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- AB
Anne-Christine Bay-Jensen, PhD, MSc
Nordic Bioscience
Herlev, Denmark
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Patryk Drobinski1, Neel I. Nissen1, morten A. Karsdal2, Nicholas Willumsen2 and Anne-Christine Bay-Jensen2, 1University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2Nordic Bioscience, Herlev, Denmark
Background/Purpose: The degree of protein citrullination and degradation by matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) play a central role in the pathology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Autoantibodies are known to target citrullinated proteins such as vimentin. Elevated levels of vimentin MMP-generated fragments are found in blood and studies have shown that blood markers such as VICM are associated with disease activity and response to treatment such anti-GM-CSF. Tocilizumab (TOCI) is a MAb targeting the IL-6 receptor. The aim of the present study was to investigate the relationship between blood levels of MMP-degraded and citrullinated Vimentin, as compared to levels of non-citrullinated vimentin (VIM), and contrast that to the standard anti-CCP biomarker in patients treated with tocilizumab (TOCI).
Methods: VIM, VICM and Anti-CCP were quantified in serum samples from baseline and week 8 of 257 RA patients treated with either TOCI (8 mg/kg), MTX (7.5-20 mg/kg) monotherapy and compared to a reference cohort of 64 healthy donors. Biomarkers were correlated to disease activity measures and the change in levels from baseline to 8 weeks were compared between treatment arms. Predictive response analyses were conducted. Marker data was LN-transformed and corrected for age, race, gender, BMI and disease duration.
Results: All measured biomarkers were significantly elevated in RA serum compared with the reference cohort: VIM, 2.2 vs 1.0 ng/mL (p< 0.05); VICM, 11.4 vs 0.4 ng/ml (p< 0.0001); Anti-CCP, 165.7 vs 4.0 RU/mL (p< 0.001). VICM but none of the other markers correlated with CRP and ESR. The level of VICM was significantly decreased in response to TOCI (2.9-fold, p< 0.0001) and to MTX (1.5-fold, p< 0.05) compared to placebo. A 1.9-fold difference was observed for VIM between MTX and TOCI (p< 0.0001). There was a 1.8- and 1.6-fold difference between TOCI, and MTX and PBO, respectively. No significant change was observed for anti-CCP. High baseline level of VICM was predictive for low disease activity (LDA) response at week 8 as the only of the three markers (table).
Conclusion: The VICM fragment is a double posttranslational epitope: it is both citrullinated and released from vimentin by the action of MMPs. It can differentiate between RA and healthy donors to the same level as anti-CCP but can also be modulated by TOCI and act as a pharmacodynamic marker, because its release is dependent on MMP activity, which is partly regulated by IL-6.
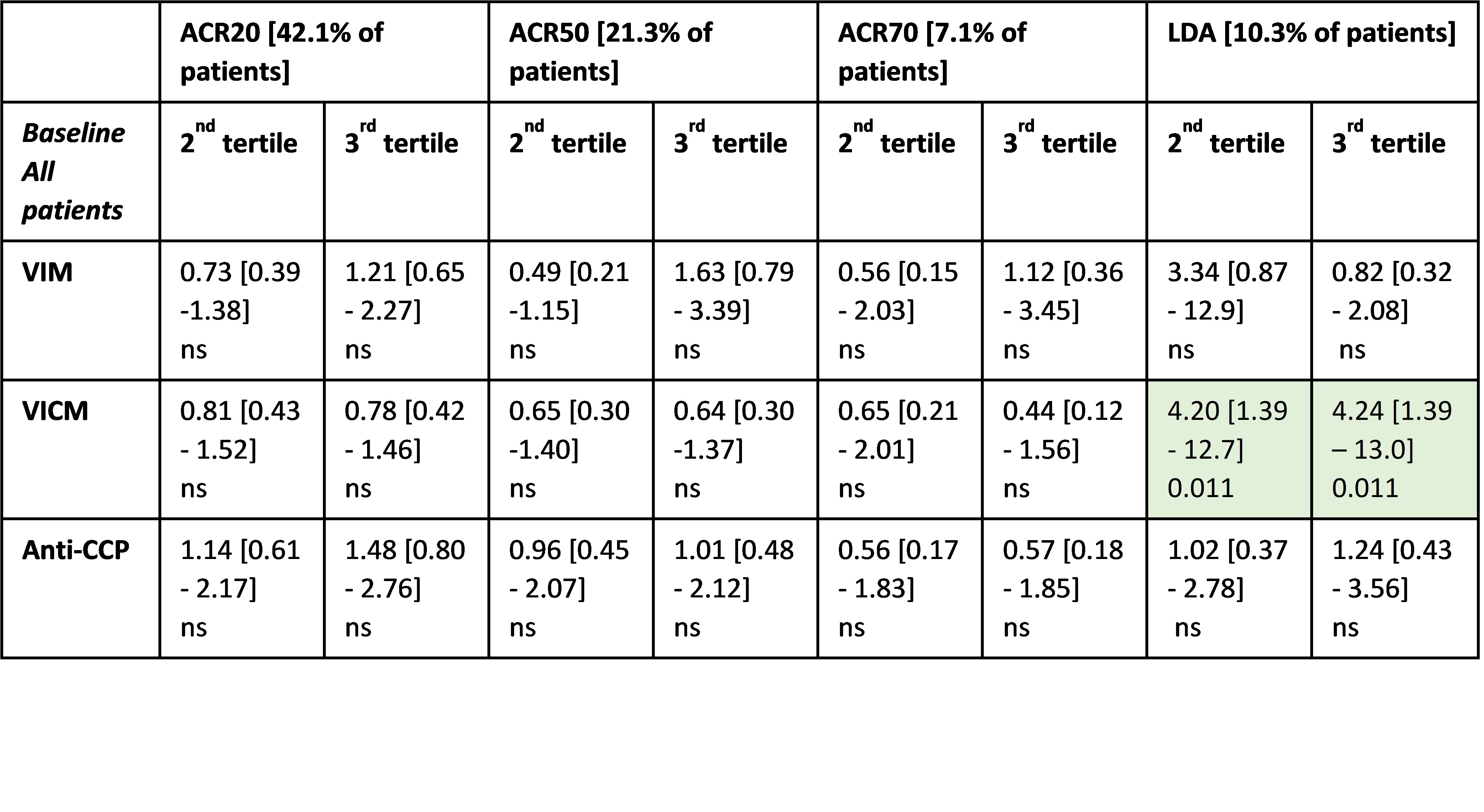 Table. Prediction of response. OR [95%-CI] for being a responder from logistic regression comparing patients with lowest level of biomarker (1st tertile) to the 2nd and 3rd tertiles at either baseline or at week 8. ORs were adjusted for baseline biomarker level (week 8 only), age, gender, BMI, and disease duration.
Table. Prediction of response. OR [95%-CI] for being a responder from logistic regression comparing patients with lowest level of biomarker (1st tertile) to the 2nd and 3rd tertiles at either baseline or at week 8. ORs were adjusted for baseline biomarker level (week 8 only), age, gender, BMI, and disease duration.
Disclosures: P. Drobinski, None; N. Nissen, Nordic Bioscience; m. Karsdal, Nordic Bioscience; N. Willumsen, Nordic Bioscience; A. Bay-Jensen, Nordic Bioscience.
Background/Purpose: The degree of protein citrullination and degradation by matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) play a central role in the pathology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Autoantibodies are known to target citrullinated proteins such as vimentin. Elevated levels of vimentin MMP-generated fragments are found in blood and studies have shown that blood markers such as VICM are associated with disease activity and response to treatment such anti-GM-CSF. Tocilizumab (TOCI) is a MAb targeting the IL-6 receptor. The aim of the present study was to investigate the relationship between blood levels of MMP-degraded and citrullinated Vimentin, as compared to levels of non-citrullinated vimentin (VIM), and contrast that to the standard anti-CCP biomarker in patients treated with tocilizumab (TOCI).
Methods: VIM, VICM and Anti-CCP were quantified in serum samples from baseline and week 8 of 257 RA patients treated with either TOCI (8 mg/kg), MTX (7.5-20 mg/kg) monotherapy and compared to a reference cohort of 64 healthy donors. Biomarkers were correlated to disease activity measures and the change in levels from baseline to 8 weeks were compared between treatment arms. Predictive response analyses were conducted. Marker data was LN-transformed and corrected for age, race, gender, BMI and disease duration.
Results: All measured biomarkers were significantly elevated in RA serum compared with the reference cohort: VIM, 2.2 vs 1.0 ng/mL (p< 0.05); VICM, 11.4 vs 0.4 ng/ml (p< 0.0001); Anti-CCP, 165.7 vs 4.0 RU/mL (p< 0.001). VICM but none of the other markers correlated with CRP and ESR. The level of VICM was significantly decreased in response to TOCI (2.9-fold, p< 0.0001) and to MTX (1.5-fold, p< 0.05) compared to placebo. A 1.9-fold difference was observed for VIM between MTX and TOCI (p< 0.0001). There was a 1.8- and 1.6-fold difference between TOCI, and MTX and PBO, respectively. No significant change was observed for anti-CCP. High baseline level of VICM was predictive for low disease activity (LDA) response at week 8 as the only of the three markers (table).
Conclusion: The VICM fragment is a double posttranslational epitope: it is both citrullinated and released from vimentin by the action of MMPs. It can differentiate between RA and healthy donors to the same level as anti-CCP but can also be modulated by TOCI and act as a pharmacodynamic marker, because its release is dependent on MMP activity, which is partly regulated by IL-6.
 Table. Prediction of response. OR [95%-CI] for being a responder from logistic regression comparing patients with lowest level of biomarker (1st tertile) to the 2nd and 3rd tertiles at either baseline or at week 8. ORs were adjusted for baseline biomarker level (week 8 only), age, gender, BMI, and disease duration.
Table. Prediction of response. OR [95%-CI] for being a responder from logistic regression comparing patients with lowest level of biomarker (1st tertile) to the 2nd and 3rd tertiles at either baseline or at week 8. ORs were adjusted for baseline biomarker level (week 8 only), age, gender, BMI, and disease duration.Disclosures: P. Drobinski, None; N. Nissen, Nordic Bioscience; m. Karsdal, Nordic Bioscience; N. Willumsen, Nordic Bioscience; A. Bay-Jensen, Nordic Bioscience.

